Book 3 Review
You will now practice all the skills you learned in Book 3. Check your work using the answer key at the end of the review.
If you can’t remember how to do a question, go back to the lesson on this topic to refresh your memory. The unit and topic for each question is listed.
Example: 1-B means Unit 1, Topic B
Book 3 Review Questions
1-A
- Find the products.
-
[latex]\begin{array}{rr}&4\\\times&9\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&7\\\times&8\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&2\\\times&6\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&9\\\times&5\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&6\\\times&10\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&0\\\times&3\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&8\\\times&4\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&5\\\times&2\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&10\\\times&10\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
-
1-B
- Find the products.
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&71\\\times&3\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&623\\\times&3\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&8431\\\times&2\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&5231\\\times&3\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- Find the products.
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&68\\\times&5\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&457\\\times&6\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&9346\\\times&7\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&1329\\\times&4\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- Find the products.
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&45\\\times&26\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&542\\\times&38\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&3829\\\times&52\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&463\\\times&179\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&6314\\\times&231\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&1425\\\times&537\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- Find the products. Use the shortcut.
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&1000\\\times&792\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&9264\\\times&100\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&1000\\\times&85\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]3609\times10=[/latex]
- [latex]100\times259=[/latex]
- [latex]10\times46=[/latex]
- [latex]5719\times1000=[/latex]
1-C
- Find an estimated product.
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&72\\\times&38\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&574\\\times&83\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&5492\\\times&87\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&792\\\times&901\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&8560\\\times&193\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&29492\\\times&585\\\hline\end{array}[/latex]
1-D
- Word Problems.
- The Great Belt Suspension Bridge in Denmark is 1624 metres. How many metres will 24 trucks travel crossing the bridge?
- How many cans of peaches are needed to pack 300 boxes, if each box has 3 rows and each row has 6 cans? (2 step question)
- The Krubera Cave in Georgia is the deepest cave in the world at 2191 metres. Estimate how many metres 348 visitors will cover going down to the cave.
2-A
- Complete this chart.
Multiplication Division Division “Say” a)
[latex]3\times8 = 24[/latex]
[latex]8\times3 = 24[/latex]
[latex]24 \div8 = 3[/latex]
[latex]24\div3 = 8[/latex]
[latex]\begin{array}{r}3\\8\enclose{longdiv}{24}\end{array}[/latex]
[latex]\begin{array}{r}8\\3\enclose{longdiv}{24}\end{array}[/latex]
"24 divided by 8 is 3" "24 divided by 3 is 8"
b)
[latex]7\times5 = 35[/latex]
c)
[latex]9\times3 = 27[/latex]
- Give the answer.
- [latex]28 \div 4 =[/latex]
- [latex]18 \div 6 =[/latex]
- [latex]64 \div 8 =[/latex]
- [latex]9\enclose{longdiv}{81}[/latex]
- [latex]5\enclose{longdiv}{40}[/latex]
- [latex]3\enclose{longdiv}{32}[/latex]
- Find the quotients.
- [latex]8\enclose{longdiv}{60}[/latex]
- [latex]5\enclose{longdiv}{49}[/latex]
- [latex]9\enclose{longdiv}{43}[/latex]
- [latex]3\enclose{longdiv}{19}[/latex]
2-B
- Using the following list of numbers, answer questions a, b, c and d. 96, 345, 3816, 6815, 38433, 95373
- Which numbers are divisible by 2?
- Which numbers are divisible by 3?
- Which numbers are divisible by 5?
- Which numbers are divisible by 9?
2-C
- Find the quotients.
- [latex]3\enclose{longdiv}{963}[/latex]
- [latex]2\enclose{longdiv}{682}[/latex]
- [latex]4\enclose{longdiv}{844}[/latex]
- [latex]5\enclose{longdiv}{550}[/latex]
- Find the quotients.
- [latex]9\enclose{longdiv}{387}[/latex]
- [latex]6\enclose{longdiv}{492}[/latex]
- [latex]5\enclose{longdiv}{915}[/latex]
- [latex]7\enclose{longdiv}{469}[/latex]
- Find the quotients.
- [latex]8\enclose{longdiv}{832}[/latex]
- [latex]4\enclose{longdiv}{836}[/latex]
- [latex]3\enclose{longdiv}{927}[/latex]
- [latex]2\enclose{longdiv}{416}[/latex]
- Find the quotients.
- [latex]5\enclose{longdiv}{92}[/latex]
- [latex]7\enclose{longdiv}{86}[/latex]
- [latex]4\enclose{longdiv}{73}[/latex]
- [latex]6\enclose{longdiv}{91}[/latex]
- Find the quotients.
- [latex]3\enclose{longdiv}{851}[/latex]
- [latex]8\enclose{longdiv}{509}[/latex]
- [latex]2\enclose{longdiv}{407}[/latex]
- [latex]7\enclose{longdiv}{954}[/latex]
2-D
- Find the quotients.
- [latex]24\enclose{longdiv}{480}[/latex]
- [latex]58\enclose{longdiv}{928}[/latex]
- [latex]36\enclose{longdiv}{1944}[/latex]
- [latex]73\enclose{longdiv}{37668}[/latex]
- Find the quotients.
- [latex]10\enclose{longdiv}{683}[/latex]
- [latex]1000\enclose{longdiv}{41839}[/latex]
- [latex]100\enclose{longdiv}{13041}[/latex]
- [latex]1000\enclose{longdiv}{63125}[/latex]
- Find the quotients.
- [latex]348\enclose{longdiv}{8010}[/latex]
- [latex]483\enclose{longdiv}{27150}[/latex]
- [latex]753\enclose{longdiv}{619345}[/latex]
- [latex]73\enclose{longdiv}{37668}[/latex]
2-E
- Give an estimated quotient. Show your rounding where needed.
- [latex]30\enclose{longdiv}{63000}[/latex]
- [latex]7000\enclose{longdiv}{8400000}[/latex]
- [latex]58\enclose{longdiv}{2894}[/latex]
- [latex]438\enclose{longdiv}{23689}[/latex]
- [latex]768\enclose{longdiv}{63875}[/latex]
- [latex]896\enclose{longdiv}{80986}[/latex]
2-F
- Word problems.
- A satellite orbits the moon every 58 minutes. How many complete orbits does it make 6728 minutes?
- It takes 73 hours to make a snow blower. How many snow blowers can be made in 47815 hours?
- There were 10780 tickets sold at the game. There were 150 tickets in each roll. How many complete rolls of tickets were used? How many were sold from the next roll?
- Solve the cost per unit price.
- 6 packages of rice for $12
- 2 tubs of yogurt for $8
- Solve the unit price and then underline the best buy.
- Dog food
8 kilograms for $16 or 15 kilograms for $45 - Movies
9 movies for $162 or 3 movies for $48
- Dog food
3-B
- Circle the number of coins or bills you would need to get from the first number to the second number. Make sure to use the least number of coins or bills.
- $58 to $60
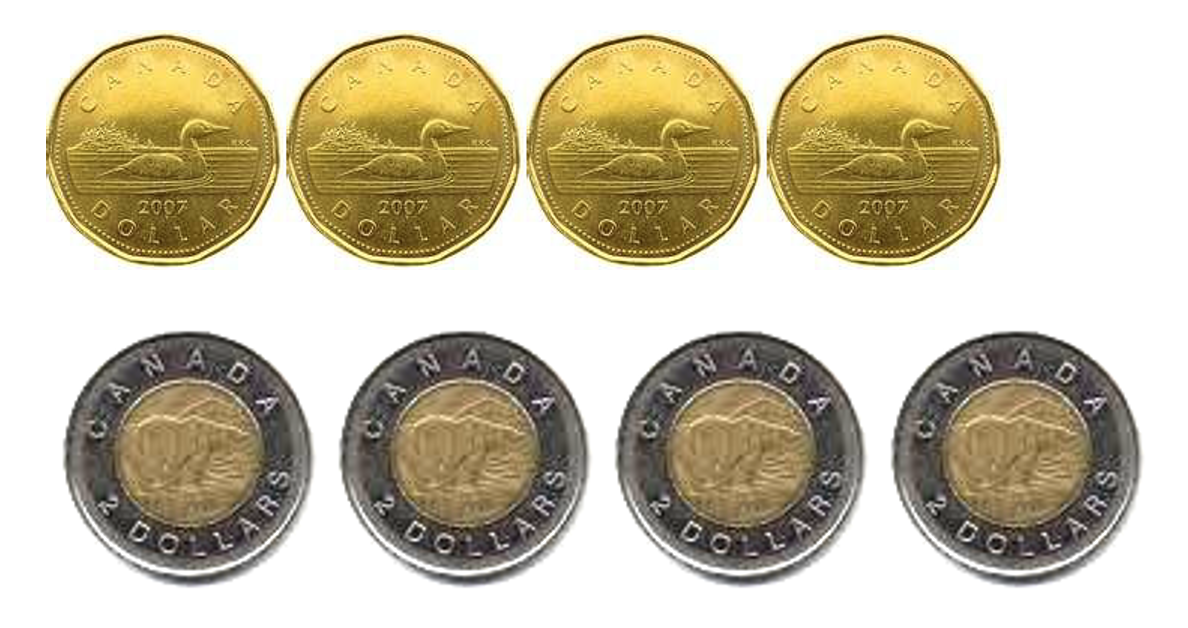

- $41 to $50
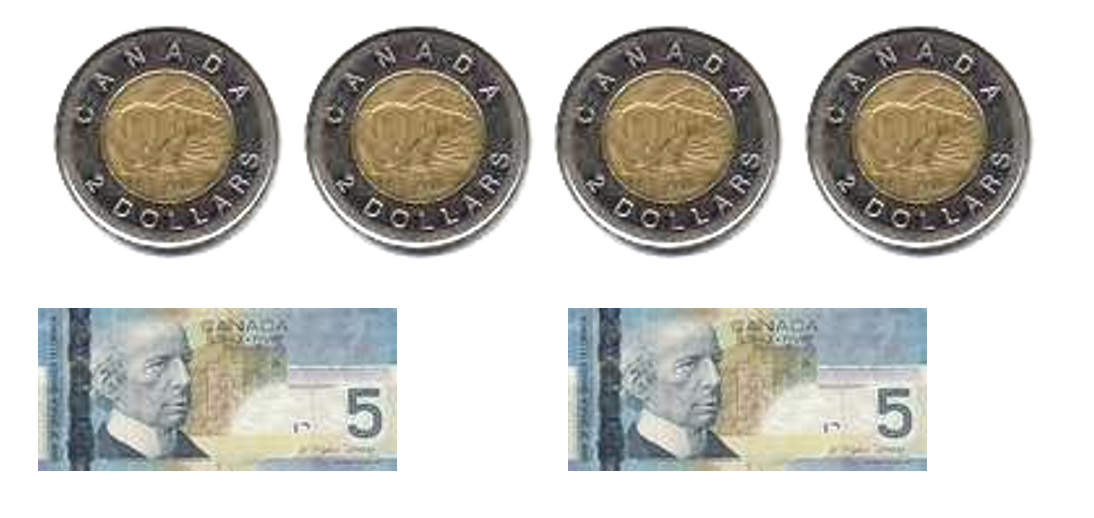

- $78 to $90
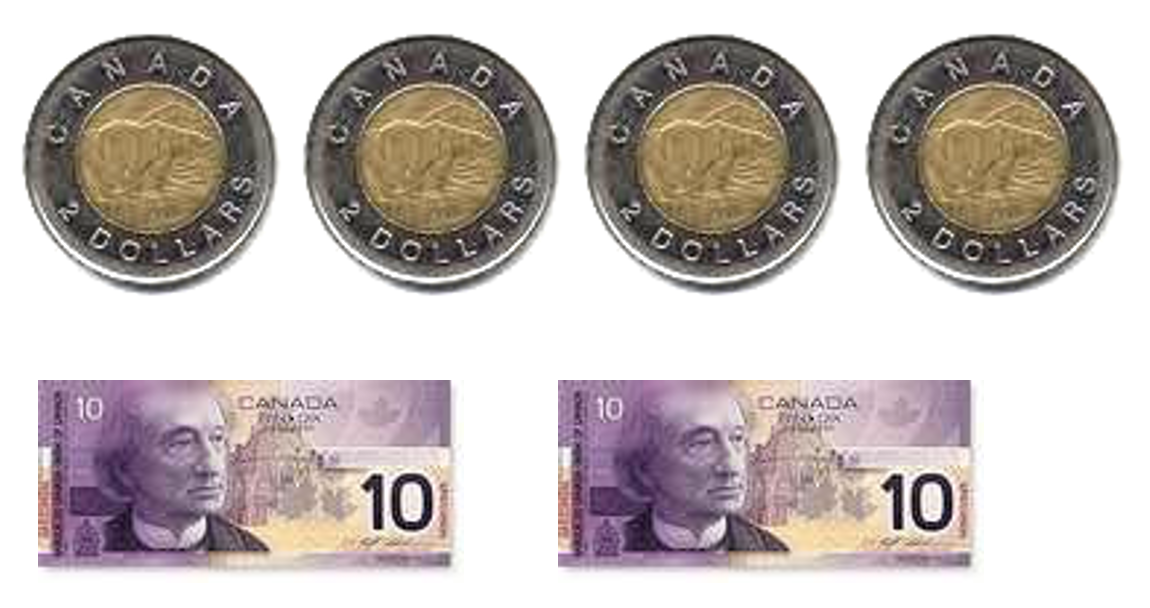

- $58 to $60
- State the number and kind of coins and bills you would need to get from the first number to the second number. Make sure you use the least number of coins and bills as possible.
- $38 to $40
- $21 to $40
- $76 to $100
- State the number and kind of coins and bills you would need to get change from the second number. Make sure you use the least number of coins and bills as possible.
-
$43 to $100 Need To get to -
$23 to $80 Need To get to -
$58.40 to $100 Need To get to -
$62.75 to $100 Need To get to
-
- State the number and kind of coins and bills you would need to get change from $100. Make sure you use the least number of coins and bills as possible.

Bread maker for $61.60
Shop vacuum cleaner for $84.45- Mrs. Chui bought building blocks for $33.45. How much change will she get from $100?
3-C
- Circle the letter of the most reasonable measure.
- Depth of the ocean
- 3926 mm
- 3926 km
- 3926 m
- Thickness of string
- 5 mm
- 5 cm
- 5 m
- Distance from the earth to moon
- 3476 m
- 3476 mm
- 3476 km
- Length of a banana
- 15 km
- 15 mm
- 15 cm
- Depth of the ocean
- Choose the most reasonable measure.
- A spoonful of medicine
- 5 L
- 5 mL
- 50 mL
- A bottle of orange juice
- 4 mL
- 4 L
- 40 L
- A tube of toothpaste holds 130 .
- The gas tank of a car holds 70 .
- A spoonful of medicine
- Choose the most reasonable measure.
- A sugar cube has a mass of
- 1 g
- 10 g
- 10 kg
- A cat weighs
- 7 mg
- 7 kg
- 7 g
- A headache pill has 375 of medicine
- A sugar cube has a mass of
- Write the base unit of measure and then the prefix if one is needed.
Item Base Prefix (if needed) a) thickness of a rope b) water in a bathtub c) a bag of rice d) length of a table - Find the area of each shape.
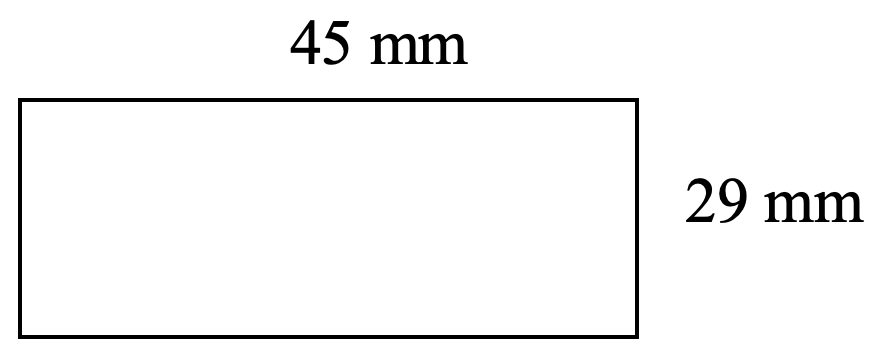
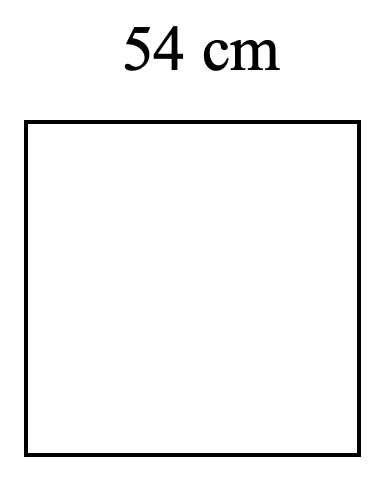
- Find the perimeter and area of each shape.
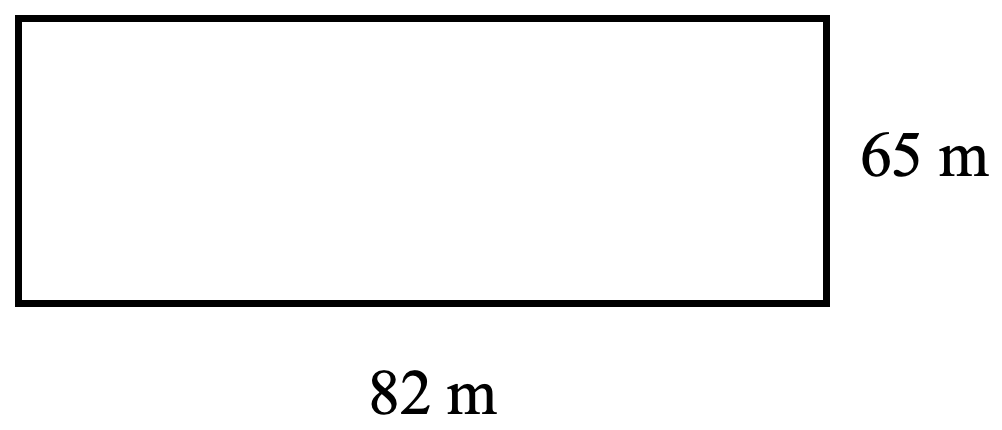
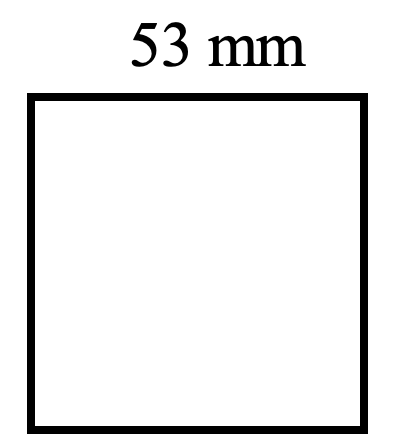
- Tiananmen Square measures 880 metres by 500 metres. Find the perimeter and area of Tiananmen.
- Andrèe wants to build a square patio whose side is 13 m. Find the perimeter and area of her new patio.
Answers to Book 3 Review
-
- 36
- 56
- 12
- 45
- 60
- 0
- 32
- 10
- 100
-
- 213
- 1869
- 16862
- 15693
-
- 340
- 2742
- 65422
- 5316
-
- 1170
- 20596
- 199108
- 82877
- 1458534
- 765225
-
- 792000
- 926400
- 85000
- 36090
- 25900
- 460
- 5719000
-
- [latex]70 \times 40 = 2800[/latex]
- [latex]600\times80=48000[/latex]
- [latex]5000\times90=450000[/latex]
- [latex]800\times900=720000[/latex]
- [latex]9000\times 200=1800000[/latex]
- [latex]30000\times600=18000000[/latex]
-
- 38976 metres
- 5400 cans
- 600000 metres
-
Multiplication Division Division “Say” a)
[latex]3 \times 8 = 24[/latex] [latex]8 \times 3 = 24[/latex]
[latex]24 \div 8= 3[/latex]
[latex]24 \div 3= 8[/latex]
[latex]\begin{array}{r}3\\8\enclose{longdiv}{24}\end{array}[/latex][latex]\begin{array}{r}8\\3\enclose{longdiv}{24}\end{array}[/latex] "24 divided by 8 is 3" "24 divided by 3 is 8"
b)
[latex]7 \times5 = 35[/latex]
[latex]5 \times 7 = 35[/latex]
[latex]35 \div 5= 7[/latex]
[latex]35 \div 7= 5[/latex]
[latex]\begin{array}{r}7\\5\enclose{longdiv}{35}\end{array}[/latex][latex]\begin{array}{r}5\\7\enclose{longdiv}{35}\end{array}[/latex] "35 divided by 5 is 7" "35 divided by 7 is 5"
c)
[latex]9 \times 3 = 27[/latex] [latex]3 \times 9 = 27[/latex]
[latex]27 \div 3 = 9[/latex] [latex]27 \div 9 = 3[/latex]
[latex]\begin{array}{r}9\\3\enclose{longdiv}{27}\end{array}[/latex][latex]\begin{array}{r}3\\9\enclose{longdiv}{27}\end{array}[/latex] "27 divided by 3 is 9" "27 divided by 9 is 3"
-
- 7
- 3
- 8
- 9
- 8
- 10 R2
-
- 7 R4
- 9 R4
- 4 R7
- 6 R1
-
- 96, 3816
- 96, 345, 3816, 38433, 95373
- 345, 6815
- 3816, 95373
-
- 321
- 341
- 211
- 110
-
- 43
- 82
- 183
- 67
-
- 104
- 209
- 309
- 208
-
- 18 R2
- 12 R2
- 18 R1
- 15 R1
-
- 283 R2
- 63 R5
- 203 R1
- 136 R2
-
- 20
- 16
- 54
- 516
-
- 68 R3
- 418 R839
- 130 R41
- 63 R125
-
- 23 R6
- 56 R102
- 822 R379
- 516
-
- 2100
- 1200
- [latex]30000\div60=50[/latex]
- [latex]24000\div400=60[/latex]
- [latex]64000\div800=80[/latex]
- [latex]81000\div900=90[/latex]
-
- 116 orbits
- 655 snow blowers
- 71 full rolls, 130 tickets
-
- $2
- $4
-
- $2, $3, best buy is 8 kilograms for $16
- $18, $16, best buy is 3 movies for $48
-
- 1 toonie
- 2 toonies, 1 $5 bill
- 1 toonie, 1 $10 bill
-
- 1 toonie
- 2 toonies, 1 $5 bill, 1 $10 bill
- 2 toonies, 1 $20 bill
-
-
$43 to $100 Need To get to 1 toonie $45 1 $5 bill $50 1 $10 bill $60 2 $20 bills $100 -
$23 to $80 Need To get to 1 toonie $25 1 $5 bill $30 1 $10 bill $40 2 $20 bills $80 -
$58.40 to $100 Need To get to 1 dime $58.50 2 quarters $59.00 1 loonie $60.00 2 $20 bills $100.00 -
$62.75 to $100 Need To get to 1 quarter $63.00 1 toonie $65.00 1 $5 bill $70.00 1 $10 bill $80.00 1 $20 bill $100.00
-
-
- 1 nickel, 1 dime, 1 quarter, 1 loonie, 1 toonie, 1 $5 bill, 1 $10 bill, 1 $20 bill
- 1 nickel, 2 quarters, 1 $5 bill, 1 $10 bill
- 1 nickel, 2 quarters, 1 loonie, 1 $5 bill, 3 $20 bill
-
- iii
- i
- iii
- iii
-
- ii
- ii
- mL
- L
-
- i
- ii
- mg
-
Item Base Prefix (if needed) a) thickness of a rope m m b) water in a bathtub L c) a bag of rice g k d) length of a table m c -
- [latex]1305 \text{ mm}^2[/latex]
- [latex]2916 \text{ cm}^2[/latex]
-
- [latex]P=294 \text{ m}[/latex], [latex]A = 5330 \text{ m}^2[/latex]
- [latex]P = 212 \text{ mm}[/latex], [latex]A = 2809 \text{ mm}^2[/latex]
- [latex]P = 2760 \text{ m}[/latex], [latex]A = 440000 \text{ m}^2[/latex]
- [latex]P = 52 \text{ m}[/latex], [latex]A = 169 \text{ m}^2[/latex]