Chapter 4. VPN
4.2 SSL VPN
Learning Objectives
- Configure a tunnel-based SSL VPN
- Configure a web-based SSL VPN (Web Portal)
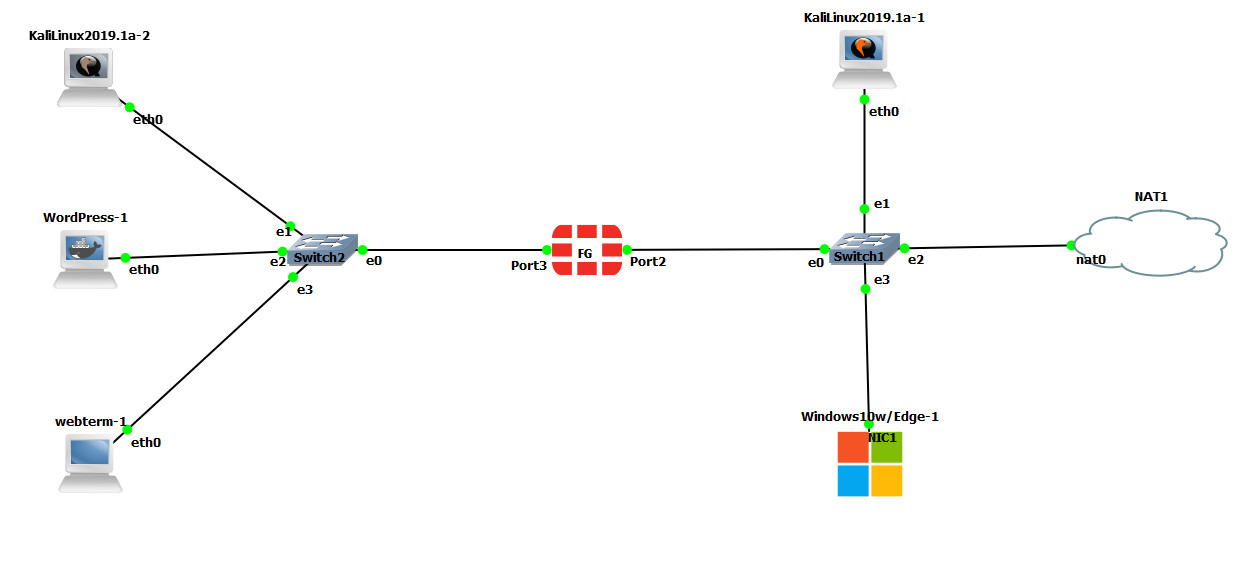
| Device | IP address | Access |
|---|---|---|
| FortiGate | Port3: 192.168.1.1/24 – DHCP (192.168.1.20 to 192.168.1.30)
Port2: DHCP Client |
ICMP-HTTP-HTTPS |
| WebTerm (FMC) | 192.168.1.2/24 | – |
| KALI Linux (SSH Server) | 192.168.1.3/24 | – |
| WordPress | 192.168.1.4/24 | |
| KALI-outside | DHCP Client | |
| Windows | DHCP Client |
Configure the interfaces of the firewall. Port2 and Port3 should be configured in the terminal to access the firewall.
- Port 3 Configuration:
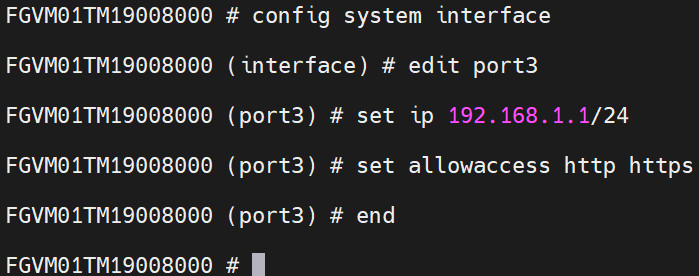
Figure 4.39: Port3 settings - Port 2 Configuration:
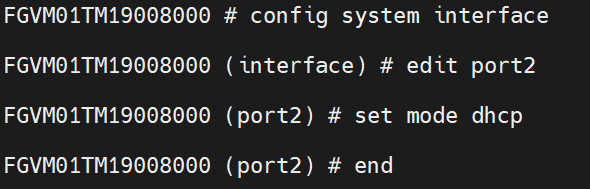
Figure 4.40: Port2 settings - Configure DHCP Server on port3.
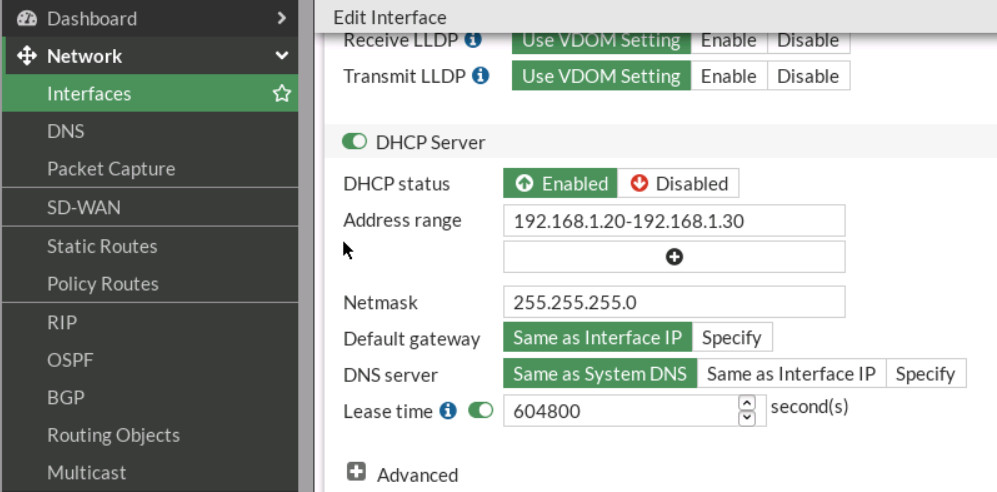
Figure 4.41: Enable DHCP Server on port3 - Configure user and user group. Go to User & Authentication > User Definition to create a local user sslvpnuser1.
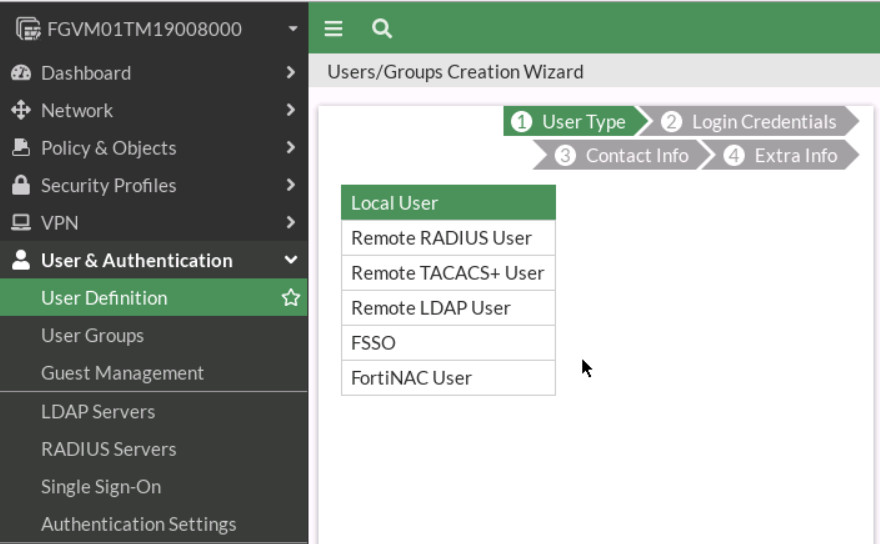
Figure 4.42: Create a local user 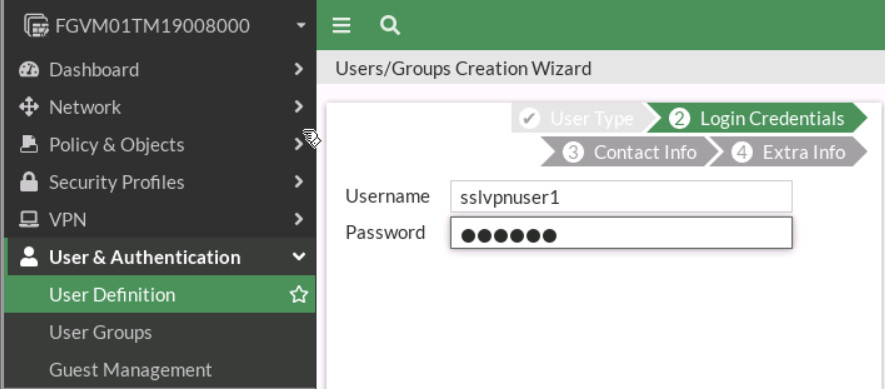
Figure 4.43: Configure login credentials Go to User & Authentication > User Groups to create a group sslvpngroup with the member sslvpnuser1.
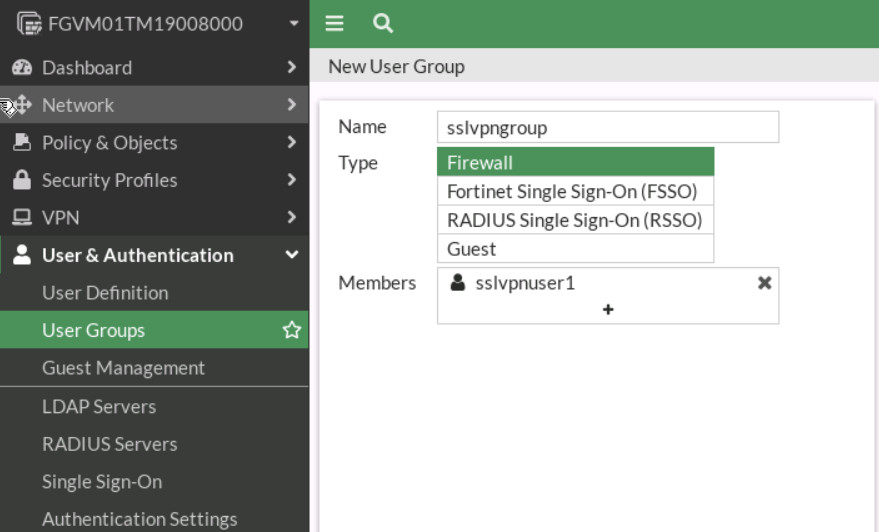
Figure 4.44: Create a group - Configure SSL VPN web portal and Tunnel mode. Go to VPN > SSL-VPN Portals:
- Split-Tunneling: Disabled
- Source IP Pools: SSLVPN_TUNNEL_ADDR1
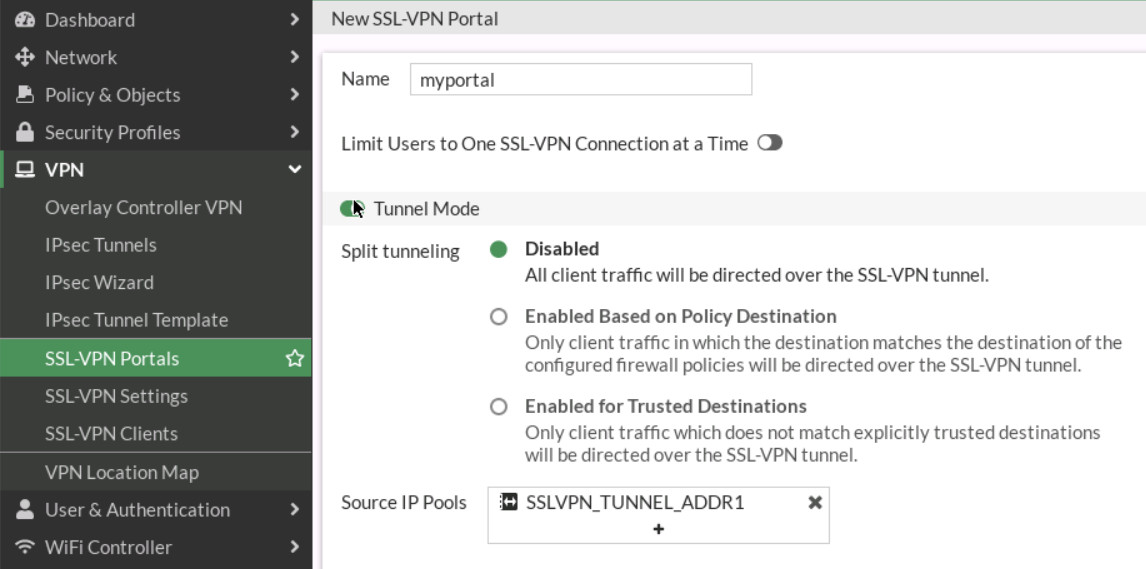
Figure 4.45: SSL-VPN Portal Go to VPN > SSL-VPN Portals, add KALI IP address (SSH Server: IP Address of Kali) and WordPress (IP Address of WordPress) in the bookmark section.
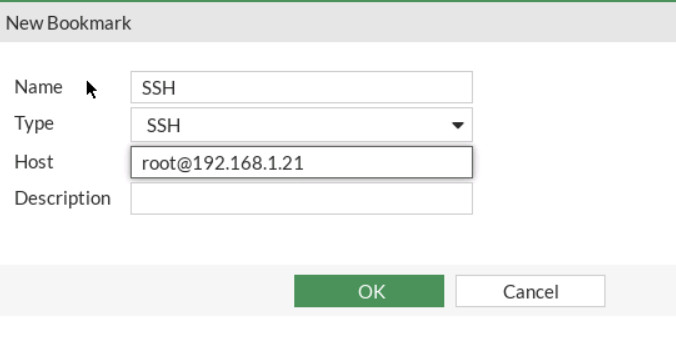
Figure 4.46: Create an SSH bookmark 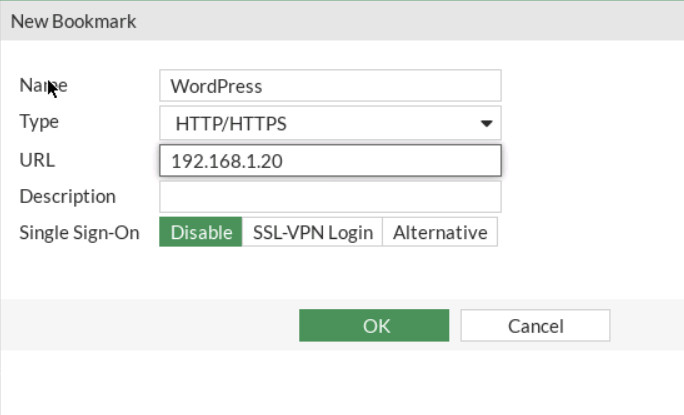
Figure 4.47: Create an HTTP/HTTPS bookmark 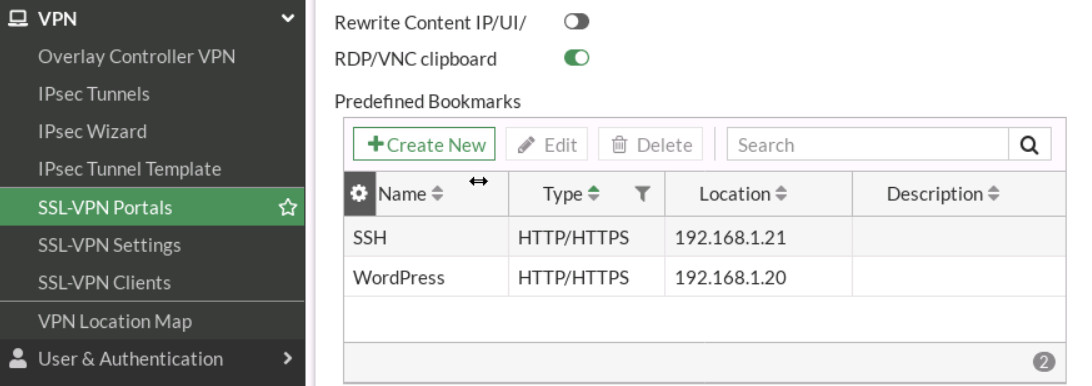
Figure 4.48: Bookmark settings - Configure SSL VPN settings. Go to VPN > SSL-VPN Settings:
- For Listen on Interface(s), select Port2.
- Set Listen on Port to 8080.
- Server Certificate: Fortinet
- In restrict Access, select “Allow access from any host”
- Address range: Automatically assign address.
- In Authentication/Portal Mapping All Other Users/Groups, set the Portal to MyPortal
- Create new Authentication/Portal Mapping for group sslvpngroup mapping portal MyPortal.
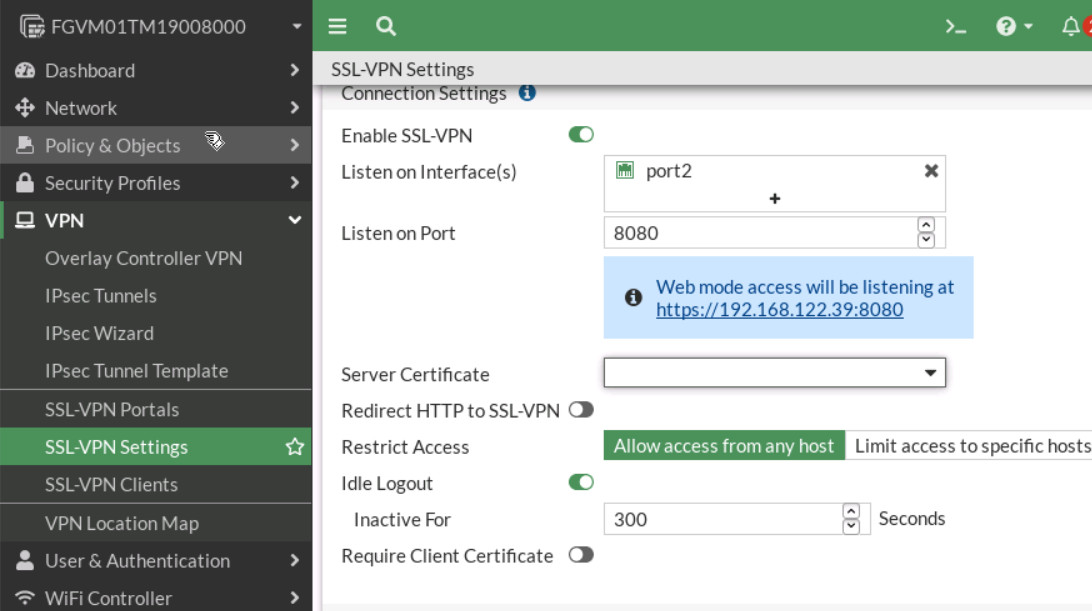
Figure 4.49: Enable SSL-VPN Settings 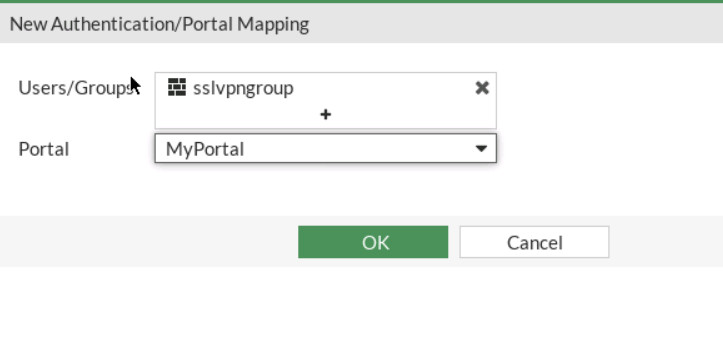
Figure 4.50: Assign sslvpngroup to MyPortal 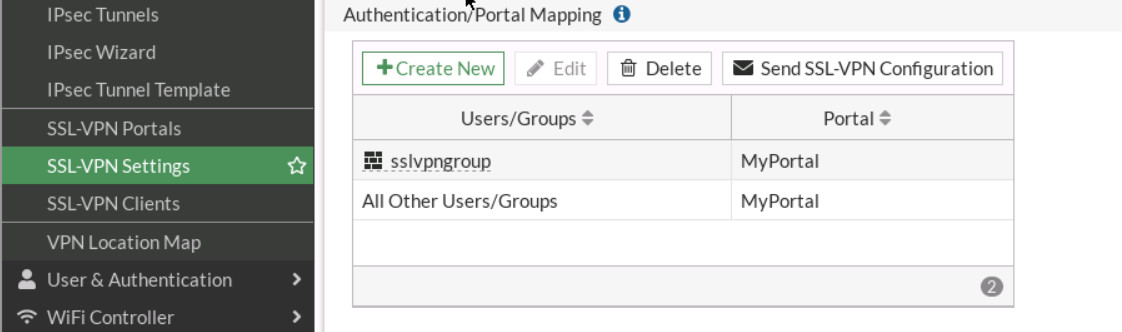
Figure 4.51: Authentication/Portal Mapping - Configure SSL VPN firewall policy:
- Go to Policy & Objects > Firewall Policy.
- Fill in the firewall policy name. In this example, SSLVPN full tunnel access.
- The incoming interface must be SSL-VPN tunnel interface(ssl.root).
- Choose an Outgoing Interface. In this example, port3.
- Set the Source to all and group to sslvpngroup.
- Set the Destination to all.
- Set Schedule to always, Service to ALL, and Action to Accept.
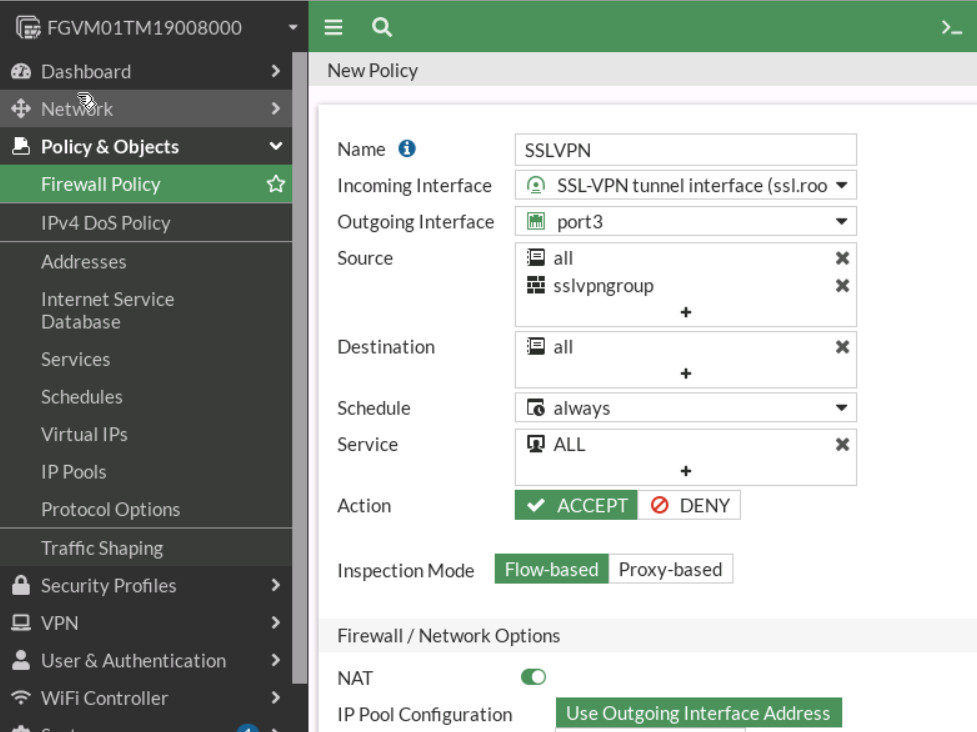
Figure 4.52: Create a Firewall Policy for SSLVPN - Now connect to Kali outside and open the browser https://IP-PORT 2-Firewall:8080
Enter the username and password you created earlier. Then try to connect to the KALI SSH Server and WordPress through the browser.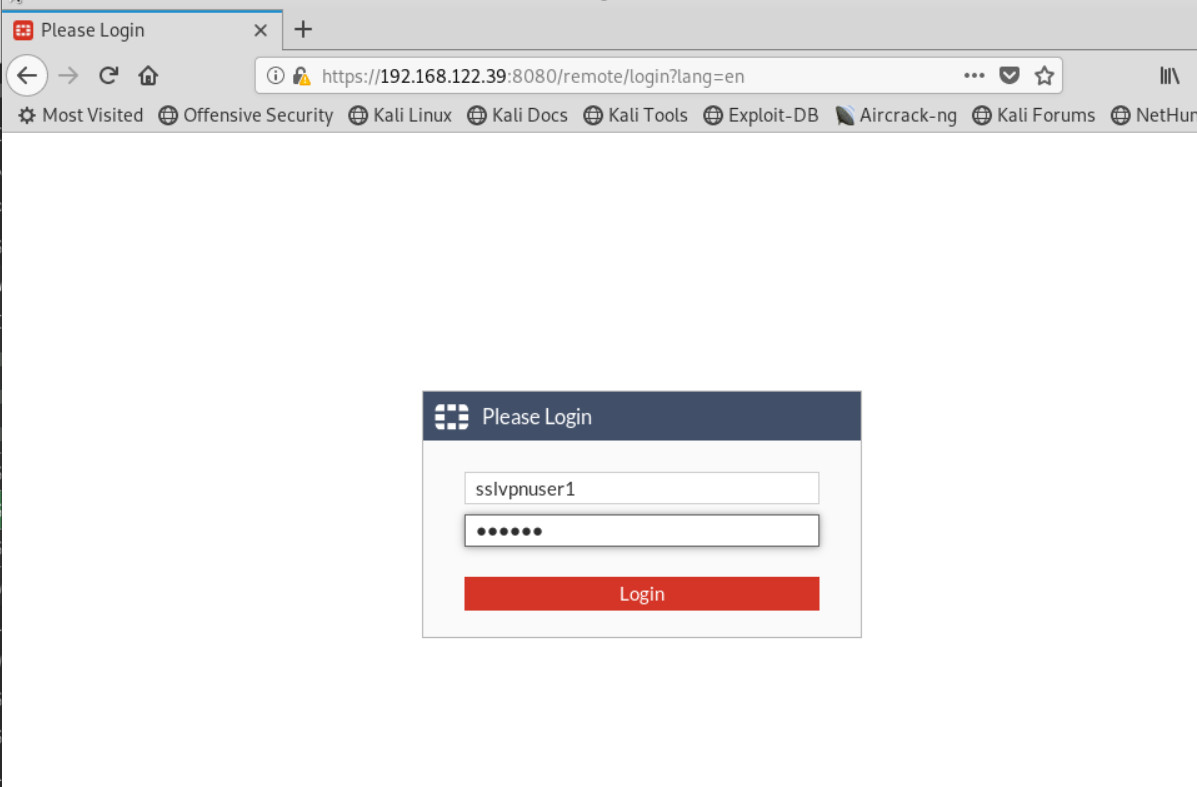
Figure 4.53: SSL-VPN Portal 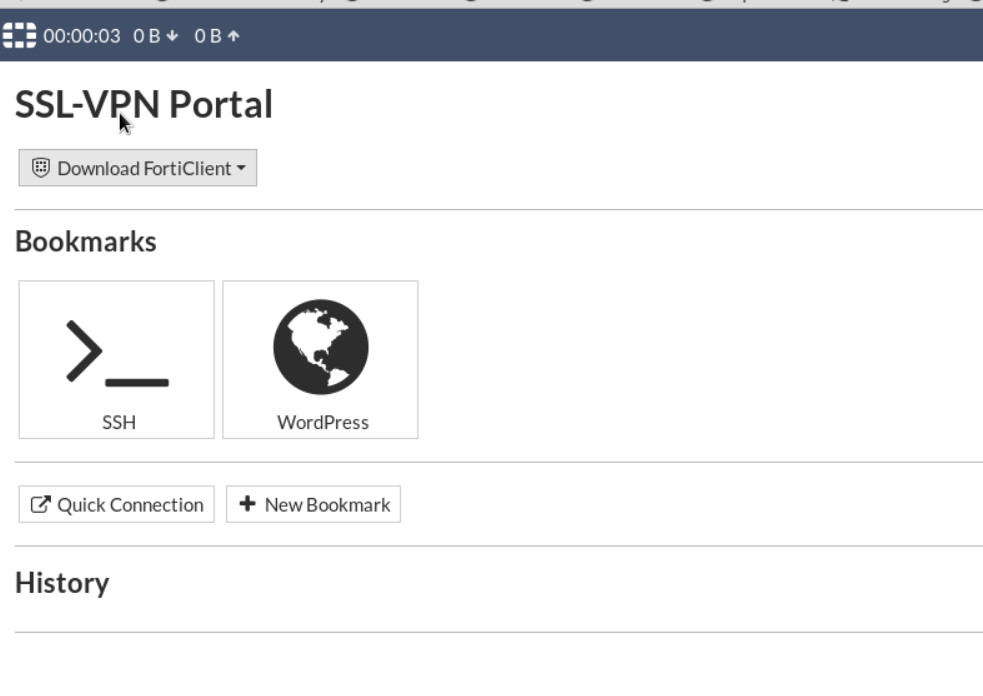
Figure 4.54: SSL-VPN Portal 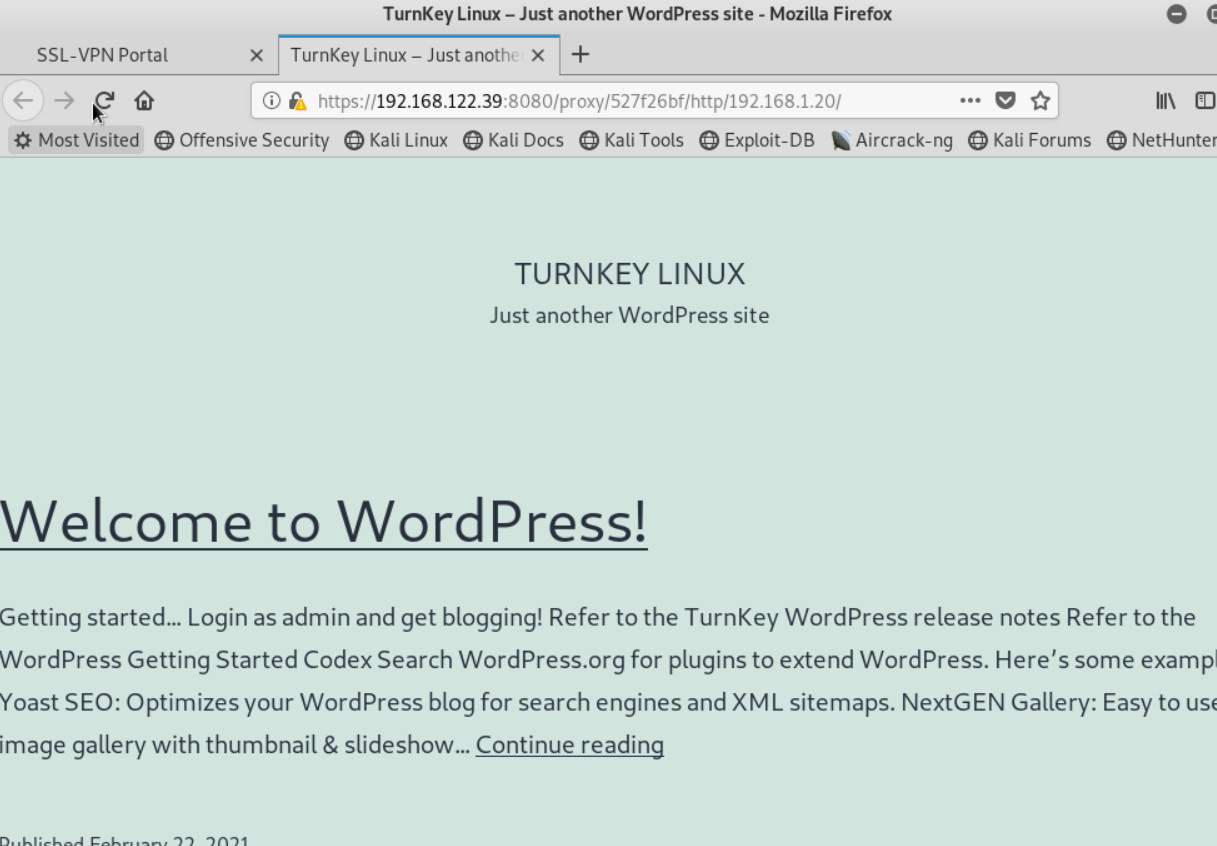
Figure 4.55: Verify WordPress 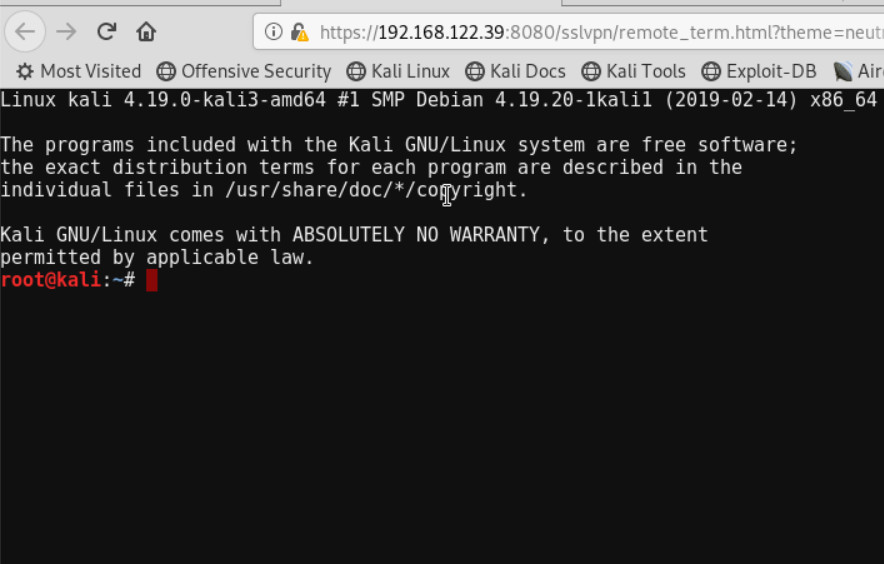
Figure 4.56: Verify SSH - Now, go to Windows and install FortiClient on Windows. Try to use FortiClient to connect through SSLVPN.
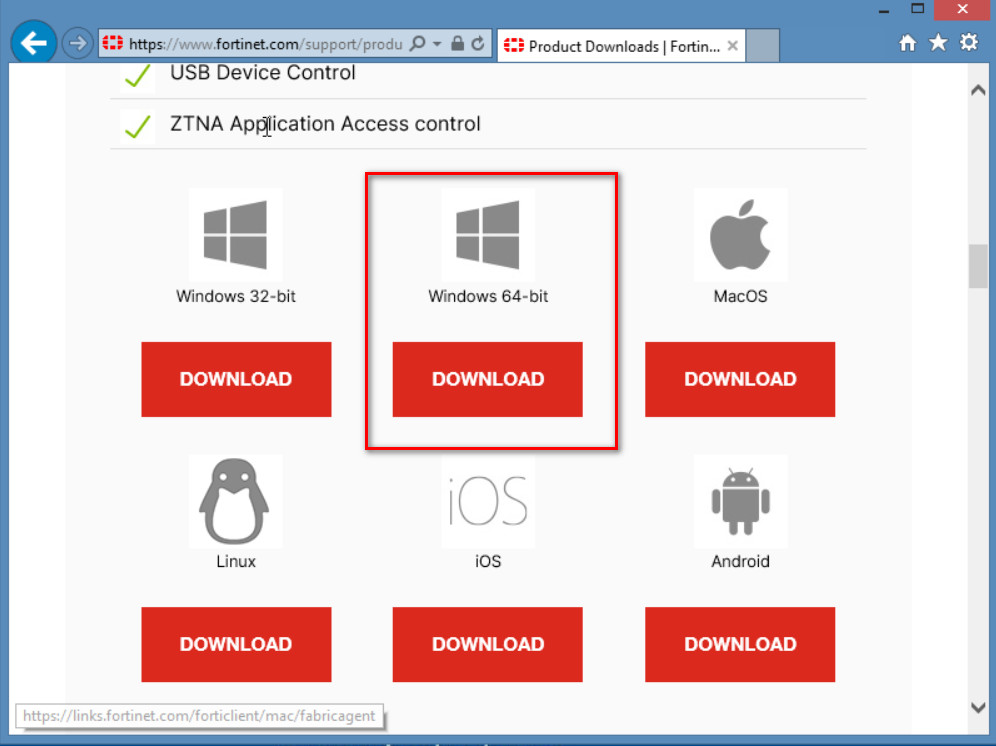
Figure 4.57: Download FortiClient 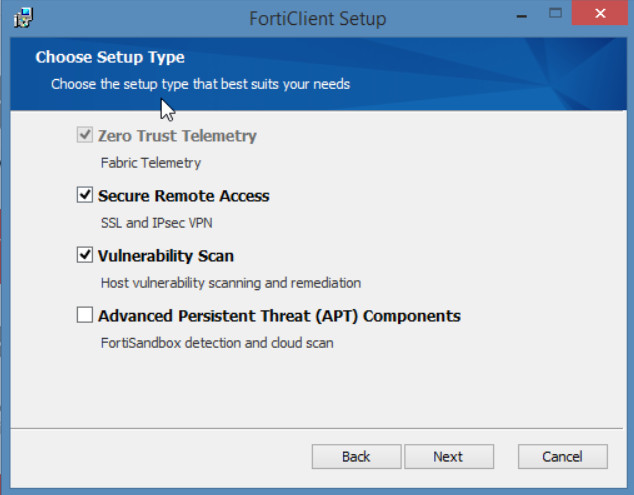
Figure 4.58: FortiClient Installation 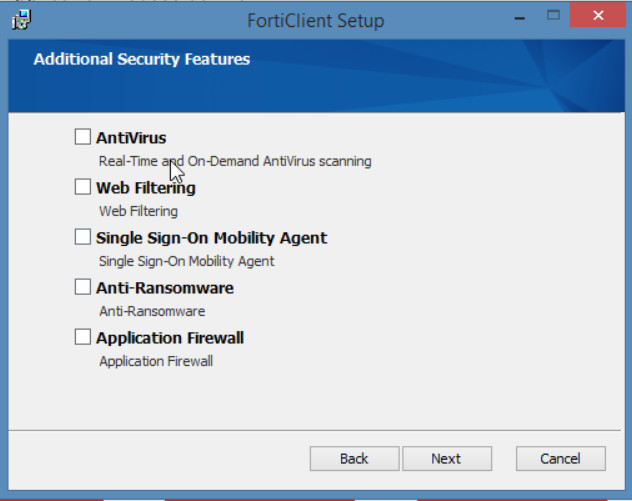
Figure 4.59: FortiClient Installation - Configure FortiClient.
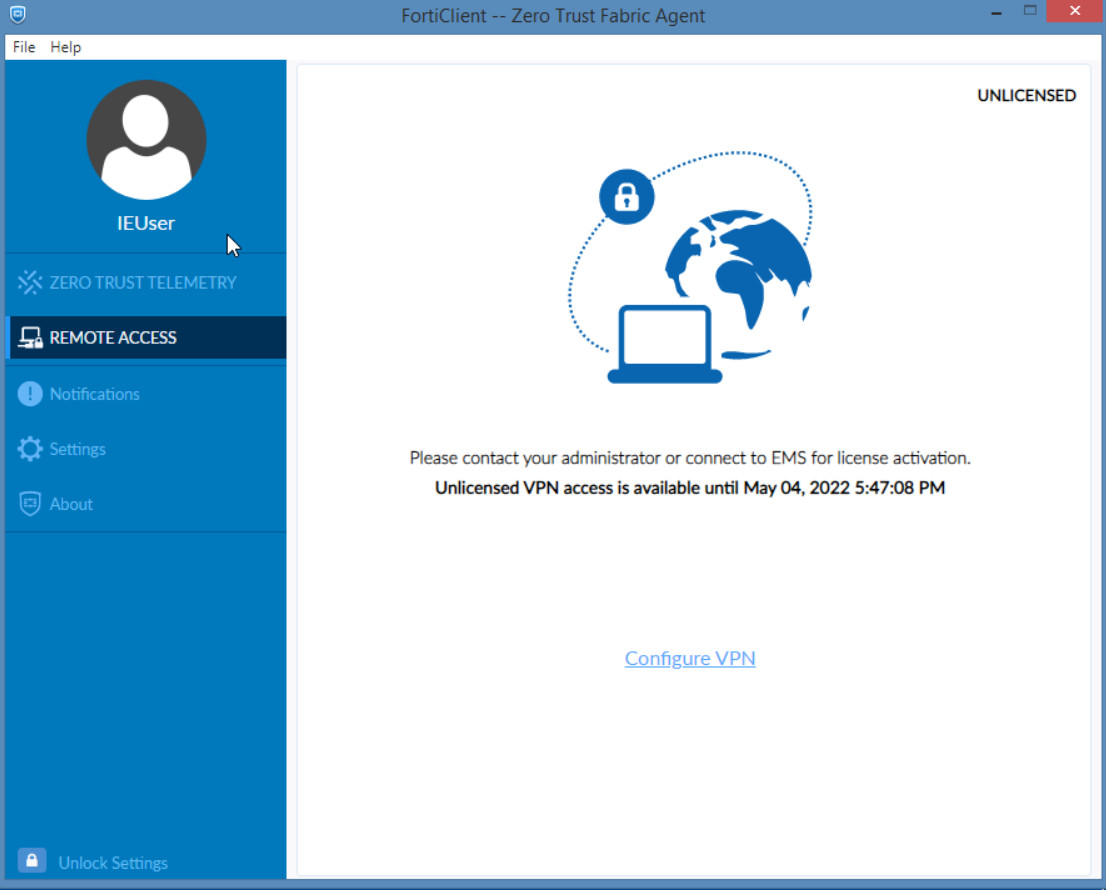
Figure 4.60: Configure FortiClient 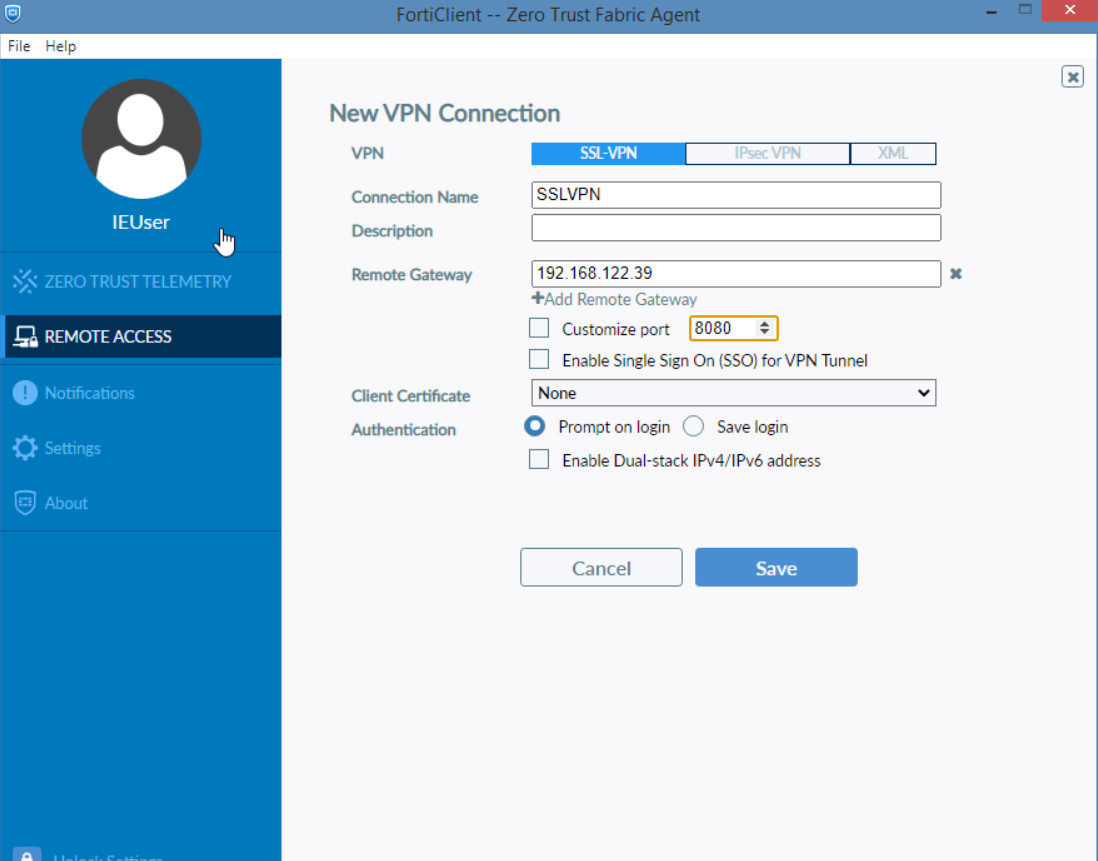
Figure 4.61: Configure SSLVPN - Verify configuration. Enter the Username and Password you have set for SSLVPN.
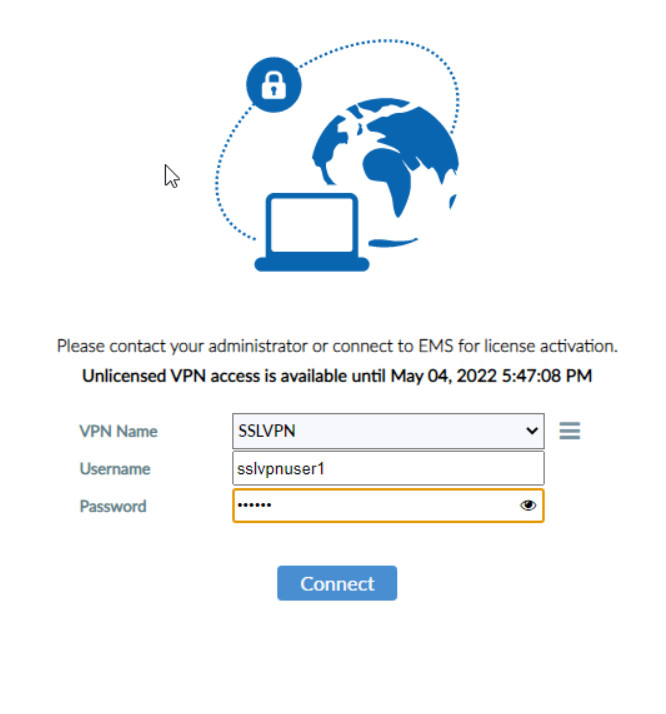
Figure 4.62: SSLVPN Credentials Accept the Certificate Issuer to have a secure connection.
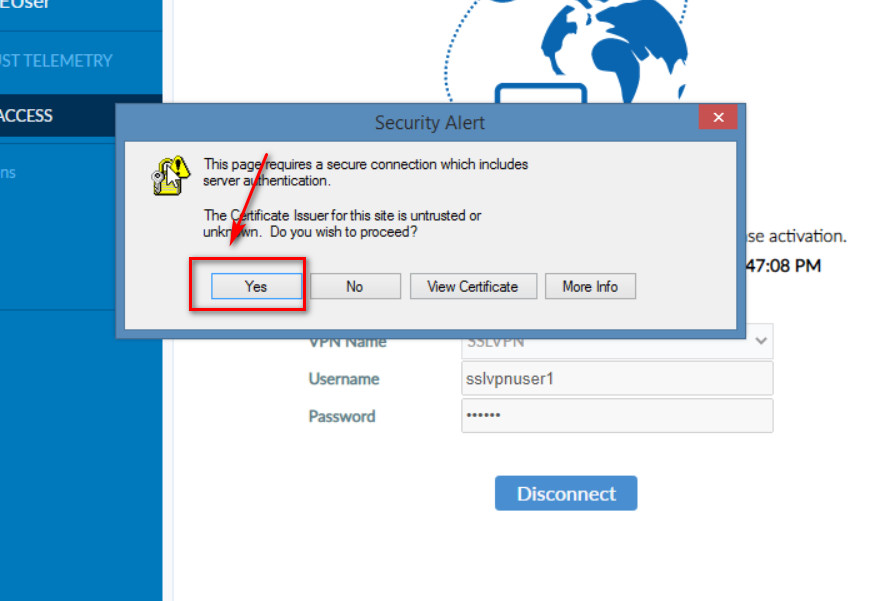
Figure 4.63: Click on Yes in Security Alert 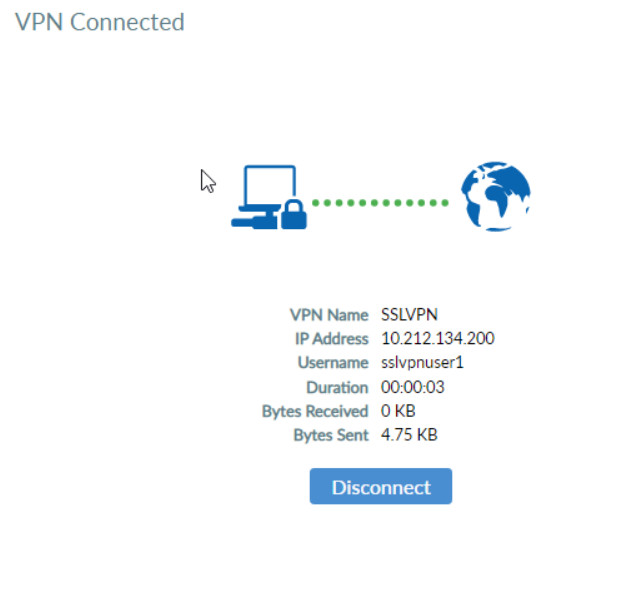
Figure 4.64: Verify SSLVPN Connection Verify your connectivity by entering the IP address of WordPress.
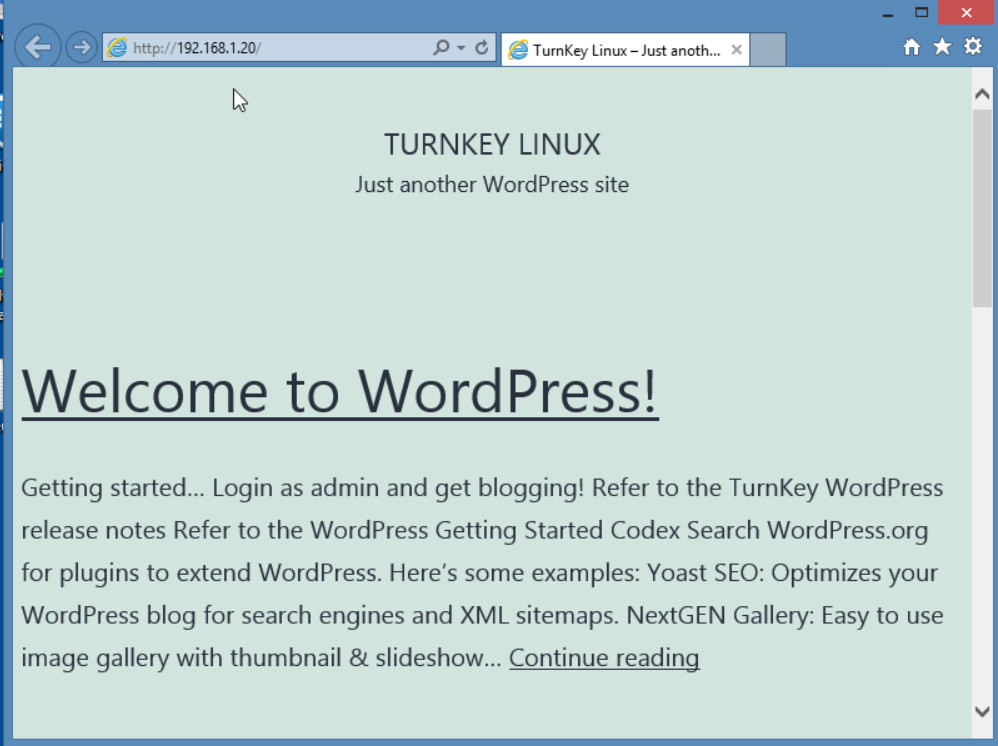
Figure 4.65: Verify WordPress Verify your connectivity by entering the IP address of SSH Server.
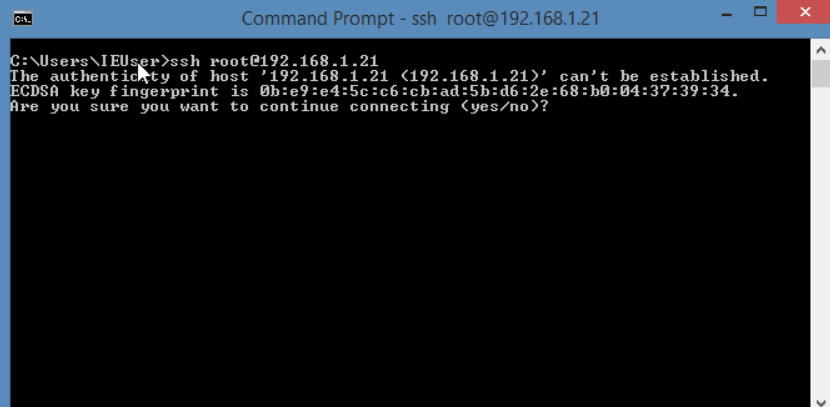
Figure 4.66: Verify SSH 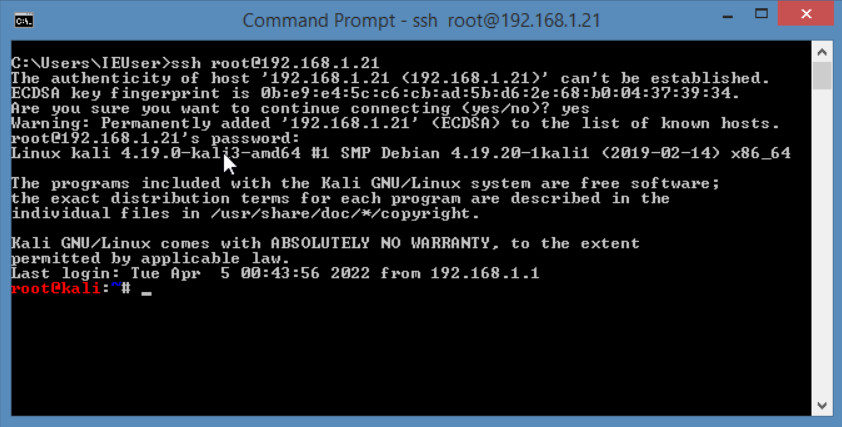
Figure 4.67: Verify SSH connection

