Main Body
The Story of Our Human Rights
Learning Goals
At the end of this lesson, you will be able to:
- Understand and use new vocabulary words
- Explain what uni- and pro- mean at the beginning of a word
- Find the topic and main idea of a text
- Find the subject and verb in a sentence
- Correctly use some common homonyms
- Summarize a paragraph
- Discuss your long-term goals

Get Ready to Read
- What rights do you think everyone should have?
- Is everyone in Canada always treated like they have the same rights?
Vocabulary
Figure out what the bold word means by looking at how it is used in the sentence. Match it to the best meaning.
| 1. The United Nations made a list of human rights that all people need to live with freedom and respect. | a. Being unable to agree |
| 2. Our government did not always believe in equal rights. In the history of Canada, people have often been treated as less than human. | b. The same for each person |
| 3. The world has big cities, powerful governments, and rapid trade. | c. Treating someone in a way that shows they are important |
| 4. History has shown that people’s differences can lead to conflict and war. | d. Fast |
Write an answer for each question. Use the word in bold and write in complete sentences.
- How do you deal with conflict?
- Have you ever stood up for someone who was not being treated with respect? What happened?
- Do you know anyone who has stood up for equal rights? What did he or she do?
Word Attack Strategy
Word Patterns
A prefix is a beginning part of a word.
- The prefix uni– means one or all together.
- The prefix pro– means to put forward.
Here are some words with the prefix uni-.
| united | Made of people who share one goal |
| unique | One of a kind |
| universe | All of space and everything in it, like the planets and the stars |
| universal | Done by or available to everyone |
| unit | One part of something larger |
| uniform | Clothing worn by all members of a group |
| union | A group of workers that come together to protect their rights |
Use the words above to fill in each blank.
1. Do you think there is life somewhere in the _____________________ besides planet Earth?
2. Our class is starting a _____________________ on human rights.
3. The _____________________ decided to go on strike.
4. Every snowflake has a _____________________ shape.
5. The _____________________ Nations is made of countries that share the goal of world peace.
6. A man once said, “Live your life as though every act were to become a _____________________ law.”
7. Should children have to wear a school _____________________?
Here are some words with the prefix pro-.
| progress | To make something better over time |
| project | A task with a goal |
| protest | To argue against something |
| propose | To put forward an idea for a plan |
| process | A way of making something happen |
| provide | To give something |
| protect | To keep something safe |
| promote | To go up in rank, make more of something, or make something well known |
Use the words above to fill in each blank.
8. She helped her kids with their science _____________________.
9. What is the _____________________ for passing a law?
10. Libraries _____________________ many programs for families.
11. He is going to _____________________ marriage to his partner tomorrow.
12. My boss might _____________________ me next week.
13. I am not done yet, but I am making _____________________.
14. The mother bear will do anything to _____________________ her cubs.
15. Lots of students came out to _____________________ the new fees.
Use Your Reading Skills
Read The Story of Our Human Rights in your reader. Return to this page when you are done.
Check Your Understanding
Find the Topic and Main Idea
The topic of a text is the person or thing that the text is written about. To find the topic, start by looking at the title of the text. The title The Story of Our Human Rights tells us that the topic of this text is human rights.
The main idea is the point the writer is making about the topic. A text is usually written for one main purpose:
| Purpose | Example |
| To describe something | What is the town of Fernie, BC, like? |
| To explain how to do something | How do you bake salmon? |
| To tell a story about something | What’s the story of how Raven stole the sun? |
| To compare different things | Do you prefer biking or taking the bus? Why? |
| To explain the advantages or disadvantages of something | What are the advantages of waking up early? |
| To summarize something | What was the movie Smoke Signals about? |
We can figure out the main idea by looking for the point of each paragraph.
1. Re-read the first paragraph of The Story of Our Human Rights. Choose the best summary of the paragraph.
a. This paragraph describes the ways human beings are different.
b. This paragraph is about the disadvantages of being a human being.
c. This paragraph compares human beings to other animals.
2. Re-read the second paragraph of The Story of Our Human Rights. Choose the best summary of the paragraph.
a. This paragraph is about the disadvantages of the United Nations.
b. This paragraph compares the United Nations to Canada.
c. This paragraph explains that the United Nations created a list of human rights to help everyone get along, even though we are all different.
3. Re-read the list in the third paragraph. Choose the best summary of the paragraph.
a. This list is about the advantages of voting.
b. This list compares human rights in different countries.
c. This list summarizes the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
4. Re-read the fourth paragraph. Choose the best summary of the paragraph.
a. This paragraph explains how to stand up for your rights in Canada.
b. This paragraph explains that Canadians have the rights in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, but we didn’t always.
c. This paragraph tells the story of a Canadian who stood up for human rights.
Summarize
The best way to make sure you understand a text is to summarize it. A summary:
- is written in your own words
- does not give your opinion
- begins with a topic sentence that shows what you are summarizing and who wrote it
- includes the main idea of each paragraph
- does not include the details that explain the main ideas

Here is an example of a summary. Fill in the blanks with words that makes sense.
The Story of Our Human Rights was written by Shantel Ivits. It describes the many ways (1)________________ beings are different. These differences have led to (2)________________, so the United (3)________________ created a list of human rights to help everyone get along. The writer summarizes this list, which is known as the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Today, (4) ________________ have the rights in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, but we didn’t always.
Read for the Details
Complete the sentences. Write your answer on the lines.
1. Human beings like us have been around for 7,000 years, right?
No, they haven’t. Human beings __________________________.
2. The United Nations was started after World War I, right?
No, it wasn’t. It ______________________________________.
3. The UN wrote something called the Universal Declaration of Freedom, right?
No, it didn’t. It _______________________________________.
4. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights says that we should have to pay fees for basic education, right?
No, it doesn’t. It says we have the right to _____________________.
5. In this book, you’ll read about the United Nations, right?
No, I won’t. I will read the stories of _________________________.
Grammar
Subjects and Verbs
Read this text about Lester Pearson. Lester Pearson was Prime Minister of Canada from 1963 to 1968.
Lester Pearson and the Peacekeepers
Lester Pearson fought in World War I as a pilot. He was deeply upset by what he saw. He wanted to help prevent future wars. So after World War II, he helped create the United Nations. Pearson came up with the idea of a UN peacekeeping force. Peacekeepers go into areas that are in conflict. They keep the peace while the two sides work toward a solution. For his idea, Pearson won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1957. To this day, thousands of Canadians serve as peacekeepers around the world.
Grammar Rule
Every sentence needs to have a subject and a verb.
- The subject is the part that tells who or what the sentence is about.
- The verb shows what the subject is or does.
In this sentence, the subject is underlined. The verb is in bold.
- Lester Pearson fought in World War I as a pilot.
- He was deeply affected by what he saw.
- He wanted to help prevent future wars.
- So after World War II, he helped create the United Nations.
For each sentence, underline the subject and circle the verb.
1. Pearson came up with the idea of a UN peacekeeping force.
2. Peacekeepers go into areas that are in conflict.
3. They keep the peace while the two sides work toward a non-violent solution.
4. For his idea, Pearson won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1957.
5. To this day, thousands of Canadians serve as peacekeepers around the world.
Homonyms
Homonyms are two words that sound the same but mean different things. The box below has some words from The Story of Our Human Rights, along with their homonym.
| right | peace | clothes | would |
| write | piece | close | wood |
Choose the best homonym to complete each sentence.
1. The United Nations works for world _____________________.
2. Do you want a _____________________________ of cake?
3. I chopped some _____________________________ for the fireplace.
4. _____________________________ you pass me the butter?
5. Basic education is a basic _____________________________.
6. He likes to _____________________________ short stories.
7. I’m cold. Can you _____________________________ the window?
8. Some people say, “The _________________________ make the man.”
Writing
At the end of each chapter, you will have one or two writing assignments to complete. Talk to your instructor about setting due dates for each assignment. Keep track of these due dates using the My Writing Assignments sheet or an agenda.
Write a Summary
Writing Task
Write a summary of the paragraph about Lester Pearson. Keep it short, with no more than three sentences.
Use this checklist to edit your work:
- Did I write it in my own words?
- Did I avoid giving my opinion?
- Did I begin with a topic sentence that says what I am summarizing and who wrote it?
- Did I include the main ideas?
- Did I leave out the less important details?
- Do all of my sentences have a subject and a verb?
- Is my summary the right length?
Ask your instructor to check your work.
Write about Long-Term Goals
A long-term goal is something you want to do in the future. It takes a lot of time and planning. It is something that you cannot do this week, this month, or even this year. For example, the long-term goal of the United Nations is world peace.
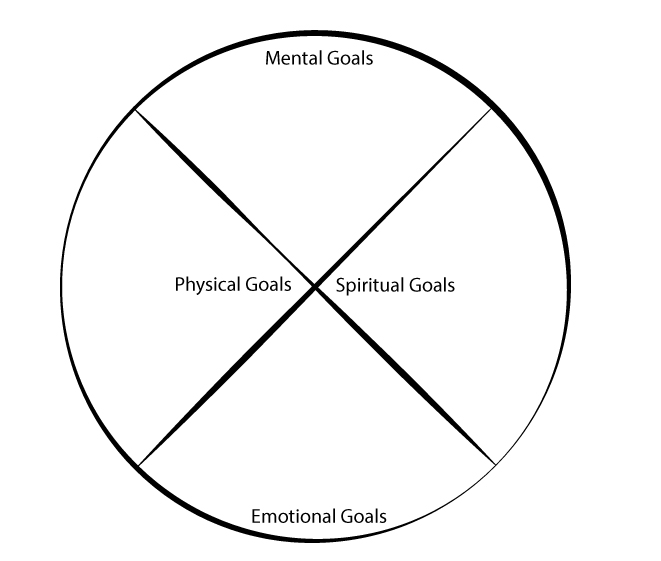
Let’s make some long-term goals using a medicine wheel. The medicine wheel is found in many First Nations cultures. It teaches us many things. One teaching is that we are all equal within the circle. Another teaching is that we are all spiritual, emotional, mental, and physical beings. Here are some of the needs we have:
| spiritual | We need to connect with the world and serve the greater good through friendship, love, volunteering, and celebrating. |
| emotional | We need to connect with our feelings, respect ourselves, feel joy, and have time for play. |
| physical | We need to take care of our bodies. We need clean air, food, exercise, rest, safety, and shelter. |
| mental | We need to learn and understand through listening, speaking, reading, remembering, reflecting, and reasoning. |
Writing Task
Think of at least one long-term goal for each part of the medicine wheel. Write it down.
Answer Key
| Vocabulary | ||
| QUESTION | ANSWER | |
| 1 | c | |
| 2 | b | |
| 3 | d | |
| 4 | a | |
| Word Attack Strategy | ||
| QUESTION | ANSWER | |
| 1 | universe | |
| 2 | unit | |
| 3 | union | |
| 4 | unique | |
| 5 | United | |
| 6 | universal | |
| 7 | uniform | |
| 8 | project | |
| 9 | process | |
| 10 | provide | |
| 11 | propose | |
| 12 | promote | |
| 13 | progress | |
| 14 | protect | |
| 15 | protest | |
| Check Your Understanding | ||
| Find the Topic and Main Idea | ||
| QUESTION | ANSWER | |
| 1 | a | |
| 2 | c | |
| 3 | c | |
| 4 | b | |
| Summarize | ||
| QUESTION | ANSWER | |
| 1 | human | |
| 2 | conflicts or wars | |
| 3 | Nations | |
| 4 | Canadians | |
| Read for the Details | ||
| QUESTION | ANSWER | |
| 1 | have been around for 100,000 years. | |
| 2 | was started after World War II. | |
| 3 | wrote something called the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. | |
| 4 | free basic education. | |
| 5 | Canadians who dared to stand up for our human rights. | |
| Grammar | ||
| Subjects and Verbs | ||
| QUESTION | SUBJECT | VERB |
| 1 | Pearson | came or came up with |
| 2 | Peacekeepers | go |
| 3 | They | keep |
| 4 | Pearson | won |
| 5 | thousands of Canadians | serve |
| Homonyms | ||
| QUESTION | ANSWER | |
| 1 | peace | |
| 2 | piece | |
| 3 | wood | |
| 4 | would | |
| 5 | right | |
| 6 | write | |
| 7 | close | |
| 8 | clothes | |
Attributions
Different people
Photo Montage by geralt is in the public domain.
Flags
Flags by wbwolfgang is in the public domain.