Anti-Racism and Anti-Hate Project Report
3 Environmental Scan
The purpose of the environmental scan was to identify resources, tools, and training already in place at 25 BC PSIs and four BC-based organizations[1] (see Appendix for the full list) that could offer robust engagement opportunities in AR and AH.
The ideal target audience of such resources are individuals beginning their journey of learning AR and AH practices. A secondary goal was to add the findings of the environment scan as a repository of resources to BCcampus’ open educational resources database. As a result, the following questions framed the environment scan:
- What tools, training or resources on AR and AH have been developed and made publicly available by BC PSIs and identified organizations?
- What framework emerges as a learning pathway for individuals working in the post-secondary sector to approach AH and AR work?
Situating this environmental scan with clear definitions is an important undertaking. AR has been clearly defined and for this reason, the definition chosen to frame the scan is as follows:
Anti-racism: “The active process of identifying, challenging, and confronting racism. This active process requires confronting systems, organizational structures, policies, practices, behaviors, and attitudes. This active process should seek to redistribute power in an effort to foster equitable outcomes.” (NADOHE, 2021, p. 8)
However, researching for a definition for AH revealed there is no clear uniformity, despite the term being utilized in critical narratives focused on creating an inclusive and safe environment. As a result, the definition selected for AH recognizes a similar active state required to engage in AR work and bridges it with what the BC’s Office of Human Rights Commissioner (2022) has available on their website with regard to hate and hate speech. The AH definition used to frame the scan is:
Anti-hate: The active process of addressing and combating the fear of losing power and the ignorance that underlies much of hate, a rise in white supremacy and deep roots in a legacy of colonialism, racism and misogyny. From hate speech to hate violence, this active process should seek to reduce hate, dismantle white supremacy and uphold legislation that supports human rights and constitutional rights that are free of hate and violence.
Recognizing the intersection of AR and AH, a glossary has been provided in the latter part of this report to clarify other key concepts that framed the scan and subsequent sections outlining the methodology and findings.
Timeline, Assumptions and Limitations
Given that the environmental scan was one component of the overall project initiated by BCcampus, the timeline described below outlines the milestones that were expected based on a project start date of January 28, 2022, and end date of March 31, 2022.
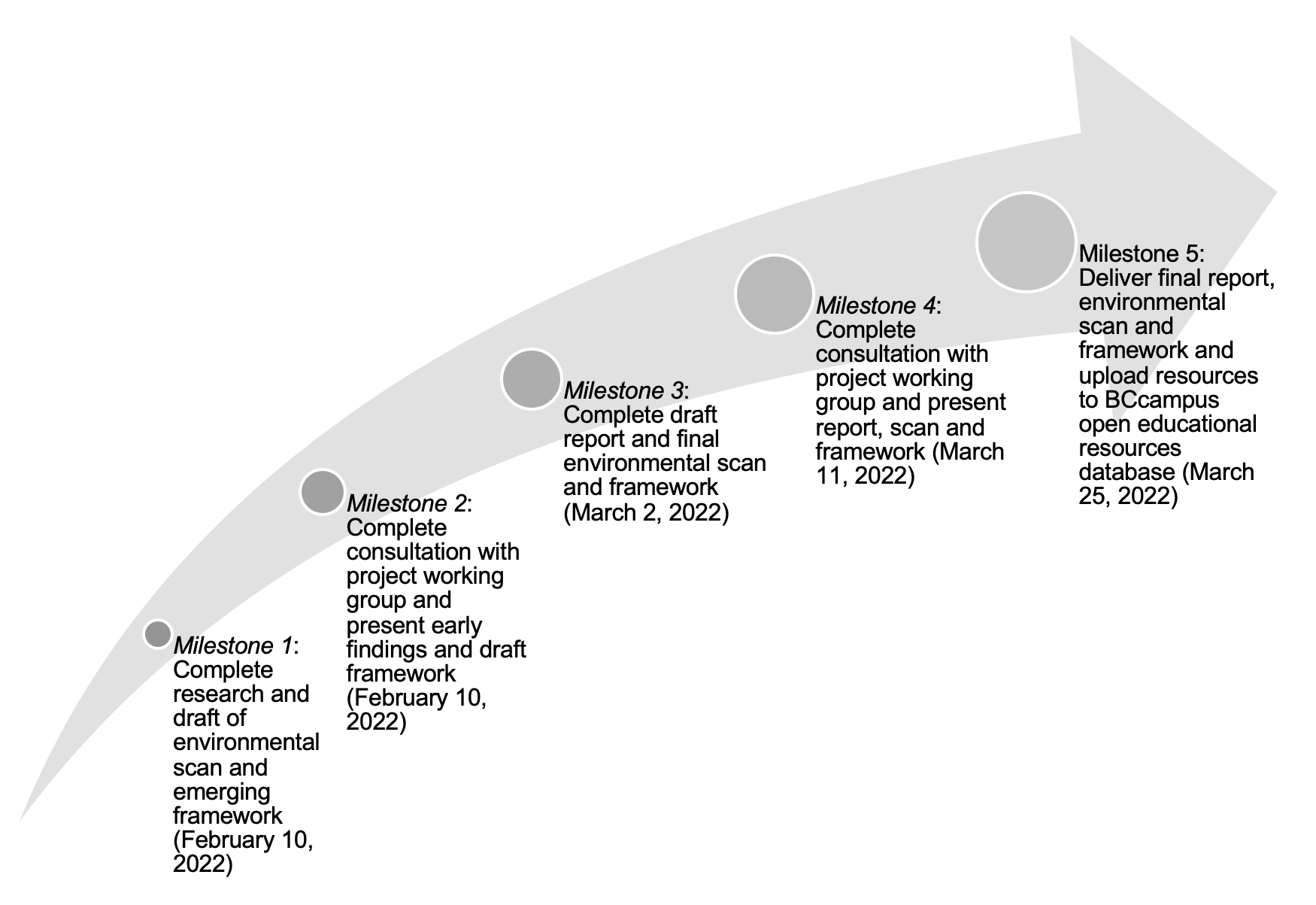
At the onset of the project, deliverables and milestones needed to be framed into what was possible, given the ambitious expectations of the project. As a result, an understanding of naming the compromise underpinned this overall project and environmental scan that led both to a recognition of what is achievable in a compressed timeline and the limitations that existed.
The following assumptions helped to frame the scope:
- The scan will not produce a comprehensive understanding of resources, tools or training available across BC PSIs.
- The scan will not be able to demonstrate the evaluation and impact of resources, tools or training available across BC PSIs.
- The scan will focus on resources, tools or training for individuals working at PSIs and are beginning their journey of learning AR and AH practices.
- The scan will exclude policies related to academic accommodations for students with disabilities, policies on sexualized violence, discrimination, harassment, student conduct, respectful environment as well as policies related to reporting violations of human rights, racism, discrimination etc. as each institution adopts and enacts these differently. While these can be viewed as resources for community members, their accessibility is not often widespread across students, staff and faculty until an incident or experience occurs. However, it is critical to highlight the presence of such policies in creating cultural safety for those impacted by harmful experiences, narratives and trauma that often intersects with racism, oppression, violence and hate.
Methodology and Process
As described in earlier sections, two overarching research questions framed the methodology:
(1) What tools, training or resources on AR and AH practices have been developed and made publicly available by BC institutions and identified organizations?
(2) What framework emerges as a learning pathway for individuals working in the post-secondary sector to approach AH and AR work?
Due to the short timeframe of this project, the process to support the scope of the scan involved an electronic search of each PSI’s website (including any pages/websites of offices tasked with anti-racism, equity, human rights or human resources) using search terms relevant to AR and AH:
- For AR, the search terms included anti-racism, racism, equity, inclusion and decolonization; and
- For AH, these included hate, bias, prejudice and anti-hate.
Three intersecting elements were key to conducting the environmental scan:
- A recognition that hate and racism are rooted in inequitable and unjust beliefs of white supremacy and colonization that have visibly and invisibly permeated institutions, structures, and systems for many years. As a result, specific populations have experienced different impacts of these deeply entrenched manifestations of historic and current systems of oppression that still exist in PSIs (and across many other sectors too). For this reason, the environmental scan highlighted resources, tools and training that brought to light AR and AH with respect to these populations, given both historical and current commitments, movements and approaches to AR and AH. These included anti-Indigenous racism, anti-Black racism, anti-Asian racism, anti-Semitism, Islamophobia, Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women and Girls, and 2SLGBTQIA+.
- An emphasis on the interconnectedness between AR and AH as well as the importance of intersectionality and the multi-complex and interdependence of different social categorizations of individuals who are both engaged in this work and individuals for whom this work is intended to impact.
- A viewpoint that the scan was a snapshot in digital time for which lived and living experiences provide richness and depth – the project working group played an integral role in addressing gaps established in the methodology, process and both early and final findings. The consultations with the working group were meaningful in recognizing that this environmental scan could only scratch the surface of what has been developed across the BC post-secondary landscape and what could be developed to move this work forward needed to happen at individual and systemic levels. The insights and recommendations sections elucidate some of the critical reflections provided by the working group.
- Organizations were selected by BCcampus in consultation with the project working group based on criteria of being BC based and involved in anti-racism, anti-oppression and social justice education and training ↵
The unfair treatment of an individual or group that results in placing a burden on them, denying them of a privilege, benefit or opportunity that is enjoyed by others, because of race, citizenship, family status, disability, sex, etc. (1)
Refers to behaviours, actions or words that can be offensive and hurtful and leave the targeted group/person feeling traumatized, excluded, unsafe, uncomfortable and sad. (1)
Refers to an intentional process that considers power, access, opportunities, treatment, impact and outcomes of a group that has been historically, systemically and persistently marginalized. (2)
Is a set of mistaken assumptions, opinions and actions that is based on a belief that one group of people characterized by a specific colour of skin or shared ancestry is inherently superior to another. Expressed as jokes, slurs, hate speech or actions, racism is deeply rooted in entrenched institutions, systems, policies, programs, practices and attitudes. (3) (8)
The unfair treatment of an individual or group that results in placing a burden on them, denying them of a privilege, benefit or opportunity that is enjoyed by others, because of race, citizenship, family status, disability, sex, etc. (1)
The ongoing process of identifying and removing forms of colonization at the structural, systemic and individual level. (1)
An unconscious way of thinking that can be explicitly or implicitly based on a stereotype or perspectives of a group of people. (1)
A state of mind that is conscious or unconscious and strongly held attitudes about a person/group that is often absent of legitimate evidence. (5)
The idea that white people and the ideas, thoughts, beliefs and actions of White people are superior to People of Colour and their ideas, thoughts, beliefs and actions. This privilege results in white People enjoying structural advantages and rights while People of Colour do not. White supremacy is deeply rooted in entrenched individual, collective and systemic levels. (9)
The invasion, dispossession and suppression of a group of individuals by another group that results in an unequal distribution of power and privilege. (2)
The ongoing race-based discrimination, negative stereotyping and injustice experienced by Indigenous Peoples and is rooted in a history of genocide, colonization and violence through evident discrimination in Canadian federal policies such as the Indian Act and the residential school system. The overt and covert racism perpetuates power imbalance, systemic racism, inequity and hostility and violence directed at Indigenous Peoples that requires ongoing and active re-addressment and dismantling in light of decolonization, truth and reconciliation. (5) (6)
Beliefs, attitudes, prejudice, stereotyping and/or discrimination that is directed at people of Black-African descent and is rooted in a history and experience of enslavement and colonization. The overt and covert racism that is both structural and systemic across policies, practices, institutions, ideologies and sectors towards people of Black-African descent requires an ongoing and active process of dismantling such reinforced and perpetuated systems of oppression. (5) (8)
Beliefs, attitudes, prejudice, stereotyping and/or discrimination that is directed at people of Asian descent based on others’ assumptions about their ethnicity and nationality. The overt and covert racism exist at individual and systemic levels and requires ongoing and active processes of dismantling such forms of racism, unequal treatment and forms of hate. (5)
A perception of Jews which is expressed as overt hostility, hatred or blame that is directed at Jewish people and results in incidents of discrimination and hate because of their religion, ethnicity and culture. (5) (6)
Includes racism, stereotypes, prejudice, fear or acts of hostility directed as Muslims or believers of Islam. From acts of intolerance, racial profiling to the treatment of being viewed as a security threat, such acts are institutional and systemic and require dismantling to ensure Muslims can live peacefully without such negative perspectives. (5) (6)
This term derived from the U.N. Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples encompasses First Nations, Métis and Inuit people, individually or collectively. (2)
Two Spirit, Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans, Queer (or Questioning), Intersex, Asexual. The ‘+’ recognizes the growth in awareness of sexual orientations and gender diversity and the intentional placement of Two Spirit (2S) is to distinguish that Indigenous Peoples are the first peoples of the land and their understanding of gender and sexuality precedes colonization. (2)
Recognizes the interconnected and overlapping nature of categorizations such as race, ethnicity, religion, class, disability, sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, that apply to individuals or groups. The interdependence of each impact the power, privilege and systems of discrimination or disadvantage that is experienced by such individuals or groups. (8) (9)

