Unit 3: Change and The Metric System
Unit 3 Review: Change and the Metric System
You will now practice all the skills you learned in Unit 3. Check your work using the answer key at the end of the review
- Circle the number of coins or bills you would need to get from the first number to the second number. Make sure to use the least number of coins or bills.
- $48 to $50
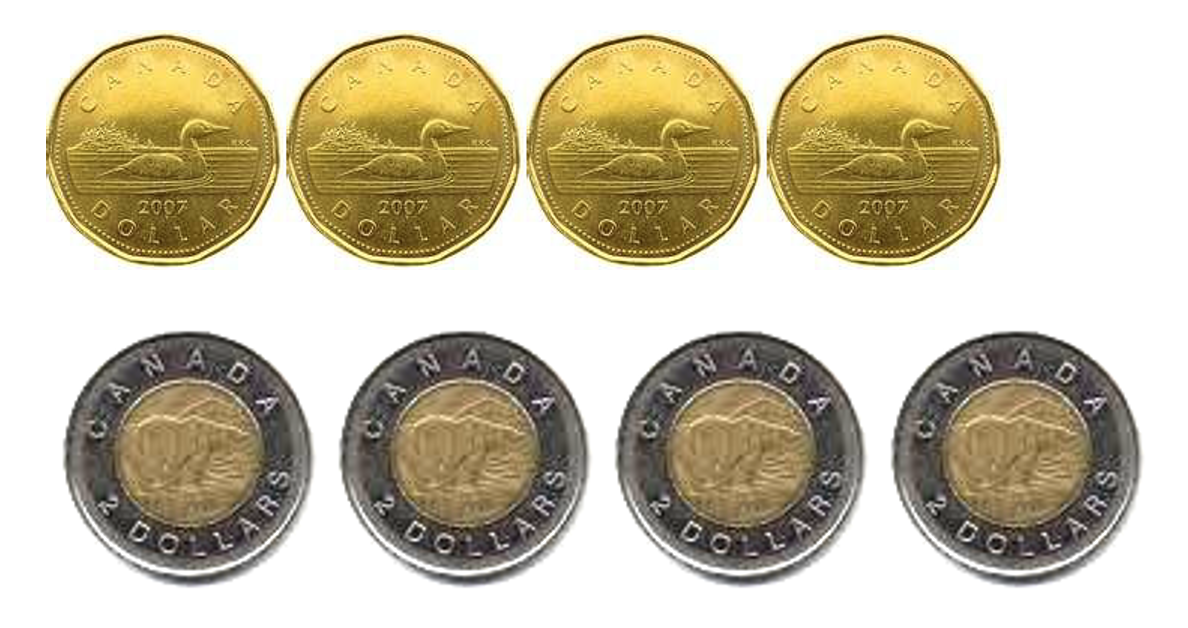

- $59 to $60

- $73 to $80
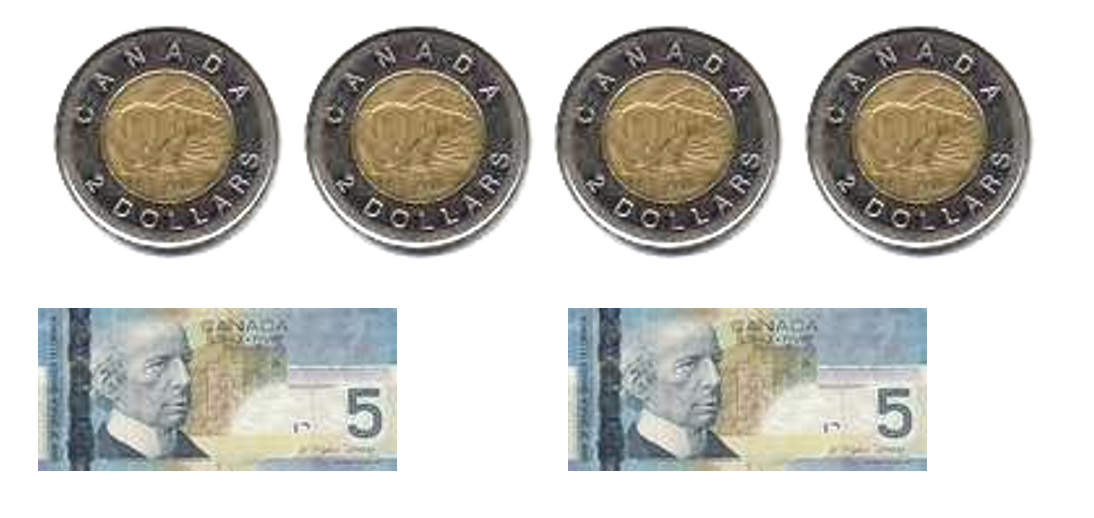

- $33 to $40

- $48 to $50
- State the number and kind of coins and bills you would need to get from the first number to the second number. Make sure you use the least number of coins and bills as possible.
- $23 to $25
- $31 to $35
- $85 to $90
- $70 to $90
- State the number and kind of coins and bills you would need to get from the first number to the second number. Make sure you use the least number of coins and bills as possible.
-
$37 to $50 Need To get to -
$53 to $60 Need To get to -
$77 to $100 Need To get to -
$21 to $50 Need To get to
-
- State the number and kind of coins and bills you would need to get from the first number to the second number. Make sure you use the least number of coins and bills as possible.
-
$63.55 to $80 Need To get to -
$32.65 to $50 Need To get to -
$20.35 to $40 Need To get to -
$72.20 to $100 Need To get to
-
- State the number and kind of coins and bills you would need to get change from $100. Make sure you use the least number of coins and bills as possible.

printer for $78.40
cordless phone for $55.65- Mrs. Kono bought a new cordless kettle for $44.80. How much change will Mrs. Kono get from $100?
- Circle the letter of the most reasonable measure.
- Diameter of a hockey puck
- 76 mm
- 76 m
- 76 cm
- Distance from the mall to home
- 10 km
- 10 m
- 10 cm
- Thickness of a blanket
- 10 m
- 10 cm
- 10 mm
- Height of a tree
- 28 mm
- 28 m
- 28 cm
- Diameter of a hockey puck
- Choose the most reasonable measure.
- Carlos drinks
- 500 L of milk
- 500 mL of milk
- 5 mL of milk
- A thermos holds
- 360 mL
- 360 L
- 36 L
- A swimming pool holds 3758 of water
- A tube of lotion is 50 .
- Carlos drinks
- Choose the most reasonable measure.
- A dog weighs
- 17 g
- 17 kg
- 17 mg
- A nickel has a mass of
- 5 g
- 5 mg
- 5 kg
- A paper clip has mass of
- 1 kg
- 1 mg
- 1 g
- Six math books have mass of
- 2 kg
- 2 mg
- 2 g
- Elena took 400 of vitamin A
- Suki bought 10 of potatoes
- A dog weighs
- Write the base unit of measure and then the prefix if one is needed.
Item Base Prefix (if needed) a) length of a garden hose b) a bottle of olive oil c) a child’s multivitamin d) distance between Jupiter and Mars e) thickness of a tissue - Write the unit of measure you would use for each item below.
- Paint thinner
- Cat litter
- Deodorant
- Length of the street
- Aspirin
- Find the area of each shape.
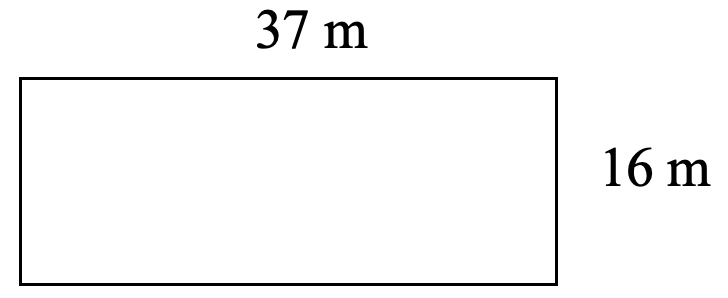
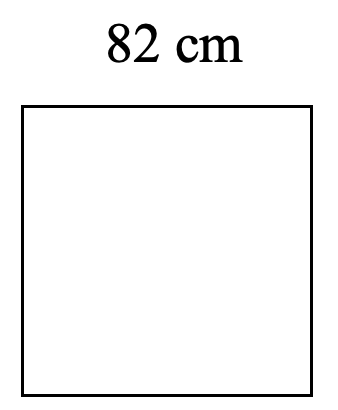
- Red Square in Moscow measures 330 m long and 70 m wide. What is the area of Red Square?
- Yoshiro is going to build a square patio whose side is 23 metres. What is the area of the patio?
- Find the perimeter and area of each shape.
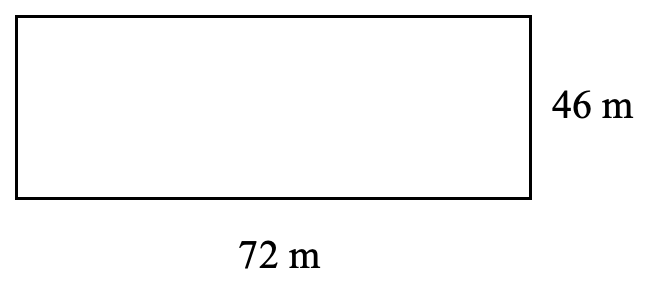
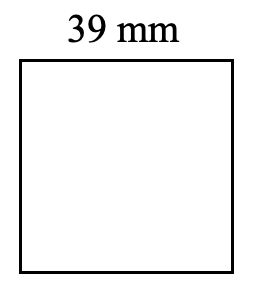
- Nadal wants to fence his garden. It is 15 m wide and 26 m long. How much fencing does Nadal need? How much space does Nadal have to plant a garden?
- Yolanda would like to buy fencing and sod for her new lawn that is 54 m long and 42 m wide. How much fencing does she need? How much sod does she need?
Answers to Unit 3 Review
- Circle the number of coins or bills you would need.
- 1 toonie
- 1 loonie
- 1 toonie, 1 $5 bill
- 1 toonie, 1 $5 bill
- State the number and kind of coins and bills you would need.
- 1 toonie
- 2 toonies
- 1 $5 bill
- 1 $20 bill
- State the number and kind of coins and bills you would need.
-
$37 to $50 Need To get to 1 loonie $38 1 toonie $40 1 $10 bill $50 -
$53 to $60 Need To get to 1 toonie $55 1 $5 bill $60 -
$77 to $100 Need To get to 1 loonie $78 1 toonie $80 1 $20 bill $100 -
$21 to $50 Need To get to 2 toonies $25 1 $5 bill $30 1 $20 bill $50
-
- State the number and kind of coins and bills you would need.
-
$63.55 to $80 Need To get to 2 dimes $63.75 1 quarter $64 1 loonie $65 1 $5 bill $70 1 $10 bill $80 -
$32.65 to $50 Need To get to 1 dime $32.75 1 quarter $33 1 toonie $35 1 $5 bill $40 1 $10 bill $50 -
$20.35 to $40 Need To get to 1 nickel $20.40 1 dime $20.50 2 quarters $21 2 toonies $25 1 $5 bill $30 1 $10 bill $40 -
$72.20 to $100 Need To get to 1 nickel $72.25 3 quarters $73 1 toonie $75 1 $5 bill $80 1 $20 bill $100
-
- State the number and kind of coins and bills you would need.
- 1 dime, 2 quarters, 1 loonie, 1 $20 bill
- 1 dime, 1 quarter, 2 toonies, 2 $20 bills
- 2 dimes, 1 $5 bill, 1 $10 bill, 2 $20 bills
- Circle the letter of the most reasonable measure.
- i
- i
- iii
- ii
- Choose the most reasonable measure.
- ii
- i
- L
- mL
- Choose the most reasonable measure.
- ii
- i
- iii
- i
- mg
- kg
- Write the base unit of measure and then the prefix if one is needed.
Item Base Prefix (if needed) a) length of a garden hose m b) a bottle of olive oil L milli c) a child’s multivitamin g milli d) distance between Jupiter and Mars m kilo e) thickness of a tissue m milli - Write the unit of measure you would use for each item below.
- L
- kg
- mL
- km
- mg
- Find the area of each shape.
- [latex]A = 592 \text{ m}^2[/latex]
- [latex]A = 6724 \text{ cm}^2[/latex]
- [latex]A = 23100 \text{ m}^2[/latex]
- [latex]A = 529 \text{ m}^2[/latex]
- Find the perimeter and area of each shape.
- [latex]P = 236 \text{ m}, A = 3312 \text{ m}^2[/latex]
- [latex]P = 156 \text{ mm}, A = 1521 \text{ mm}^2[/latex]
- [latex]P = 82 \text{ m}, A = 390 \text{ m}^2[/latex]
- [latex]P = 192 \text{ m}, A = 2268\text{ m}^2[/latex]

