Unit 4: Dividing Decimals
Topic A: Dividing Decimals
Dividing decimals uses the same method that you learned for dividing whole numbers.
Vocabulary Review
[latex]\require{enclose} \begin{array}{r} \text{quotient}\\ \text{divisor}\enclose{longdiv}{\text{dividend}} \\ \end{array}[/latex]
dividend ÷ divisor = quotient
Using the above diagram, write the definitions.
Divisor:
Dividend:
Quotient:
Remember to use zeros to hold the places in the quotient if there is no other digit.
[latex]\begin{array}{r}\downarrow \phantom{0}\\1\mathbf{0}4\\9\enclose{longdiv}{936} \\9\downarrow \;\;\\\hline 03\phantom{0}\\0\downarrow\\\hline 36\\36\\ \hline0\end{array}[/latex]
Where Do You Place the Decimal Point?
Dividing decimals follows almost the same steps as dividing whole numbers. Here you will be shown two ways to figure out where to place the decimal point.
Method One
One way is to estimate the quotient using rounded whole numbers.
Example A
[latex]17.7 \div3[/latex]
Estimate: 17.7 ÷ 3 ≈ 18 ÷ 3 = 6
This tells us that the correct answer will be around 6 (which is one whole number place).
We know that the answer will not be around 0.6 and it will not be around 60.
If we take the decimals out and just divide the digits, the answer is 59.
[latex]\begin{array}{r}59\\3\enclose{longdiv}{177}\end{array}[/latex]
The estimate shows that the the decimal point will come after one whole number.
17.7 ÷ 3 = 5.9
Example B
[latex]137.88\div18[/latex]
Estimate: 137.88 ÷ 18 ≈ 140 ÷ 20 = 7
The answer will be around 7. It will not be around 0.7 or 70 or 700.
If we take the decimals out and just divide the digits, the answer is 7.66.
[latex]\begin{array}{r}7.66\\18\enclose{longdiv}{137.88}\end{array}[/latex]
The estimate shows that the the decimal point will come after one whole number.
137.88 ÷ 18 = 7.66
To check the accuracy of your division, multiply the quotient by the divisor.
dividend ÷ divisor = quotient
quotient × divisor = dividend
The product will equal the dividend if your arithmetic is correct.
23.72 ÷ 8 = 2.965 [latex]\begin{array}{rr}&2.965\\ \times&8\\ \hline &23.720\end{array}[/latex]
Exercise 1
The division has been done. Your task is to put the decimal point in the quotient by doing a whole number estimate of the question.
- [latex]\begin{array}{r}10.8\\2\enclose{longdiv}{21.6}\\ \end{array}[/latex] [latex]\left(\begin{array}{r}10\\2\enclose{longdiv}{20}\\ \end{array}\right)[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{r}1.3\\8\enclose{longdiv}{10.4}\\ \end{array}[/latex] [latex]\left(\begin{array}{r}1\\8\enclose{longdiv}{10}\\ \end{array}\right)[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{r}236\\6\enclose{longdiv}{14.16}\\ \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{r}53\\7\enclose{longdiv}{37.4}\\ \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{r}434\\4\enclose{longdiv}{173.6}\\ \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{r}345\\5\enclose{longdiv}{17.25}\\ \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{r}864\\7\enclose{longdiv}{60.48}\\ \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{r}182\\6\enclose{longdiv}{10.92}\\ \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{r}3369\\2\enclose{longdiv}{6.738}\\ \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{r}18\\37\enclose{longdiv}{66.6}\\ \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{r}243\\18\enclose{longdiv}{43.74}\\ \end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]\begin{array}{r}43\\21\enclose{longdiv}{90.3}\\ \end{array}[/latex]
Answers to Exercise 1
- 10.8
- 1.3
- 2.36
- 5.3
- 43.4
- 3.45
- 8.64
- 1.82
- 3.369
- 1.8
- 2.43
- 4.3
Method Two (If the Divisor is a Whole Number)
Have you found the shortcut?
If the divisor is a whole number, put the decimal point in the quotient right above the decimal point in the dividend.
Then just go ahead and divide, ignoring the decimal point all together.
Example C
[latex]18.45\div9 =[/latex]
[latex]\begin{array}{r}\mathbf{.}\phantom{45}\\9\enclose{longdiv}{18\mathbf{.}45}\\ \end{array}[/latex]
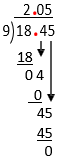
Example D
[latex]420.75\div25 =[/latex]
[latex]\begin{array}{r}\mathbf{.}\phantom{75}\\25\enclose{longdiv}{420\mathbf{.}75}\\ \end{array}[/latex]
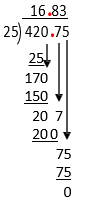
Exercise 2
Find the quotients. Check the answer by multiplying the quotient by the divisor.
Example
[latex]\begin{array}[t]{r}0.24\\60\enclose{longdiv}{14.40}\\ 12\downarrow\phantom{0}\\ \hline24\downarrow\\ 240\\ \hline0\end{array}[/latex] Check: [latex]\begin{array}[t]{r}&0.24\\ \times &60\\ \hline &14.40\end{array}[/latex]
- [latex]91\enclose{longdiv}{263.9}[/latex]
- [latex]25\enclose{longdiv}{207.5}[/latex]
- [latex]57\enclose{longdiv}{96.9}[/latex]
- [latex]63\enclose{longdiv}{176.4}[/latex]
Answers to Exercise 2
- 2.9
- 8.3
- 1.7
- 2.8
Method 3 (If the Divisor is a Decimal)
The past section taught us that if the divisor is a whole number, we put the decimal point in the quotient right above the decimal point in the dividend. Then we just go ahead and divide.
But what if the divisor has a decimal in it? A decimal divisor must be changed to a whole number before we can divide.
Remember:
- Multiplying by 10, 100 or 1000, etc. moves the decimal point as many places to the right as there are zeros in the 10, 100, 1000.
- 46 × 10 = 460, 4.6 × 10 = 46. The decimal moved over one spot because of the one zero in 10
- 46 × 100 = 4600, 4.6 × 100 = 460. The decimal moved over two spot because of the two zero in 100
- When the divisor and dividend are both multiplied by the same number, the quotient is not changed.
Your instructor will give you more information about why this method works if you wish to know.
Example E
[latex]0.05\enclose{longdiv}{1.255}[/latex]
If the divisor has a decimal, do this:
- Move the decimal point in the divisor as many places to the right as needed to make a whole number. In this example, the decimal is moved two places, which is like multiplying by 100.[latex]005.\enclose{longdiv}{1.255}[/latex]
- Now move the decimal point in the dividend the same number of places to the right (like multiplying by 100).[latex]005.\enclose{longdiv}{125.5}[/latex]
- Put the decimal point in the quotient directly above the new place in the dividend. Now divide.[latex]\begin{array}{r}25\mathbf{.}1\\5\enclose{longdiv}{125.5}\end{array}[/latex]
1.255 ÷ 0.05 = 25.1
Note: Zeros may have to be put at the end of the dividend when you move the decimal point.
Example F
48.6 ÷ 0.24 =
[latex]0.24\enclose{longdiv}{48.6}[/latex] changes to [latex]24.\enclose{longdiv}{4860.}[/latex]
There is nothing here, so we must add a zero.
Remember that if the dividend is a whole number, put a decimal to the right of it first, and then move the decimal as needed to match what you did to the divisor. You will need to add zeros to hold the places.
Example G
[latex]3.6 ÷ 1.8 =[/latex]
[latex]1.8\enclose{longdiv}{36.}[/latex] Put a decimal to the right of the dividend.
[latex]18.\enclose{longdiv}{360.}[/latex] Move the decimals for both numbers one place to the left. This is like multiplying both numbers by ten. Add a zero to the dividend to hold the tens place.
[latex]\begin{array}{r}.\hspace{0.2em}\\18.\enclose{longdiv}{360.}\end{array}[/latex] Put the decimal directly above the decimal in the dividend.
Exercise 3
Find the quotients.
- [latex]3.4\enclose{longdiv}{3.808}[/latex]
- [latex]6.6\enclose{longdiv}{19.14}[/latex]
- [latex]0.04\enclose{longdiv}{15.2}[/latex]
- [latex]0.67\enclose{longdiv}{6.164}[/latex]
Answers to Exercise 3
- 1.12
- 2.9
- 380
- 9.2
If you are having any difficulty with this exercise, ask your instructor for help before you go any further.
Exercise 4
Now try these:
- [latex]0.5\enclose{longdiv}{0.2635}[/latex]
- [latex]1.7\enclose{longdiv}{15.47}[/latex]
- [latex]0.003\enclose{longdiv}{42.12}[/latex]
- [latex]0.33\enclose{longdiv}{0.1452}[/latex]
Answers to Exercise 4
- 0.527
- 9.1
- 14040
- 0.44
Exercise 5
Set the question up for long division and find the quotient. Check your answers by multiplying quotient divisor. The product should equal the dividend.
Example
0.2448 ÷ 0.008 =
[latex]\begin{array}[t]{r}30.6\\0.008.\enclose{longdiv}{0.224\mathbf{.}8}\\24\downarrow\,\downarrow\\ \hline 04\downarrow\\0\downarrow\\ \hline 48\\48\\ \hline 0\end{array}[/latex] Check: [latex]\begin{array}[t]{rr}&30.6\\ \times& 0.008\\ \hline &0.2448\end{array}[/latex]
- 2.3412 ÷ 0.6 =
- 25.6 ÷ 0.008 =
- 2.176 ÷ 3.4=
- 205 ÷ 4.1 =
- 2.1122 ÷ 59 =
Answers to Exercise 5
- 3.902
- 3200
- 0.64
- 50
- 0.0358
What About Remainders?
The questions that you have been practicing all work out evenly. But, as you know, the world is seldom perfect and division questions often have remainders! For everyday uses of mathematics, answers to the hundredths or thousandths decimal places are accurate enough.
This is what you do if the division problem does not work out evenly:
- Do the long division until you have worked out three or four decimal places in your quotient. Add zeros to the decimal in the dividend as necessary.
- Round the quotient to the nearest tenth, hundredth, or thousandth as you are asked or as you need for your own use. Review rounding if you need to. (In this course, round to the nearest thousandth unless you are asked otherwise.)
- When you are planning to round the quotient, do the long division only to one decimal place past where you will round. It is not necessary to divide any further.
- If rounding the quotient to the nearest tenths, divide to the hundredths place (2 decimal places).
- If rounding the quotient to the nearest hundredths, divide to the thousandths place (3 decimal places).
- If rounding the quotient to the nearest thousandths, divide to the ten-thousandths place (4 decimal places).
Example H
422 ÷ 1.7 =
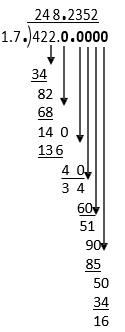
The quotient 248.2352 will round this way:
- To the nearest thousandth 248.235
- To the nearest hundredth 248.24
- To the nearest tenth 248.2
Example I
12.5 ÷ 7 =
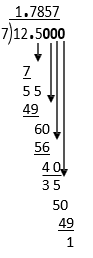
The quotient 1.7857 will round this way:
- To the nearest thousandth 1.786
- To the nearest hundredth 1.79
- To the nearest tenth 1.8
Always round money to the nearest cent.
Example J
$47.26 ÷ 3 =
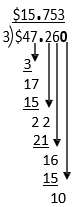
$15.753 ≈ $15.75
Sometimes numbers repeat when you divide. This will go on forever — to infinity.
Example K
100 ÷ 3 =
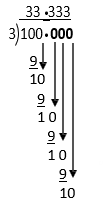
To show that the 3 keeps repeating as a decimal fraction, put a · (dot) or a ¯ (bar) above the repeating decimal digit.
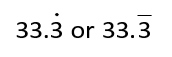
Sometimes a group of digits will repeat. Put a bar above the repeating decimal digits. For example 2.341341341341
![]()
Exercise 6
Use long division to find the quotient. Round the quotient to the nearest tenth.
- 7.359 ÷ 1.3 =
- 15.68÷ 2.2 =
- 4.93 ÷ 6 =
- 59 ÷ 8 =
Answers to Exercise 6
- 5.7
- 7.1
- 0.8
- 7.4
Exercise 7
Divide and round the quotient to the nearest hundredth.
- 43.893 ÷ 1.1 =
- 1.9525 ÷ 0.6 =
- 0.4474 ÷ 0.7 =
- 10.48 ÷ 1.5 =
Answers to Exercise 7
- 39.90
- 3.25
- 0.64
- 6.99
Dividing by 10, 100, 1000, 10000, etc.
Multiplication and division are opposite operations. Multiplying by ten, hundred, etc. moves the decimal point the same number of decimal places to the right as there are zeros in the 10, 100, 1000, etc. Moving a decimal point to the right gives a larger number.
Therefore, dividing by ten, hundred, etc. must move the decimal point to the left. Remember that moving a decimal point to the left gives a smaller number. Study the examples.
- 4.6 ÷ 10 = .46 = 0.46
- 29.6 ÷ 10 = 2.9.6 = 2.96
- 27.4 ÷ 100 = .27.4 = 0.274
- 185.4 ÷ 100 = 1.85.4 = 1.854
- 325 ÷ 1000 = 325. ÷ 1000 = .325. = 0.325
- 2567. 3 ÷ 1000 = 2.567.3 = 2.5673
You may need to prefix zeros. Look at these examples:
- 0.3 ÷ 10 = .0.3 = 0.03
- 1.75 ÷ 100 = ._1.75 = 0.0175
- 0.5 ÷ 1000 = ._ _ _.5 = 0.0005
Exercise 8
Write the quotient. Use the short method you have just learned.
- 7 ÷ 10 =
- 14 ÷ 100 =
- 6.5 ÷ 10 =
- 74.35 ÷ 10 =
- 43.2 ÷ 100 =
- 147.6 ÷ 100 =
- 183.75 ÷ 1000 =
- 2374.5 ÷ 1000 =
- 0.63 ÷ 10 =
- 7.46 ÷ 100 =
- 0.035 ÷ 10 =
- 366 ÷ 100 =
- 0.1 ÷ 1000 =
- 100.1 ÷ 10 =
- 16.2 ÷ 100 =
- 5692.1 ÷ 10 =
- 0.025 ÷ 100 =
- 3.31 ÷ 10 =
Answers to Exercise 8
- 0.7
- 0.14
- 0.65
- 7.435
- 0.432
- 1.476
- 0.18375
- 2.3745
- 0.063
- 0.0746
- 0.0035
- 3.66
- 0.0001
- 10.01
- 0.162
- 569.21
- 0.00025
- 0.331
Word Problems Using Division of Decimals
Division problems usually give information about groups of things and ask you to find the information for one thing.
Some key words which point to division include:
- separated
- split
- cut
- shared
- What is the cost per…?
- unit price
- What is the distance per…?
- average (speed, cost, weight, time)
Exercise 9
Solve these division problems. Look carefully for the pattern of the problems and underline any key words which point to division. Do an estimation before you find the actual solution.
- Joanne’s little car has a 44.5 L tank. She can drive 525 km on a tank of gas. What is the average distance she can travel per litre of gas? (The answer will be kilometres per litre, so you must divide the kilometres by the litres.)
- Estimation: 520 km ÷ 40 L ≈ 13 km/L
- Actual Solution:
[latex]\begin{array}[b]{l}\phantom{0000p0}11.798\\445\enclose{longdiv}{5250.0}\end{array}[/latex] ← move the decimal over one spot in both numbers and add the appropriate number of zeros.
525 km ÷ 44.5 L = 11.798 km/L - Answer: Joanne’s car travels an average of 11.798 kilometres per litre of gas.
- Three villages are organizing a feast in Prince Rupert to celebrate the start of the All Native Basketball tournament (ANT). The total cost for the feast will be $8972.43. How much will each community pay?
- Estimation:
- Actual Solution:
- Answer:
- If you can solve 30 math questions in 1.5 hours, how long would it take to solve just one?
Hint: You want the average time per question. The answer will be less than one hour, so it may be easier to work out the problem using minutes. Change hours to minutes by multiplying the hours by 60 minutes. [ 1.5 hours × 60 minutes = number of minutes]- Estimation:
- Actual Solution:
- Answer:
- During her shift at the container port, Lucinda used a forklift to load 3675.6 kilograms of crated goods onto four and a half pallets. How many kilograms did she load onto each pallet?
- Estimation:
- Actual Solution:
- Answer:
- Murray buys a double-double from Tim Hortons before class every morning and another on his lunch break. On weekends he only has one each day. He spends $113.40 in four and a half weeks. How much does he pay for each coffee?
- Estimation:
- Actual Solution:
- Answer:
Answers to Exercise 9
- Estimation: 520 km ÷ 40 L ≈ 13 km/L
Actual Solution: 525 km÷ 44.5 L = 11.798 km/L
Answer: Joanne‘s car travels an average of 11.798 kilometres per litre of gas. - Estimation: 9000 ÷ 3 ≈ 3000
Actual Solution: 8972.43 ÷ 3 = 2990.81
Answer: Each village will pay $2990.81. - Estimation: 90 minutes ÷ 30 questions ≈ 3 minutes
Actual Solution: 90 minutes÷30 questions = 3
Answer: It takes you 3 minutes to solve one math question. - Estimation: 3700 kg ÷ 5 kg ≈ 740
Actual Solution: 3675.6 kg ÷ 4.5 kg = 816.8 kg
Answer: Lucinda loaded 816.8 kg onto each pallet. - Step 1:
How many coffees per week? 12
How many coffees in 4.5 weeks? 54
Step 2:
Estimation: 100 ÷ 50 = 2
Actual Solution: 113.40 ÷ 54 = 2.10
Answer: Murray pays $2.10 for each coffee.
Topic A: Self-Test
Mark /13 Aim 10/13
- Find the quotients. (2 marks)
- [latex]4\enclose{longdiv}{17.6}[/latex]
- [latex]0.3\enclose{longdiv}{396}[/latex]
- Divide and round the quotient to: (4 marks)
- the nearest tenth [latex]2.3\enclose{longdiv}{10.4}[/latex]
- the nearest hundredth [latex]0.12\enclose{longdiv}{0.4739}[/latex]
- Find the quotients. (3 marks)
- 51 ÷ 10 =
- 81.81 ÷ 100 =
- 62.811 ÷ 1000 =
- Problems. (4 marks)
- A train travelled 252.5 km in 4.25 hours. What was its average speed in kilometres per hour?
- Estimation:
- Actual Solution:
- Answer:
- The office manager ordered t-shirts for the staff for Orange Shirt Day. The shirts cost $181.30 in total. How much should the manager charge each of the fourteen staff members for a shirt?
- Estimation:
- Actual Solution:
- Answer:
- A train travelled 252.5 km in 4.25 hours. What was its average speed in kilometres per hour?
Answers to Topic A Self-Test
- Find the quotients.
- 4.4
- 1320
- Divide and round the quotient.
- 4.5
- 3.95
- Find the quotients.
- 5.1
- 0.8181
- 0.062811
- Problems.
- Average speed of train
- Estimation: 250 km ÷ 5 hours ≈ 50 km/hr
- Actual Solution: 252.5 km ÷ 4.25 hours = 59.411764 km/hr
- Answer: The average speed is 59.41 kilometres per hour.
- Cost per t-shirt.
- Estimation: $180 ÷ 15 ≈ $12
- Actual Solution: $181.30 ÷14 = $12.95
- Answer: The manager should charge each team member $12.95.
- Average speed of train
The result of a division question; the quotient tells how many times one number is contained in the other.
Any of the ten numerals (0 to 9) are digits. This term comes from our ten fingers which are called digits. The numerals came to be called "digits" from the practice of counting on the fingers!
Make an approximate answer. Use the sign ≈ to mean approximately equal.
The number of groups or the quantity into which a number (the dividend) is to be separated.
The result of a multiplying question, the answer.
The number or quantity to be divided; what you start with before you divide.
The amount left when a divisor does not divide evenly into the dividend. The remainder must be less than the divisor.
Without end, without limit.
The price for a set amount. E.g., price per litre, price per gram.

