Main Body
Chapter 1. An Introduction to Sociology

Learning Objectives
- Explain concepts central to sociology
- Describe the different levels of analysis in sociology: micro-sociology and macro-sociology
- Understand how different sociological perspectives have developed
- Explain why sociology emerged when it did
- Describe the central ideas of the founders of sociology
- Describe how sociology became a separate academic discipline
- Explain what sociological theories are and how they are used
- Describe sociology as a multi-perspectival social science, which is divided into positivist, interpretive and critical paradigms
- Understand the similarities and differences between structural functionalism, critical sociology, and symbolic interactionism
- Explain why it is worthwhile to study sociology
- Identify ways sociology is applied in the real world
Introduction to Sociology
Concerts, sports games, and political rallies can have very large crowds. When you attend one of these events, you may know only the people you came with. Yet you may experience a feeling of connection to the group. You are one of the crowd. You cheer and applaud when everyone else does. You boo and yell alongside them. You move out of the way when someone needs to get by, and you say “excuse me” when you need to leave. You know how to behave in this kind of crowd.
It can be a very different experience if you are travelling in a foreign country and find yourself in a crowd moving down the street. You may have trouble figuring out what is happening. Is the crowd just the usual morning rush, or is it a political protest of some kind? Perhaps there was some sort of accident or disaster. Is it safe in this crowd, or should you try to extract yourself? How can you find out what is going on? Although you are in it, you may not feel like you are part of this crowd. You may not know what to do or how to behave.
Even within one type of crowd, different groups exist and different behaviours are on display. At a rock concert, for example, some may enjoy singing along, others may prefer to sit and observe, while still others may join in a mosh pit or try crowd surfing. On February 28, 2010, Sydney Crosby scored the winning goal against the United States team in the gold medal hockey game at the Vancouver Winter Olympics. Two hundred thousand jubilant people filled the streets of downtown Vancouver to celebrate and cap off two weeks of uncharacteristically vibrant, joyful street life in Vancouver. Just over a year later, on June 15, 2011, the Vancouver Canucks lost the seventh hockey game of the Stanley Cup finals against the Boston Bruins. One hundred thousand people had been watching the game on outdoor screens. Eventually 155,000 people filled the downtown streets. Rioting and looting led to hundreds of injuries, burnt cars, trashed storefronts and property damage totaling an estimated $4.2 million. Why was the crowd response to the two events so different?

A key insight of sociology is that the simple fact of being in a group changes your behaviour. The group is a phenomenon that is more than the sum of its parts. Why do we feel and act differently in different types of social situations? Why might people of a single group exhibit different behaviours in the same situation? Why might people acting similarly not feel connected to others exhibiting the same behaviour? These are some of the many questions sociologists ask as they study people and societies.
1.1. What Is Sociology?

A dictionary defines sociology as the systematic study of society and social interaction. The word “sociology” is derived from the Latin word socius (companion) and the Greek word logos (speech or reason), which together mean “reasoned speech about companionship”. How can the experience of companionship or togetherness be put into words or explained? While this is a starting point for the discipline, sociology is actually much more complex. It uses many different methods to study a wide range of subject matter and to apply these studies to the real world.
The sociologist Dorothy Smith (1926 – ) defines the social as the “ongoing concerting and coordinating of individuals’ activities” (Smith 1999). Sociology is the systematic study of all those aspects of life designated by the adjective “social.” These aspects of social life never simply occur; they are organized processes. They can be the briefest of everyday interactions—moving to the right to let someone pass on a busy sidewalk, for example—or the largest and most enduring interactions—such as the billions of daily exchanges that constitute the circuits of global capitalism. If there are at least two people involved, even in the seclusion of one’s mind, then there is a social interaction that entails the “ongoing concerting and coordinating of activities.” Why does the person move to the right on the sidewalk? What collective process lead to the decision that moving to the right rather than the left is normal? Think about the T-shirts in your drawer at home. What are the sequences of linkages and social relationships that link the T-shirts in your chest of drawers to the dangerous and hyper-exploitive garment factories in rural China or Bangladesh? These are the type of questions that point to the unique domain and puzzles of the social that sociology seeks to explore and understand.
What Are Society and Culture?
Sociologists study all aspects and levels of society. A society is a group of people whose members interact, reside in a definable area, and share a culture. A culture includes the group’s shared practices, values, beliefs, norms and artifacts. One sociologist might analyze video of people from different societies as they carry on everyday conversations to study the rules of polite conversation from different world cultures. Another sociologist might interview a representative sample of people to see how email and instant messaging have changed the way organizations are run. Yet another sociologist might study how migration determined the way in which language spread and changed over time. A fourth sociologist might study the history of international agencies like the United Nations or the International Monetary Fund to examine how the globe became divided into a First World and a Third World after the end of the colonial era.
These examples illustrate the ways society and culture can be studied at different levels of analysis, from the detailed study of face-to-face interactions to the examination of large-scale historical processes affecting entire civilizations. It is common to divide these levels of analysis into different gradations based on the scale of interaction involved. As discussed in later chapters, sociologists break the study of society down into four separate levels of analysis: micro, meso, macro, and global. The basic distinction, however, is between micro-sociology and macro-sociology.
The study of cultural rules of politeness in conversation is an example of micro-sociology. At the micro-level of analysis, the focus is on the social dynamics of intimate, face-to-face interactions. Research is conducted with a specific set of individuals such as conversational partners, family members, work associates, or friendship groups. In the conversation study example, sociologists might try to determine how people from different cultures interpret each other’s behaviour to see how different rules of politeness lead to misunderstandings. If the same misunderstandings occur consistently in a number of different interactions, the sociologists may be able to propose some generalizations about rules of politeness that would be helpful in reducing tensions in mixed-group dynamics (e.g., during staff meetings or international negotiations). Other examples of micro-level research include seeing how informal networks become a key source of support and advancement in formal bureaucracies or how loyalty to criminal gangs is established.
Macro-sociology focuses on the properties of large-scale, society-wide social interactions: the dynamics of institutions, classes, or whole societies. The example above of the influence of migration on changing patterns of language usage is a macro-level phenomenon because it refers to structures or processes of social interaction that occur outside or beyond the intimate circle of individual social acquaintances. These include the economic and other circumstances that lead to migration; the educational, media, and other communication structures that help or hinder the spread of speech patterns; the class, racial, or ethnic divisions that create different slangs or cultures of language use; the relative isolation or integration of different communities within a population; and so on. Other examples of macro-level research include examining why women are far less likely than men to reach positions of power in society or why fundamentalist Christian religious movements play a more prominent role in American politics than they do in Canadian politics. In each case, the site of the analysis shifts away from the nuances and detail of micro-level interpersonal life to the broader, macro-level systematic patterns that structure social change and social cohesion in society.
The relationship between the micro and the macro remains one of the key problems confronting sociology. The German sociologist Georg Simmel pointed out that macro-level processes are in fact nothing more than the sum of all the unique interactions between specific individuals at any one time (1908), yet they have properties of their own which would be missed if sociologists only focused on the interactions of specific individuals. Émile Durkheim’s classic study of suicide (1897) is a case in point. While suicide is one of the most personal, individual, and intimate acts imaginable, Durkheim demonstrated that rates of suicide differed between religious communities—Protestants, Catholics, and Jews—in a way that could not be explained by the individual factors involved in each specific case. The different rates of suicide had to be explained by macro-level variables associated with the different religious beliefs and practices of the faith communities. We will return to this example in more detail later. On the other hand, macro-level phenomena like class structures, institutional organizations, legal systems, gender stereotypes, and urban ways of life provide the shared context for everyday life but do not explain its nuances and micro-variations very well. Macro-level structures constrain the daily interactions of the intimate circles in which we move, but they are also filtered through localized perceptions and “lived” in a myriad of inventive and unpredictable ways.
The Sociological Imagination
Although the scale of sociological studies and the methods of carrying them out are different, the sociologists involved in them all have something in common. Each of them looks at society using what pioneer sociologist C. Wright Mills called the sociological imagination, sometimes also referred to as the “sociological lens” or “sociological perspective.” In a sense, this was Mills’ way of addressing the dilemmas of the macro/micro divide in sociology. Mills defined sociological imagination as how individuals understand their own and others’ pasts in relation to history and social structure (1959). It is the capacity to see an individual’s private troubles in the context of the broader social processes that structure them. This enables the sociologist to examine what Mills called “personal troubles of milieu” as “public issues of social structure,” and vice versa.
Mills reasoned that private troubles like being overweight, being unemployed, having marital difficulties, or feeling purposeless or depressed can be purely personal in nature. It is possible for them to be addressed and understood in terms of personal, psychological, or moral attributes, either one’s own or those of the people in one’s immediate milieu. In an individualistic society like our own, this is in fact the most likely way that people will regard the issues they confront: “I have an addictive personality;” “I can’t get a break in the job market;” “My husband is unsupportive;” etc. However, if private troubles are widely shared with others, they indicate that there is a common social problem that has its source in the way social life is structured. At this level, the issues are not adequately understood as simply private troubles. They are best addressed as public issues that require a collective response to resolve.
Obesity, for example, has been increasingly recognized as a growing problem for both children and adults in North America. Michael Pollan cites statistics that three out of five Americans are overweight and one out of five is obese (2006). In Canada in 2012, just under one in five adults (18.4 percent) were obese, up from 16 percent of men and 14.5 percent of women in 2003 (Statistics Canada 2013). Obesity is therefore not simply a private trouble concerning the medical issues, dietary practices, or exercise habits of specific individuals. It is a widely shared social issue that puts people at risk for chronic diseases like hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. It also creates significant social costs for the medical system.
Pollan argues that obesity is in part a product of the increasingly sedentary and stressful lifestyle of modern, capitalist society, but more importantly it is a product of the industrialization of the food chain, which since the 1970s has produced increasingly cheap and abundant food with significantly more calories due to processing. Additives like corn syrup, which are much cheaper to produce than natural sugars, led to the trend of super-sized fast foods and soft drinks in the 1980s. As Pollan argues, trying to find a processed food in the supermarket without a cheap, calorie-rich, corn-based additive is a challenge. The sociological imagination in this example is the capacity to see the private troubles and attitudes associated with being overweight as an issue of how the industrialization of the food chain has altered the human/environment relationship, in particular with respect to the types of food we eat and the way we eat them.
By looking at individuals and societies and how they interact through this lens, sociologists are able to examine what influences behaviour, attitudes, and culture. By applying systematic and scientific methods to this process, they try to do so without letting their own biases and pre-conceived ideas influence their conclusions.
Studying Patterns: How Sociologists View Society
All sociologists are interested in the experiences of individuals and how those experiences are shaped by interactions with social groups and society as a whole. To a sociologist, the personal decisions an individual makes do not exist in a vacuum. Cultural patterns and social forces put pressure on people to select one choice over another. Sociologists try to identify these general patterns by examining the behaviour of large groups of people living in the same society and experiencing the same societal pressures.
Understanding the relationship between the individual and society is one of the most difficult sociological problems, however. Partly this is because of the reified way these two terms are used in everyday speech. Reification refers to the way in which abstract concepts, complex processes, or mutable social relationships come to be thought of as “things.” A prime example of this is when people say that “society” caused an individual to do something or to turn out in a particular way. In writing essays, first-year sociology students sometimes refer to “society” as a cause of social behaviour or as an entity with independent agency. On the other hand, the “individual” is a being that seems solid, tangible, and independent of anything going on outside of the skin sack that contains its essence. This conventional distinction between society and the individual is a product of reification in so far as both society and the individual appear as independent objects. A concept of “the individual” and a concept of “society” have been given the status of real, substantial, independent objects. As we will see in the chapters to come, society and the individual are neither objects, nor are they independent of one another. An “individual” is inconceivable without the relationships to others that define his or her internal subjective life and his or her external socially defined roles.
The problem for sociologists is that these concepts of the individual and society and the relationship between them are thought of in terms established by a very common moral framework in modern democratic societies, namely that of individual responsibility and individual choice. Often in this framework, any suggestion that an individual’s behaviour needs to be understood in terms of that person’s social context is dismissed as “letting the individual off” of taking personal responsibility for their actions.
Talking about society is akin to being morally soft or lenient. Sociology, as a social science, remains neutral on these type of moral questions. The conceptualization of the individual and society is much more complex. The sociological problem is to be able to see the individual as a thoroughly social being and yet as a being who has agency and free choice. Individuals are beings who do take on individual responsibilities in their everyday social roles and risk social consequences when they fail to live up to them. The manner in which they take on responsibilities and sometimes the compulsion to do so are socially defined however. The sociological problem is to be able to see society as a dimension of experience characterized by regular and predictable patterns of behaviour that exist independently of any specific individual’s desires or self-understanding. Yet at the same time a society is nothing but the ongoing social relationships and activities of specific individuals.
Making Connections: Sociology in the Real World
The Individual in Society: Choices of Aboriginal Gang Members
In 2010 the CBC program The Current aired a report about several young aboriginal men who were serving time in prison in Saskatchewan for gang-related activities (CBC 2010). They all expressed desires to be able to deal with their drug addiction issues, return to their families, and assume their responsibilities when their sentences were complete. They wanted to have their own places with nice things in them. However, according to the CBC report, 80 percent of the prison population in the Saskatchewan Correctional Centre were aboriginal and 20 percent of those were gang members. This is consistent with national statistics on aboriginal incarceration which showed that in 2010–2011, the aboriginal incarceration rate was 10 times higher than for the non-aboriginal population. While aboriginal people account for about 4 percent of the Canadian population, in 2013 they made up 23.2 percent of the federal penitentiary population. In 2001 they made up only 17 percent of the penitentiary population. Aboriginal overrepresentation in prisons has continued to grow substantially (Office of the Correctional Investigator 2013).The outcomes of aboriginal incarceration are also bleak. The federal Office of the Correctional Investigator summarized the situation as follows. Aboriginal inmates are:
- Routinely classified as higher risk and higher need in categories such as employment, community reintegration, and family supports
- Released later in their sentence (lower parole grant rates); most leave prison at Statutory Release or Warrant Expiry dates
- Overrepresented in segregation and maximum security populations
- Disproportionately involved in use-of-force interventions and incidents of prison self-injury
- More likely to return to prison on revocation of parole, often for administrative reasons, not criminal violations (2013)
The federal report notes that “the high rate of incarceration for aboriginal peoples has been linked to systemic discrimination and attitudes based on racial or cultural prejudice, as well as economic and social disadvantage, substance abuse and intergenerational loss, violence and trauma” (2013).
This is clearly a case in which the situation of the incarcerated inmates interviewed on the CBC program has been structured by historical social patterns and power relationships that confront aboriginal people in Canada generally. How do we understand it at the individual level however, at the level of personal decision making and individual responsibilities? One young inmate described how, at the age of 13, he began to hang around with his cousins who were part of a gang. He had not grown up with “the best life” with family members suffering from addiction issues and traumas. The appeal of what appeared as a fast and exciting lifestyle—the sense of freedom and of being able to make one’s own life, instead of enduring poverty—was compelling. He began to earn money by “running dope” but also began to develop addictions. He was expelled from school for recruiting gang members. The only job he ever had was selling drugs. The circumstances in which he and the other inmates had entered the gang life and the difficulties getting out of it they knew awaited them when they left prison reflect a set of decision-making parameters fundamentally different than those facing most non-aboriginal people in Canada.
A key basis of the sociological perspective is the concept that the individual and society are inseparable. It is impossible to study one without the other. German sociologist Norbert Elias called the process of simultaneously analyzing the behaviour of individuals and the society that shapes that behaviour figuration. He described it through a metaphor of dancing. There can be no dance without the dancers, but there can be no dancers without the dance. Without the dancers, a dance is just an idea about motions in a choreographer’s head. Without a dance, there is just a group of people moving around a floor. Similarly, there is no society without the individuals that make it up, and there are also no individuals who are not affected by the society in which they live (Elias 1978).
1.2. The History of Sociology

Since ancient times, people have been fascinated by the relationship between individuals and the societies to which they belong. The ancient Greeks might be said to have provided the foundations of sociology through the distinction they drew between physis (nature) and nomos (law or custom). Whereas nature or physis for the Greeks was “what emerges from itself” without human intervention, nomos in the form of laws or customs, were human conventions designed to constrain human behaviour. Histories by Herodotus (484–425 BCE) was a proto-anthropological work that described the great variations in the nomos of different ancient societies around the Mediterranean, indicating that human social life was not a product of nature but a product of human creation. If human social life was the product of an invariable human or biological nature, all cultures would be the same. The concerns of the later Greek philosophers Socrates (469–399 BCE), Plato (428–347 BCE), and Aristotle (384–322 BCE) with the ideal form of human community (the polis or city-state) can be derived from the ethical dilemmas of this difference between human nature and human norms. The modern sociological term “norm” (i.e., a social rule that regulates human behaviour) comes from the Greek term nomos.
In the 13th century, Ma Tuan-Lin, a Chinese historian, first recognized social dynamics as an underlying component of historical development in his seminal encyclopedia, General Study of Literary Remains. The study charted the historical development of Chinese state administration from antiquity in a manner akin to contemporary institutional analyses. The next century saw the emergence of the historian some consider to be the world’s first sociologist, the Berber scholar Ibn Khaldun (1332–1406) of Tunisia. His Muqaddimah: An Introduction to History is known for going beyond descriptive history to an analysis of historical processes of change based on an understanding of “the nature of things which are born of civilization” (Khaldun quoted in Becker and Barnes 1961). Key to his analysis was the distinction between the sedentary life of cities and the nomadic life of pastoral peoples like the Bedouin and Berbers. The nomads, who exist independent of external authority, developed a social bond based on blood lineage and “esprit de corps” (‘Asabijja),” which enabled them to mobilize quickly and act in a unified and concerted manner in response to the rugged circumstances of desert life. The sedentaries of the city entered into a different cycle in which esprit de corp is subsumed to institutional power and political factions and the need to be focused on subsistence is replaced by a trend toward increasing luxury, ease and refinements of taste. The relationship between the two poles of existence, nomadism and sedentary life, was at the basis of the development and decay of civilizations” (Becker and Barnes 1961).
However, it was not until the 19th century that the basis of the modern discipline of sociology can be said to have been truly established. The impetus for the ideas that culminated in sociology can be found in the three major transformations that defined modern society and the culture of modernity: the development of modern science from the 16th century onward, the emergence of democratic forms of government with the American and French Revolutions (1775–1783 and 1789–1799 respectively), and the Industrial Revolution beginning in the 18th century. Not only was the framework for sociological knowledge established in these events, but also the initial motivation for creating a science of society. Early sociologists like Comte and Marx sought to formulate a rational, evidence-based response to the experience of massive social dislocation and unprecedented social problems brought about by the transition from the European feudal era to capitalism. Whether the intention was to restore order to the chaotic disintegration of society, as in Comte’s case, or to provide the basis for a revolutionary transformation in Marx’s, a rational and scientifically comprehensive knowledge of society and its processes was required. It was in this context that “society” itself, in the modern sense of the word, became visible as a phenomenon to early investigators of the social condition.

The development of modern science provided the model of knowledge needed for sociology to move beyond earlier moral, philosophical, and religious types of reflection on the human condition. Key to the development of science was the technological mindset that Max Weber termed the disenchantment of the world: “principally there are no mysterious incalculable forces that come into play, but rather one can, in principle, master all things by calculation” (1919). Modern science abandoned the medieval view of the world in which God, “the unmoved mover,” defined the natural and social world as a changeless, cyclical creation ordered and given purpose by divine will. Instead modern science combined two philosophical traditions that had historically been at odds: Plato’s rationalism and Aristotle’s empiricism. Rationalism sought the laws that governed the truth of reason and ideas, and in the hands of early scientists like Galileo and Newton, found its highest form of expression in the logical formulations of mathematics. Empiricism sought to discover the laws of the operation of the world through the careful, methodical, and detailed observation of the world. The new scientific worldview therefore combined the clear and logically coherent conceptual formulation of propositions from rationalism with an empirical method of inquiry based on observation through the senses. Sociology adopted these core principles to emphasize that claims about society had to be clearly formulated and based on evidence-based procedures.
The emergence of democratic forms of government in the 18th century demonstrated that humans had the capacity to change the world. The rigid hierarchy of medieval society was not a God-given eternal order, but a human order that could be challenged and improved upon through human intervention. Society came to be seen as both historical and the product of human endeavours. Age of Enlightenment philosophers like Locke, Voltaire, Montaigne, and Rousseau developed general principles that could be used to explain social life. Their emphasis shifted from the histories and exploits of the aristocracy to the life of ordinary people. Mary Wollstonecraft’s A Vindication of the Rights of Women (1792) extended the critical analysis of her male Enlightenment contemporaries to the situation of women. Significantly for modern sociology they proposed that the use of reason could be applied to address social ills and to emancipate humanity from servitude. Wollstonecraft for example argued that simply allowing women to have a proper education would enable them to contribute to the improvement of society, especially through their influence on children. On the other hand, the bloody experience of the democratic revolutions, particularly the French Revolution, which resulted in the “Reign of Terror” and ultimately Napoleon’s attempt to subjugate Europe, also provided a cautionary tale for the early sociologists about the need for sober scientific assessment of society to address social problems.
The Industrial Revolution in a strict sense refers to the development of industrial methods of production, the introduction of industrial machinery, and the organization of labour in new manufacturing systems. These economic changes emblemize the massive transformation of human life brought about by the creation of wage labour, capitalist competition, increased mobility, urbanization, individualism, and all the social problems they wrought: poverty, exploitation, dangerous working conditions, crime, filth, disease, and the loss of family and other traditional support networks, etc. It was a time of great social and political upheaval with the rise of empires that exposed many people—for the first time—to societies and cultures other than their own. Millions of people were moving into cities and many people were turning away from their traditional religious beliefs. Wars, strikes, revolts, and revolutionary actions were reactions to underlying social tensions that had never existed before and called for critical examination. August Comte in particular envisioned the new science of sociology as the antidote to conditions that he described as “moral anarchy.”
Sociology therefore emerged as an extension of the new worldview of science; as a part of the Enlightenment project and its appreciation of historical change, social injustice, and the possibilities of social reform; and as a crucial response to the new and unprecedented types of social problems that appeared in the 19th century. It did not emerge as a unified science, however, as its founders brought distinctly different perspectives to its early formulations.
August Comte: The Father of Sociology
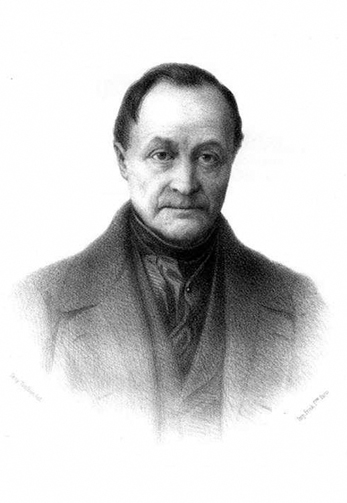
The term sociology was first coined in 1780 by the French essayist Emmanuel-Joseph Sieyès (1748–1836) in an unpublished manuscript (Fauré et al. 1999). In 1838, the term was reinvented by Auguste Comte (1798–1857). The contradictions of Comte’s life and the times he lived through can be in large part read into the concerns that led to his development of sociology. He was born in 1798, year 6 of the new French Republic, to staunch monarchist and Catholic parents, who lived comfortably off the father’s earnings as a minor bureaucrat in the tax office. Comte originally studied to be an engineer, but after rejecting his parents’ conservative views and declaring himself a republican and free spirit at the age of 13, he got kicked out of school at 18 for leading a school riot, which ended his chances of getting a formal education and a position as an academic or government official.
He became a secretary of the utopian socialist philosopher Claude Henri de Rouvroy Comte de Saint-Simon (1760–1825) until they had a falling out in 1824 (after St. Simon perhaps purloined some of Comte’s essays and signed his own name to them). Nevertheless, they both thought that society could be studied using the same scientific methods utilized in the natural sciences. Comte also believed in the potential of social scientists to work toward the betterment of society and coined the slogan “order and progress” to reconcile the opposing progressive and conservative factions that had divided the crisis-ridden, post-revolutionary French society. Comte proposed a renewed, organic spiritual order in which the authority of science would be the means to reconcile the people in each social strata with their place in the order. It is a testament to his influence that the phrase “order and progress” adorns the Brazilian coat of arms (Collins and Makowsky 1989).
Comte named the scientific study of social patterns positivism. He described his philosophy in a well-attended and popular series of lectures, which he published as The Course in Positive Philosophy (1830–1842) and A General View of Positivism (1848). He believed that using scientific methods to reveal the laws by which societies and individuals interact would usher in a new “positivist” age of history. His main sociological theory was the law of three stages, which held that all human societies and all forms of human knowledge evolve through three distinct stages from primitive to advanced: the theological, the metaphysical, and the positive.The key variable in defining these stages was the way a people understand the concept of causation or think about their place in the world.
In the theological stage, humans explain causes in terms of the will of anthropocentric gods (the gods cause things to happen). In the metaphysical stage, humans explain causes in terms of abstract, “speculative” ideas like nature, natural rights, or “self-evident” truths. This was the basis of his critique of the Enlightenment philosophers whose ideas about natural rights and freedoms had led to the French Revolution but also to the chaos of its aftermath. In his view, the “negative” or metaphysical knowledge of the philosophers was based on dogmatic ideas that could not be reconciled when they were in contraction. This lead to irreconcilable conflict and moral anarchy. Finally, in the positive stage, humans explain causes in terms of scientific procedures and laws (i.e., “positive” knowledge based on propositions limited to what can be empirically observed). Comte believed that this would be the final stage of human social evolution because science would reconcile the division between political factions of order and progress by eliminating the basis for moral and intellectual anarchy. The application of positive philosophy would lead to the unification of society and of the sciences (Comte 1830).
Although Comte’s positivism is a little odd by today’s standards, it inaugurated the development of the positivist tradition within sociology. In principle, positivism is the sociological perspective that attempts to approach the study of society in the same way that the natural sciences approach the natural world. In fact, Comte’s preferred term for this approach was “social physics”—the “sciences of observation” applied to social phenomena, which he saw as the culmination of the historical development of the sciences. More specifically, for Comte, positivism:
- “Regards all phenomena as subjected to invariable natural laws”
- Pursues “an accurate discovery of these laws, with a view of reducing them to the smallest possible number”
- Limits itself to analyzing the observable circumstances of phenomena and to connecting them by the “natural relations of succession and resemblance” instead of making metaphysical claims about their essential or divine nature (Comte 1830)
While Comte never in fact conducted any social research and took, as the object of analysis, the laws that governed what he called the general human “mind” of a society (difficult to observe empirically), his notion of sociology as a positivist science that might effectively socially engineer a better society was deeply influential. Where his influence waned was a result of the way in which he became increasingly obsessive and hostile to all criticism as his ideas progressed beyond positivism as the “science of society” to positivism as the basis of a new cult-like, technocratic “religion of humanity.” The new social order he imagined was deeply conservative and hierarchical, a kind of a caste system with every level of society obliged to reconcile itself with its “scientifically” allotted place. Comte imagined himself at the pinnacle of society, taking the title of “Great Priest of Humanity.” The moral and intellectual anarchy he decried would be resolved, but only because the rule of sociologists would eliminate the need for unnecessary and divisive democratic dialogue. Social order “must ever be incompatible with a perpetual discussion of the foundations of society” (Comte 1830).
Karl Marx: The Ruthless Critique of Everything Existing
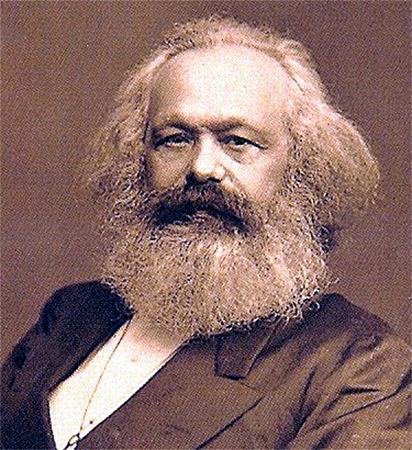

Karl Marx (1818–1883) was a German philosopher and economist. In 1848 he and Friedrich Engels (1820–1895) co-authored the Communist Manifesto. This book is one of the most influential political manuscripts in history. It also presents in a highly condensed form Marx’s theory of society, which differed from what Comte proposed. Whereas Comte viewed the goal of sociology as recreating a unified, post-feudal spiritual order that would help to institutionalize a new era of political and social stability, Marx developed a critical analysis of capitalism that saw the material or economic basis of inequality and power relations as the cause of social instability and conflict. The focus of sociology, or what Marx called historical materialism (the “materialist conception of history”), should be the “ruthless critique of everything existing,” as he said in a letter to his friend Arnold Ruge. In this way the goal of sociology would not simply be to scientifically analyze or objectively describe society, but to use a rigorous scientific analysis as a basis to change it. This framework became the foundation of contemporary critical sociology.
Marx rejected Comte’s positivism with its emphasis on describing the logical laws of the general “mind.” For Marx, Comte’s sociology was a form of idealism, a way of explaining the nature of society based on the ideas that people hold. In an idealist perspective, people invent ideas of “freedom,” “morality,” or “causality,” etc. and then change their lives and society’s institutions to conform to these ideas. This type of understanding could only ever lead to a partial analysis of social life according to Marx. Instead he believed that societies grew and changed as a result of the struggles of different social classes over control of the means of production. Historical materialism is an approach to understanding society that explains social change and human ideas in terms of underlying changes in the “mode of production” or economy; i.e., the historical transformations in the way human societies act upon their material world (the environment and its resources) in order to use it to meet their needs. Marx argues therefore that the consciousness or ideas people have about the world develop from changes in this material, economic basis. As such, the ideas of people in hunter-gatherer societies will be different than the ideas of people in feudal societies, which in turn will be different from the ideas of people in capitalist societies.
The source of historical change and transition between different historical types of society was class struggle. At the time Marx was developing his theories, the Industrial Revolution and the rise of capitalism had led to a massive increase in the wealth of society but also massive disparities in wealth and power between the owners of the factories (the bourgeoisie) and workers (the proletariat). Capitalism was still a relatively new economic system, an economic system characterized by private or corporate ownership of goods and the means to produce them. It was also a system that was inherently unstable and prone to crisis, yet increasingly global in its reach.
As Marx demonstrated in his masterpiece Capital (1867), capitalism’s instability is based on the processes by which capitalists accumulate their capital or assets, namely by engaging in cold-blooded competition with each other through the sale of commodities in the competitive market. There is a continuous need to expand markets for goods and to reduce the costs of production in order to create ever cheaper and more competitive products. This leads to a downward pressure on wages, the introduction of labour-saving technologies that increase unemployment, the failure of non-competitive businesses, periodic economic crises and recessions, and the global expansion of capitalism as businesses seek markets to exploit and cheaper sources of labour. Yet as he pointed out, it was the workers’ labour that actually produces wealth. The capitalists who owned the factories and means of production were in a sense parasitic on workers’ labour. The injustice of the system was palpable. Marx predicted that inequalities of capitalism would become so extreme that workers would eventually recognize their common class interests, develop a common “class consciousness” or understanding of their situation, and revolt. Class struggle would lead to the destruction of the institution of private capital and to the final stage in human history, which he called “communism.”
Although Marx did not call his analysis sociology, his sociological innovation was to provide a social analysis of the economic system. Whereas Adam Smith (1723–1790) and the political economists of the 19th century tried to explain the economic laws of supply and demand solely as a market mechanism (similar to the abstract discussions of stock market indices and investment returns in business pages of newspapers today), Marx’s analysis showed the social relationships that had created the market system and the social repercussions of their operation. As such, his analysis of modern society was not static or simply descriptive. He was able to put his finger on the underlying dynamism and continuous change that characterized capitalist society. In a famous passage from The Communist Manifesto, he and Engels described the restless and destructive penchant for change inherent in the capitalist mode of production:
The bourgeoisie cannot exist without constantly revolutionizing the instruments of production, and thereby the relations of production, and with them the whole relations of society. Conservation of the old modes of production in unaltered form, was, on the contrary, the first condition of existence for all earlier industrial classes. Constant revolutionizing of production, uninterrupted disturbance of all social conditions, everlasting uncertainty, and agitation distinguish the bourgeois epoch from all earlier ones. All fixed, fast frozen relations, with their train of ancient and venerable prejudices and opinions, are swept away, all new-formed ones become antiquated before they can ossify. All that is solid melts into air, all which is holy is profaned, and man is at last compelled to face with sober senses his real condition of life and his relations with his kind (Marx and Engels 1848).
Marx was also able to create an effective basis for critical sociology in that what he aimed for in his analysis was, as he put it in another letter to Arnold Ruge, “the self-clarification of the struggles and wishes of the age.” While he took a clear and principled value position in his critique, he did not do so dogmatically, based on an arbitrary moral position of what he personally thought was good and bad. He felt rather that a critical social theory must engage in clarifying and supporting the issues of social justice that were inherent within the existing struggles and wishes of the age. In his own work, he endeavoured to show how the variety of specific work actions, strikes, and revolts by workers in different occupations for better pay, safer working conditions, shorter hours, the right to unionize, etc. contained the seeds for a vision of universal equality, collective justice, and ultimately the ideal of a classless society.
Harriet Martineau: The First Woman Sociologist?

Harriet Martineau (1802–1876) was one of the first women sociologists in the 19th century. There are a number of other women who might compete with her for the title of the first woman sociologist, such as Catherine Macauley, Mary Wollstonecraft, Flora Tristan, and Beatrice Webb, but Martineau’s specifically sociological credentials are strong. She was for a long time known principally for her English translation of Comte’s Course in Positive Philosophy. Through this popular translation she introduced the concept of sociology as a methodologically rigorous discipline to an English-speaking audience. But she also created a body of her own work in the tradition of the great social reform movements of the 19th century and introduced a sorely missing woman’s perspective into the discourse on society.
It was a testament to her abilities that after she became impoverished at the age of 24 with the death of her father, brother, and fiancé, she was able to earn her own income as the first woman journalist in Britain to write under her own name. From the age of 12, she suffered from severe hearing loss and was obliged to use a large ear trumpet to converse. She impressed a wide audience with a series of articles on political economy in 1832. In 1834 she left England to engage in two years of study of the new republic of the United States and its emerging institutions: prisons, insane asylums, factories, farms, Southern plantations, universities, hospitals, and churches. On the basis of extensive research, interviews and observations, she published Society in America and worked with abolitionists on the social reform of slavery (Zeitlin 1997). She also worked for social reform in the situation of women: the right to vote, have an education, pursue an occupation, and enjoy the same legal rights as men. Together with Florence Nightingale, she worked on the development of public health care, which led to early formulations of the welfare system in Britain (McDonald 1998).
Particularly innovative was her early work on sociological methodology, How to Observe Manners and Morals (1838). In this volume she developed the ground work for a systematic social-scientific approach to studying human behaviour. She recognized that the issues of the researcher/subject relationship would have to be addressed differently in a social, as opposed to a natural, science. The observer, or “traveller,” as she put it, needed to respect three criteria to obtain valid research: impartiality, critique, and sympathy. The impartial observer could not allow herself to be “perplexed or disgusted” by foreign practices that she could not personally reconcile herself with. Yet at the same time she saw the goal of sociology to be the fair but critical assessment of the moral status of a culture. In particular, the goal of sociology was to challenge forms of racial, sexual, or class domination in the name of autonomy: the right of every person to be a “self-directing moral being.” Finally, what distinguished the science of social observation from the natural sciences was that the researcher had to have unqualified sympathy for the subjects being studied (Lengermann and Niebrugge 2007). This later became a central principle of Max Weber’s interpretive sociology, although it is not clear that Weber read Martineau’s work.
A large part of her research in the United States analyzed the situations of contradiction between stated public morality and actual moral practices. For example, she was fascinated with the way that the formal democratic right to free speech enabled slavery abolitionists to hold public meetings, but when the meetings were violently attacked by mobs, the abolitionists and not the mobs were accused of inciting the violence (Zeitlin 1997). This emphasis on studying contradictions followed from the distinction she drew between morals—society’s collective ideas of permitted and forbidden behaviour—and manners—the actual patterns of social action and association in society. As she realized the difficulty in getting an accurate representation of an entire society based on a limited number of interviews, she developed the idea that one could identify key “Things” experienced by all people—age, gender, illness, death, etc.—and examine how they were experienced differently by a sample of people from different walks of life (Lengermann and Niebrugge 2007). Martineau’s sociology therefore focused on surveying different attitudes toward “Things” and studying the anomalies that emerged when manners toward them contradicted a society’s formal morals.
Émile Durkheim: The Pathologies of the Social Order

Émile Durkheim (1858–1917) helped establish sociology as a formal academic discipline by establishing the first European department of sociology at the University of Bordeaux in 1895 and by publishing his Rules of the Sociological Method in 1895. He was born to a Jewish family in the Lorraine province of France (one of the two provinces along with Alsace that were lost to the Germans in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871). With the German occupation of Lorraine, the Jewish community suddenly became subject to sporadic anti-Semitic violence, with the Jews often being blamed for the French defeat and the economic/political instability that followed. Durkheim attributed this strange experience of anti-Semitism and scapegoating to the lack of moral purpose in modern society.
As in Comte’s time, France in the late 19th century was the site of major upheavals and sharp political divisions: the loss of the Franco-Prussian War, the Paris Commune (1871) in which 20,000 workers died, the fall and capture of Emperor Napoleon III (Napoleon I’s nephew), the creation of the Third Republic, and the Dreyfus Affair. This undoubtedly led to the focus in Durkheim’s sociology on themes of moral anarchy, decadence, disunity, and disorganization. For Durkheim, sociology was a scientific but also a “moral calling” and one of the central tasks of the sociologist was to determine “the causes of the general temporary malajustment being undergone by European societies and remedies which may relieve it” (1897). In this respect, Durkheim represented the sociologist as a kind of medical doctor, studying social pathologies of the moral order and proposing social remedies and cures. He saw healthy societies as stable, while pathological societies experienced a breakdown in social norms between individuals and society. The state of normlessness or anomie—the lack of norms that give clear direction and purpose to individual actions—was the result of “society’s insufficient presence in individuals” (1897).
His father was the eighth in a line of father-son rabbis. Although Émile was the second son, he was chosen to pursue his father’s vocation and was given a good religious and secular education. He abandoned the idea of a religious or rabbinical career, however, and became very secular in his outlook. His sociological analysis of religion in The Elementary Forms of the Religious Life (1912) was an example of this. In this work he was not interested in the theological questions of God’s existence or purpose, but in developing a very secular, sociological question: Whether God exists or not, how does religion function socially in a society? He argued that beneath the irrationalism and the “barbarous and fantastic rites” of both the most primitive and the most modern religions is their ability to satisfy real social and human needs. “There are no religions which are false” (Durkheim 1912) he said. Religion performs the key function of providing social solidarity in a society. The rituals, the worship of icons, and the belief in supernatural beings “excite, maintain or recreate certain mental states” (Durkheim 1912) that bring people together, provide a ritual and symbolic focus, and unify them. This type of analysis became the basis of the functionalist perspective in sociology. He explained the existence and persistence of religion on the basis of the necessary function it performed in unifying society.
Durkheim was also a key figure in the development of positivist sociology. He did not adopt the term positivism, because of the connection it had with Comte’s quasi-religious sociological cult. However, in Rules of the Sociological Method he defined sociology as the study of objective social facts. Social facts are those things like law, custom, morality, religious beliefs and practices, language, systems of money, credit and debt, business or professional practices, etc. that are defined externally to the individual. Social facts:
- Precede the individual and will continue to exist after he or she is gone
- Consist of details and obligations of which individuals are frequently unaware
- Are endowed with an external coercive power by reason of which individuals are controlled
For Durkheim, social facts were like the facts of the natural sciences. They could be studied without reference to the subjective experience of individuals. He argued that “social facts must be studied as things, that is, as realities external to the individual” (Durkheim 1895). Individuals experience them as obligations, duties, and restraints on their behaviour, operating independently of their will. They are hardly noticeable when individuals consent to them but provoke reaction when individuals resist.
In this way, Durkheim was very influential in defining the subject matter of the new discipline of sociology. For Durkheim, sociology was not about just any phenomena to do with the life of human beings but only those phenomena which pertained exclusively to a social level of analysis. It was not about the biological or psychological dynamics of human life, for example, but about the social facts through which the lives of individuals were constrained. Moreover, the dimension of human experience described by social facts had to be explained in its own terms. It could not be explained by biological drives or psychological characteristics of individuals. It was a dimension of reality sui generis (of its own kind, unique in its characteristics). It could not be explained by, or reduced to, its individual components without missing its most important features. As Durkheim put it, “a social fact can only be explained by another social fact” (Durkheim 1895).
This is the framework of Durkheim’s famous study of suicide. In Suicide: A Study in Sociology (1897), Durkheim attempted to demonstrate the effectiveness of his rules of social research by examining suicide statistics in different police districts. Suicide is perhaps the most personal and most individual of all acts. Its motives would seem to be absolutely unique to the individual and to individual psychopathology. However, what Durkheim observed was that statistical rates of suicide remained fairly constant year by year and region by region. There was no correlation between rates of suicide and rates of psychopathology. Suicide rates did vary, however, according to the social context of the suicides: namely the religious affiliation of suicides. Protestants had higher rates of suicide than Catholics, whereas Catholics had higher rates of suicide than Jews. Durkheim argued that the key factor that explained the difference in suicide rates (i.e., the statistical rates, not the purely individual motives for the suicides) were the different degrees of social integration of the different religious communities, measured by the amount of ritual and degree of mutual involvement in religious practice. The religious groups had differing levels of anomie, or normlessness, which Durkheim associated with high rates of suicide. Durkheim’s study was unique and insightful because he did not try to explain suicide rates in terms of individual psychopathology. Instead, he regarded the regularity of the suicide rates as a factual order, implying “the existence of collective tendencies exterior to the individual” (Durkheim 1897), and explained their variation with respect to another social fact: “Suicide varies inversely with the degree of integration of the social groups of which the individual forms a part” (Durkheim 1897).
Max Weber: Verstehende Soziologie

Prominent sociologist Max Weber (1864–1920) established a sociology department in Germany at the Ludwig Maximilians University of Munich in 1919. Weber wrote on many topics related to sociology including political change in Russia, the condition of German farm workers, and the history of world religions. He was also a prominent public figure, playing an important role in the German peace delegation in Versailles and in drafting the ill-fated German (Weimar) constitution following the defeat of Germany in World War I.
Weber is known best for his 1904 book, The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism. He noted that in modern industrial societies, business leaders and owners of capital, the higher grades of skilled labour, and the most technically and commercially trained personnel were overwhelmingly Protestant. He also noted the uneven development of capitalism in Europe, and in particular how capitalism developed first in those areas dominated by Protestant sects. He asked, “Why were the districts of highest economic development at the same time particularly favourable to a revolution in the Church?” (i.e., the Protestant Reformation (1517–1648)) (Weber 1904). His answer focused on the development of the Protestant ethic—the duty to “work hard in one’s calling”—in particular Protestant sects such as Calvinism, Pietism, and Baptism.
As opposed to the traditional teachings of the Catholic Church in which poverty was a virtue and labour simply a means for maintaining the individual and community, the Protestant sects began to see hard, continuous labour as a spiritual end in itself. Hard labour was firstly an ascetic technique of worldly renunciation and a defence against temptations and distractions: the unclean life, sexual temptations, and religious doubts. Secondly, the Protestant sects believed that God’s disposition toward the individual was predetermined and could never be known or influenced by traditional Christian practices like confession, penance, and buying indulgences. However, one’s chosen occupation was a “calling” given by God, and the only sign of God’s favour or recognition in this world was to receive good fortune in one’s calling. Thus material success and the steady accumulation of wealth through personal effort and prudence was seen as a sign of an individual’s state of grace. Weber argued that the ethic, or way of life, that developed around these beliefs was a key factor in creating the conditions for both the accumulation of capital, as the goal of economic activity, and for the creation of an industrious and disciplined labour force.
In this regard, Weber has often been seen as presenting an idealist explanation of the development of capital, as opposed to Marx’s historical materialist explanation. It is an element of cultural belief that leads to social change rather than the concrete organization and class struggles of the economic structure. It might be more accurate, however, to see Weber’s work building on Marx’s and to see his Protestant ethic thesis as part of a broader set of themes concerning the process of rationalization. Why did the Western world modernize and develop modern science, industry, and democracy when, for centuries, the Orient, the Indian subcontinent, and the Middle East were technically, scientifically, and culturally more advanced than the West? Weber argued that the modern forms of society developed in the West because of the process of rationalization: the general tendency of modern institutions and most areas of life to be transformed by the application of instrumental reason—rational bureaucratic organization, calculation, and technical reason—and the overcoming of “magical” thinking (which we earlier referred to as the “disenchantment of the world”). As the impediments toward rationalization were removed, organizations and institutions were restructured on the principle of maximum efficiency and specialization, while older, traditional (inefficient) types of organization were gradually eliminated.
The irony of the Protestant ethic as one stage in this process was that the rationalization of capitalist business practices and organization of labour eventually dispensed with the religious goals of the ethic. At the end of The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism, Weber pessimistically describes the fate of modern humanity as an “iron cage.” The iron cage is Weber’s metaphor for the condition of modern humanity in a technical, rationally defined, and “efficiently” organized society. Having forgotten its spiritual or other purposes of life, humanity succumbs to an order “now bound to the technical and economic conditions of machine production” (Weber 1904). The modern subject in the iron cage is “only a single cog in an ever-moving mechanism which prescribes to him an essentially fixed route of march” (Weber 1922).
Weber also made a major contribution to the methodology of sociological research. Along with the philosophers Wilhelm Dilthey (1833–1911) and Heinrich Rickert (1863–1936), Weber believed that it was difficult if not impossible to apply natural science methods to accurately predict the behaviour of groups as positivist sociology hoped to do. They argued that the influence of culture on human behaviour had to be taken into account. What was distinct about human behaviour was that it is essentially meaningful. Human behaviour could not be understood independently of the meanings that individuals attributed to it. A Martian’s analysis of the activities in a skateboard park would be hopelessly confused unless it understood that the skateboarders were motivated by the excitement of risk taking and the pleasure in developing skills. This insight into the meaningful nature of human behaviour even applied to the sociologists themselves, who, they believed, should be aware of how their own cultural biases could influence their research. To deal with this problem, Weber and Dilthey introduced the concept of Verstehen, a German word that means to understand in a deep way. In seeking Verstehen, outside observers of a social world—an entire culture or a small setting—attempt to understand it empathetically from an insider’s point of view.
In his essay “The Methodological Foundations of Sociology,” Weber described sociology as “a science which attempts the interpretive understanding of social action in order thereby to arrive at a causal explanation of its course and effects” (Weber 1922). In this way he delimited the field that sociology studies in a manner almost opposite to that of Émile Durkheim. Rather than defining sociology as the study of the unique dimension of external social facts, sociology was concerned with social action: actions to which individuals attach subjective meanings. “Action is social in so far as, by virtue of the subjective meaning attached to it by the acting individual (or individuals), it takes account of the behaviour of others and is thereby oriented in its course” (Weber 1922). The actions of the young skateboarders can be explained because they hold the experienced boarders in esteem and attempt to emulate their skills even if it means scraping their bodies on hard concrete from time to time. Weber and other like-minded sociologists founded interpretive sociology whereby social researchers strive to find systematic means to interpret and describe the subjective meanings behind social processes, cultural norms, and societal values. This approach led to research methods like ethnography, participant observation, and phenomenological analysis whose aim was not to generalize or predict (as in positivistic social science), but to systematically gain an in-depth understanding of social worlds. The natural sciences may be precise, but from the interpretive sociology point of view their methods confine them to study only the external characteristics of things.
Georg Simmel: A Sociology of Forms

Georg Simmel (1858–1918) was one of the founding fathers of sociology, although his place in the discipline is not always recognized. In part, this oversight may be explained by the fact that Simmel was a Jewish scholar in Germany at the turn of 20th century, and until 1914 was unable to attain a proper position as a professor due to anti-Semitism. Despite the brilliance of his sociological insights, the quantity of his publications, and the popularity of his public lectures as Privatdozent at the University of Berlin, his lack of a regular academic position prevented him from having the kind of student following that would create a legacy around his ideas. It might also be explained by some of the unconventional and varied topics that he wrote on: the structure of flirting, the sociology of adventure, the importance of secrecy, the patterns of fashion, the social significance of money, etc. He was generally seen at the time as not having a systematic or integrated theory of society. However, his insights into how social forms emerge at the micro-level of interaction and how they relate to macro-level phenomena remain valuable in contemporary sociology.
Simmel’s sociology focused on the key question, “How is society possible?” His answer led him to develop what he called formal sociology, or the sociology of social forms. In his essay “The Problem of Sociology,” Simmel reaches a strange conclusion for a sociologist: “There is no such thing as society ‘as such.’” “Society” is just the name we give to the “extraordinary multitude and variety of interactions [that] operate at any one moment” (Simmel 1908). This is a basic insight of micro-sociology. However useful it is to talk about macro-level phenomena like capitalism, the moral order, or rationalization, in the end what these phenomena refer to is a multitude of ongoing, unfinished processes of interaction between specific individuals. Nevertheless, the phenomena of social life do have recognizable forms, and the forms do guide the behaviour of individuals in a regularized way. A bureaucracy is a form of social interaction that persists from day to day. One does not come into work one morning to discover that the rules, job descriptions, paperwork, and hierarchical order of the bureaucracy have disappeared. Simmel’s questions were: How do the forms of social life persist? How did they emerge in the first place? What happens when they get fixed and permanent?
Simmel notes that “society exists where a number of individuals enter into interaction” (1908). What he means is that whenever people gather, something happens that would not have happened if the individuals had remained alone. People attune themselves to one another in a way that is very similar to musicians tuning their instruments to one another. A pattern or form of interaction emerges that begins to guide or coordinate the behaviour of the individuals. An example Simmel uses is of a cocktail party where a subtle set of instructions begins to emerge which defines what can and cannot be said. In a cocktail party where the conversation is light and witty, the effect would be jarring of someone suddenly trying to sell you an insurance policy or talking about the spousal abuse they had suffered. The person would be thought of as being crass or inappropriate. Similarly in the pleasant pastime of flirtation, if one of the parties began to press the other to consummate the flirtation by having sex, the flirtation would be over. Flirtation is a form of interaction in which the answer to the question of having sex—yes or no—is perpetually suspended.
In both examples, Simmel argued that the social interaction had taken on a specific form. Both were examples of what he called the play form of social interaction, or pure “sociability”: the pleasure people experience from the mere fact of being together, regardless of the content of the interaction (Simmel 1910). If the cocktail party conversation suddenly turns to a business proposition or an overly personal confession, it is no longer playful. The underlying form of the interaction has been violated, even if the participants were not consciously aware that they had adopted a particular form of interaction. Simmel proposed that sociology would be the study of the social forms that recur in different contexts and with different social contents. The same play form governs the interaction in two different contexts with two different contents of interaction: one is the free-ranging content of polite conversation; the other is sexual desire. Among other common forms that Simmel studied were superiority and subordination, cooperation, competition, division of labour, and money transactions. These forms can be applied in a variety of different contexts to give social form to a variety of different contents or specific drives: erotic, spiritual, acquisitive, defensive, playful, etc. The emphasis on forms is why Simmel called his approach to the study of society “formal sociology.”
Simmel’s focus on how social forms emerge became very important for micro-sociology, symbolic interactionism, and the studies of hotel lobbies, cigarette girls, and street-corner societies, etc. popularized by the Chicago School in the mid-20th century. His analysis of the creation of new social forms was particularly tuned in to capturing the fragmentary everyday experience of modern social life that was bound up with the unprecedented nature and scale of the modern city. In his lifetime, the city of Berlin where he lived and taught for most of his career had become a major European metropolis of 4 million people by 1900, after the unification of Germany in the 1870s. However, his work was not confined to micro-level interactions. He developed an analysis of the tragedy of culture in which he argued that the cultural creations of “subjective culture”—like the emergent social forms created by people in their face-to-face interactions, as well as art, literature, political analyses, etc.—tended to detach themselves from lived experience and become fixed and elaborated in the form of “objective culture”—the accumulated products of human cultural creation. There are intrinsic limits to an individual’s ability to organize, appreciate, and assimilate these forms. As the quantity of objective culture increases and becomes more complex, it becomes progressively more alienating, incomprehensible, and overwhelming. It takes on a life of its own and the individual can no longer see him- or herself reflected in it. Music, for example, can be enriching, but going to an orchestral performance of contemporary music can often be baffling, as if you need an advanced music degree just to be able to understand that what you are hearing is music.
In his famous study “The Metropolis and Mental Life,” Simmel described how the built environment and the sheer size and anonymity of the city had become a social form, which he called the “metropolitan way of life.” Although the metropolis, its architecture, and the variety of ways of life it contained were products of human creation and expression, as an entity it confronted the individual as a kind of overwhelming monstrosity that threatened to swallow him or her up in its “social-technological mechanism” (Simmel 1903). As a means of self-protection against the city’s overpowering sensory input, people cut themselves off from potentially enriching contact with others and become cold, callous, indifferent, impatient, and blasé.
Making Connections: Social Policy & Debate
How Do Working Moms Impact Society?
What constitutes a “typical family” in Canada has changed tremendously over the past decades. One of the most notable changes has been the increasing number of mothers who work outside the home. Earlier in Canadian society, most family households consisted of one parent working outside the home and the other being the primary child care provider. Because of traditional gender roles and family structures, this was typically a working father and a stay-at-home mom. Research shows that in 1951 only 24 percent of all women worked outside the home (Li 1996). In 2009, 58.3 percent of all women did, and 64.4 percent of women with children younger than three years of age were employed (Statistics Canada 2011).
Sociologists interested in this topic might approach its study from a variety of angles. One might be interested in its impact on a child’s development, another may explore its effect on family income, while a third might examine how other social institutions have responded to this shift in society. A sociologist studying the impact of working mothers on a child’s development might ask questions about children raised in child care settings. How is a child socialized differently when raised largely by a child care provider rather than a parent? Do early experiences in a school-like child care setting lead to improved academic performance later in life? How does a child with two working parents perceive gender roles compared to a child raised with a stay-at-home parent? Another sociologist might be interested in the increase in working mothers from an economic perspective. Why do so many households today have dual incomes? Has this changed the income of families substantially? How do women’s dual roles in the household and in the wider economy affect their occupational achievements and ability to participate on an equal basis with men in the workforce? What impact does the larger economy play in the economic conditions of an individual household? Do people view money—savings, spending, debt—differently than they have in the past?
Curiosity about this trend’s influence on social institutions might lead a researcher to explore its effect on the nation’s educational and child care systems. Has the increase in working mothers shifted traditional family responsibilities onto schools, such as providing lunch and even breakfast for students? How does the creation of after-school care programs shift resources away from traditional school programs? What would the effect be of providing a universal, subsidized child care program on the ability of women to pursue uninterrupted careers?
As these examples show, sociologists study many real-world topics. Their research often influences social policies and political issues. Results from sociological studies on this topic might play a role in developing federal policies like the Employment Insurance maternity and parental benefits program, or they might bolster the efforts of an advocacy group striving to reduce social stigmas placed on stay-at-home dads, or they might help governments determine how to best allocate funding for education. Many European countries like Sweden have substantial family support policies, such as a full year of parental leave at 80 percent of wages when a child is born and heavily subsidized, high-quality daycare and preschool programs. In Canada, a national subsidized daycare program existed briefly in 2005 but was scrapped in 2006 by the Conservative government and replaced with a $100-a-month direct payment to parents for each child. Sociologists might be interested in studying whether the benefits of the Swedish system—in terms of children’s well-being, lower family poverty, and gender equality—outweigh the drawbacks of higher Swedish tax rates.
1.3. Theoretical Perspectives

Sociologists study social events, interactions, and patterns. They then develop theories to explain why these occur and what can result from them. In sociology, a theory is a way to explain different aspects of social interactions and create testable propositions about society (Allan 2006). For example, Durkheim’s proposition that differences in suicide rate can be explained by differences in the degree of social integration in different communities is a theory.
As this brief survey of the history of sociology suggests, however, there is considerable diversity in the theoretical approaches sociology takes to studying society. Sociology is a multi-perspectival science: a number of distinct perspectives or paradigms offer competing explanations of social phenomena. Paradigms are philosophical and theoretical frameworks used within a discipline to formulate theories, generalizations, and the research performed in support of them. They refer to the underlying organizing principles that tie different constellations of concepts, theories, and ways of formulating problems together (Drengson 1983). Talcott Parsons’ reformulation of Durkheim’s and others work as structural functionalism in the 1950s is an example of a paradigm because it provided a general model of analysis suited to an unlimited number of research topics. Parsons proposed that any identifiable structure (e.g., roles, families, religions, or states) could be explained by the particular function it performed in maintaining the operation of society as a whole. Critical sociology and symbolic interactionism would formulate the explanatory framework and research problem differently.
The multi-perspectival approach of sociology can be confusing to the newcomer, especially given most people’s familiarity with the more “unified perspective” of the natural sciences where divisions in perspective are less visible. The natural sciences are largely able to dispense with issues of multiple perspective and build cumulative explanations based on the “facts” because the objects they study are indifferent to their observation. The chemical composition and behaviour of a protein can be assumed to be the same wherever it is observed and by whomever it is observed. The same cannot be said of social phenomena, which are mediated by meanings and interpretations, divided by politics and value orientations, subject to historical change and human agency, characterized by contradictions and reconciliations, and transfigured if they are observed at a micro or macro-level. Social reality is different, depending on the historical moment, the perspective, and the criteria from which it is viewed.
Nevertheless, the different sociological paradigms do rest on a form of knowledge that is scientific, if science is taken in the broad sense to mean the use of reasoned argument, the ability to see the general in the particular, and the reliance on evidence from systematic observation of social reality. Within this general scientific framework, however, sociology is broken into the same divisions that separate the forms of modern knowledge more generally. By the time of the Enlightenment the unified perspective of Christendom had broken into three distinct spheres of knowledge: the natural sciences, hermeneutics (or interpretive sciences), and critique (Habermas 1972). Sociology is similarly divided into three types of sociological knowledge, each with its own strengths, limitations, and practical uses: positivist sociology, interpretive sociology, and critical sociology. Within these three types of sociological knowledge, four paradigms have come to dominate sociological thinking: structural functionalism, critical sociology, feminism, and symbolic interactionism.
Positivism
The positivist perspective in sociology—introduced above with regard to the pioneers of the discipline August Comte and Émile Durkheim—is most closely aligned with the forms of knowledge associated with the natural sciences. The emphasis is on empirical observation and measurement (i.e., observation through the senses), value neutrality or objectivity, and the search for law-like statements about the social world (analogous to Newton’s laws of gravity for the natural world). Since mathematics and statistical operations are the main forms of logical demonstration in the natural scientific explanation, positivism relies on translating human phenomena into quantifiable units of measurement. It regards the social world as an objective or “positive” reality, in no essential respects different from the natural world. Positivism is oriented to developing a knowledge useful for controlling or administering social life, which explains its ties to the projects of social engineering going back to Comte’s original vision for sociology. Two forms of positivism have been dominant in sociology since the 1940s: quantitative sociology and structural functionalism.
Quantitative Sociology
In contemporary sociology, positivism is based on four main “rules” that define what constitutes valid knowledge and what types of questions may be reasonably asked (Bryant 1985):
- The rule of empiricism: We can only know about things that are actually given in experience. We cannot validly make claims about things that are invisible, unobservable, or supersensible like metaphysical, spiritual, or moral truths.
- The rule of value neutrality: Scientists should remain value-neutral in their research because it follows from the rule of empiricism that “values” have no empirical content that would allow their validity to be scientifically tested.
- The unity of the scientific method: All sciences have the same basic principles and practices whether their object is natural or human.
- Law-like statements: The type of explanation sought by scientific inquiry is the formulation of general laws (like the law of gravity) to explain specific phenomena (like the falling of a stone).
Much of what is referred to today as quantitative sociology fits within this paradigm of positivism. Quantitative sociology uses statistical methods such as surveys with large numbers of participants. Researchers analyze data using statistical techniques to see if they can uncover patterns of human behaviour. Law-like relationships between variables are often posed in the form of statistical relationships or multiple linear regression formulas that quantify the degree of influence different causal or independent variables have on a particular outcome (or dependent variable). For example, the degree of religiosity of an individual in Canada, measured by the frequency of church attendance or religious practice, can be predicted by a combination of different independent variables such as age, gender, income, immigrant status, and region (Bibby 2012).
Structural Functionalism
Structural Functionalism also falls within the positivist tradition in sociology due to Durkheim’s early efforts to describe the subject matter of sociology in terms of objective social facts—“social facts must be studied as things, that is, as realities external to the individual” (Durkheim 1895)—and to explain them in terms of their social functions. Durkheim argued that in order to study society, sociologists have to look beyond individuals to social facts: the laws, morals, values, religious beliefs, customs, fashions, rituals, and all of the cultural rules that govern social life (Durkheim 1895). Each of these social facts serves one or more functions within a society. For example, one function of a society’s laws may be to protect society from violence, while another is to punish criminal behaviour, while another is to preserve public health.
Following Durkheim’s insight, structural functionalism sees society as a structure with interrelated parts designed to meet the biological and social needs of individuals who make up that society. In this respect, society is like a body that relies on different organs to perform crucial functions. In fact the English philosopher and biologist Herbert Spencer (1820–1903) likened society to a human body. He argued that just as the various organs in the body work together to keep the entire system functioning and regulated, the various parts of society work together to keep the entire society functioning and regulated (Spencer 1898). By parts of society, Spencer was referring to such social institutions as the economy, political systems, health care, education, media, and religion. Spencer continued the analogy by pointing out that societies evolve just as the bodies of humans and other animals do (Maryanski and Turner 1992).
As we have seen, Émile Durkheim developed a similar analogy to explain the structure of societies and how they change and survive over time. Durkheim believed that earlier, more primitive societies were held together because most people performed similar tasks and shared values, language, and symbols. There was a low division of labour, a common religious system of social beliefs, and a low degree of individual autonomy. Society was held together on the basis of mechanical solidarity: a shared collective consciousness with harsh punishment for deviation from the norms. Modern societies, according to Durkheim, were more complex. People served many different functions in society and their ability to carry out their function depended upon others being able to carry out theirs. Modern society was held together on the basis of a division of labour or organic solidarity: a complex system of interrelated parts, working together to maintain stability, i.e., an organism (Durkheim 1893). According to this sociological paradigm, the parts of society are interdependent. The academic relies on the mechanic for the specialized skills required to fix his or her car, the mechanic sends his or her children to university to learn from the academic, and both rely on the baker to provide them with bread for their morning toast. Each part influences and relies on the others.
According to American sociologist Talcott Parsons (1881–1955), in a healthy society, all of these parts work together to produce a stable state called dynamic equilibrium (Parsons 1961). Parsons was a key figure in systematizing Durkheim’s views in the 1940s and 1950s. He argued that a sociological approach to social phenomena must emphasize the systematic nature of society at all levels of social existence: the relation of definable “structures” to their “functions” in relation to the needs or “maintenance” of the system. His AGIL schema provided a useful analytical grid for sociological theory in which an individual, an institution, or an entire society could be seen as a system composed of structures that satisfied four primary functions:
- Adaptation (A): how the system adapts to its environment
- Goal attainment (G): how the system determines what its goals are and how it will attain them
- Integration (I): how the system integrates its members into harmonious participation and social cohesion
- (Latent) Pattern Maintenance (L): how basic cultural patterns, values, belief systems, etc. are regulated and maintained
So for example, the social system as a whole relied on the economy to distribute goods and services as its means of adaptation to the natural environment; on the political system to make decisions as it means of goal attainment; on roles and norms to regulate social behaviour as its means of social integration; and on culture to institutionalize and reproduce common values as its means of latent pattern maintenance. Following Durkheim, he argued that these explanations of social functions had to be made at the level of systems and not involve the specific wants and needs of individuals. In a system, there is an interrelation of component parts where a change in one component affects the others regardless of the perspectives of individuals.
Another noted structural functionalist, Robert Merton (1910–2003), pointed out that social processes often have many functions. Manifest functions are the consequences of a social process that are sought or anticipated, while latent functions are the unsought consequences of a social process. A manifest function of college education, for example, includes gaining knowledge, preparing for a career, and finding a good job that utilizes that education. Latent functions of your college years include meeting new people, participating in extracurricular activities, or even finding a spouse or partner. Another latent function of education is creating a hierarchy of employment based on the level of education attained. Latent functions can be beneficial, neutral, or harmful. Social processes that have undesirable consequences for the operation of society are called dysfunctions. In education, examples of dysfunction include getting bad grades, truancy, dropping out, not graduating, and not finding suitable employment.
Criticism
The main criticisms of both quantitative positivism and structural functionalism have to do with the way in which social phenomena are turned into objective social facts. On one hand, interpretive sociology suggests that the quantification of variables in quantitative sociology reduces the rich complexity and ambiguity of social life to an abstract set of numbers and statistical relationships that cannot capture the meaning it holds for individuals. Measuring someone’s depth of religious belief or “religiosity” by the number of times they attend church in a week explains very little about the religious experience. Similarly, interpretive sociology argues that structural functionalism, with its emphasis on systems of structures and functions tends to reduce the individual to the status of a sociological dupe, assuming pre-assigned roles and functions without any individual agency or capacity for self-creation.
On the other hand, critical sociology challenges the conservative tendencies of quantitative sociology and structural functionalism. Both types of positivist analysis represent themselves as being objective, or value-neutral, which is a problem in the context of critical sociology’s advocacy for social justice. However, both types of positivism also have conservative assumptions built into their basic approach to social facts. The focus in quantitative sociology on observable facts and law-like statements presents a historical and deterministic picture of the world that cannot account for the underlying historical dynamics of power relationships and class or other contradictions. One can empirically observe the trees but not the forest so to speak. Similarly, the focus on the needs and the smooth functioning of social systems in structural functionalism supports a conservative viewpoint because it tends to see the functioning and dynamic equilibrium of society as good or normal, whereas change is pathological. In Davis and Moore’s famous essay “Some Principles of Stratification” (1944) for example, the authos argued that social inequality was essentially “good” because it functioned to preserve the motivation of individuals to work hard to get ahead. Critical sociology challenges both the justice and practical consequences of social inequality.
Table 1.1. Sociological Theories or Perspectives. Different sociological perspectives enable sociologists to view social issues through a variety of useful lenses.
| Sociological Paradigm | Level of Analysis | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Structural Functionalism | Macro | How each part of society functions together to contribute to the whole |
| Symbolic Interactionism | Micro | One-to-one interactions and communications |
| Critical Sociology | Macro | How inequalities contribute to social differences and perpetuate differences in power |
Interpretive Sociology
The interpretive perspective in sociology is aligned with the hermeneutic traditions of the humanities like literature, philosophy, and history. The focus is on understanding or interpreting human activity in terms of the meanings that humans attribute to it. Max Weber’s Verstehende (understanding) sociology is often cited as the origin of this perspective in sociology because of his emphasis on the centrality of meaning and intention in social action:
Sociology… is a science which attempts the interpretive understanding of social action in order thereby to arrive at a causal explanation of its course and effects. In “action” is included all human behaviour when and in so far as the acting individual attaches a subjective meaning to it…. [Social action is] action mutually oriented to that of each other (Weber 1922).
This emphasis on the meaningfulness of social action is taken up later by phenomenology, ethnomethodology, and symbolic interactionism. The interpretive perspective is concerned with developing a knowledge of social interaction as a meaning-oriented practice. It promotes the goal of greater mutual understanding and the possibility of consensus among members of society.
Symbolic Interactionism
Symbolic interactionism provides a theoretical perspective that helps scholars examine the relationship of individuals within their society. This perspective is centred on the notion that communication—or the exchange of meaning through language and symbols—is how people make sense of their social worlds. As pointed out by Herman and Reynolds (1994), this viewpoint sees people as active in shaping their world, rather than as entities who are acted upon by society (Herman and Reynolds 1994). This approach looks at society and people from a micro-level perspective.
George Herbert Mead (1863–1931) is considered one of the founders of symbolic interactionism. His work in Mind, Self and Society (1934) on the “self” as a social structure and on the stages of child development as a sequence of role-playing capacities provides the classic analyses of the perspective.
His student Herbert Blumer (1900–1987) synthesized Mead’s work and popularized the theory. Blumer coined the term “symbolic interactionism” and identified its three basic premises:
- Humans act toward things on the basis of the meanings they ascribe to those things.
- The meaning of such things is derived from, or arises out of, the social interaction that one has with others and the society.
- These meanings are handled in, and modified through, an interpretative process used by the person in dealing with the things he or she encounters (Blumer 1969).
In other words, human interaction is not determined in the same manner as natural events. Nor do people directly react to each other as forces acting upon forces or as stimuli provoking automatic responses. Rather people interact indirectly, by interpreting the meaning of each other’s actions, gestures, or words. Interaction is symbolic in the sense that it occurs through the mediation, exchange, and interpretation of symbols. One person’s action refers beyond itself to a meaning that calls out for the response of the other: it indicates what the receiver is supposed to do; it indicates what the actor intends to do; and together they form a mutual definition of the situation, which enables joint action to take place. Social life can be seen as the stringing together or aligning of multiple joint actions.
Social scientists who apply symbolic-interactionist thinking look for patterns of interaction between individuals. Their studies often involve observation of one-on-one interactions. For example, while a structural functionalist studying a political protest might focus on the function protest plays in realigning the priorities of the political system, a symbolic interactionist would be more interested in seeing the ways in which individuals in the protesting group interact, or how the signs and symbols protesters use enable a common definition of the situation—e.g., an environmental or social justice “issue”—to get established.
The focus on the importance of symbols in building a society led sociologists like Erving Goffman (1922–1982) to develop a framework called dramaturgical analysis. Goffman used theatre as an analogy for social interaction and recognized that people’s interactions showed patterns of cultural “scripts.” In social encounters, individuals make a claim for a positive social status within the group—they present a “face”—but it is never certain that their audience will accept their claim. There is always the possibility that individuals will make a gaff that prevents them from successfully maintaining face. They have to manage the impression they are making in the same way and often using the same type of “props” as an actor. Moreover, because it can be unclear what part a person may play in a given situation, he or she has to improvise his or her role as the situation unfolds. This led to Goffman’s focus on the ritual nature of social interaction—the way in which the “scripts” of social encounters become routine, repetitive, and unconscious. Nevertheless, the emphasis in Goffman’s analysis, as in symbolic interactionism as a whole, is that the social encounter, and social reality itself, is open and unpredictable. Social reality is not predetermined by structures, functions, roles, or history (Goffman 1958).
Symbolic interactionism has also been important in bringing to light the experiences and worlds of individuals who are typically excluded from official accounts of the world. Howard Becker’s Outsiders (1963) for example described the process of labelling in which individuals come to be characterized or labelled as deviants by authorities. The sequence of events in which a young person is picked up by police for an offence, defined as a “young offender,” processed by the criminal justice system, and then introduced to the criminal subculture through contact with experienced convicts is told from the subjective point of view of the young person. The significance of labelling theory is to show that individuals are not born deviant or criminal, but become criminal through an institutionalized symbolic interaction with authorities. As Becker says:
…social groups create deviance by making rules whose infraction creates deviance, and by applying those roles to particular people and labelling them as outsiders. From this point of view, deviance is not a quality of the act the person commits, but rather a consequence of the application by other of rules and sanctions to an “offender.” The deviant is one to whom that label has been successfully applied; deviant behavior is behaviour that people so label (1963).
Studies that use the symbolic interactionist perspective are more likely to use qualitative research methods, such as in-depth interviews or participant observation, because they seek to understand the symbolic worlds in which research subjects live.
Criticism
Research done from this perspective is often scrutinized because of the difficulty of remaining objective. Others criticize the extremely narrow focus on symbolic interaction. Proponents, of course, consider this one of its greatest strengths.
One of the problems of sociology that focuses on micro-level interactions is that it is difficult to generalize from very specific situations, involving very few individuals, to make social scientific claims about the nature of society as a whole. The danger is that, while the rich texture of face-to-face social life can be examined in detail, the results will remain purely descriptive without any explanatory or analytical strength. In a similar fashion, it is very difficult to get at the historical context or relations of power that structure or condition face-to-face symbolic interactions. The perspective on social life as an unstructured and unconstrained domain of agency and subjective meanings has difficulty accounting for the ways that social life does become structured and constrained.
Making Connections: The Big Picture
A Global Culture?

Sociologists around the world are looking closely for signs of what would be an unprecedented event: the emergence of a global culture. In the past, empires such as those that existed in China, Europe, Africa, and Central and South America linked people from many different countries, but those people rarely became part of a common culture. They lived too far from each other, spoke different languages, practised different religions, and traded few goods. Today, increases in communication, travel, and trade have made the world a much smaller place. More and more people are able to communicate with each other instantly—wherever they are located—by telephone, video, and text. They share movies, television shows, music, games, and information over the internet. Students can study with teachers and pupils from the other side of the globe. Governments find it harder to hide conditions inside their countries from the rest of the world.
Sociologists are researching many different aspects of this potential global culture. Some are exploring the dynamics involved in the social interactions of global online communities, such as when members feel a closer kinship to other group members than to people residing in their own country. Other sociologists are studying the impact this growing international culture has on smaller, less-powerful local cultures. Yet other researchers are exploring how international markets and the outsourcing of labour impact social inequalities. Sociology can play a key role in people’s ability to understand the nature of this emerging global culture and how to respond to it.
Critical Sociology
The critical perspective in sociology has its origins in social activism, social justice movements, revolutionary struggles, and radical critique. As Karl Marx put it, its focus was the “ruthless critique of everything existing” (Marx 1843). The key elements of this analysis are the emphases on power relations and the understanding of society as historical—subject to change, struggle, contradiction, instability, social movement and radical transformation. Rather than objectivity and value neutrality, the tradition of critical sociology promotes practices of liberation and social change in order to achieve universal social justice. As Marx stated, “the philosophers have only interpreted the world, in various ways; the point is to change it” (1845). This is why it is misleading to call critical sociology “conflict theory” as some introductory textbooks do. While conflict is certainly central to the critical analyses of power and domination, the focus of critical sociology is on developing types of knowledge and political action that enable emancipation from power relations (i.e., from the conditions of conflict in society). Historical materialism, feminism, environmentalism, anti-racism, queer studies, and poststructuralism are all examples of the critical perspective in sociology.
One of the outcomes of a systematic analysis such as these is that it generates questions about the relationship between our everyday life and issues concerning social justice and environmental sustainability. In line with the philosophical traditions of the Enlightenment, critical sociology is sociology with an “emancipatory interest” (Habermas 1972); that is, a sociology that seeks not simply to understand or describe the world, but to use sociological knowledge to change and improve the world, to emancipate people from conditions of servitude. What does the word critical mean in this context? Critical sociologists argue that it is important to understand that the critical tradition in sociology is not about complaining or being “negative.” Nor is it about adopting a moral position from which to judge people or society. It is not about being “subjective” or “biased” as opposed to “objective.” As Herbert Marcuse put it in One Dimensional Man (1964), critical sociology involves two value judgments:
- The judgment that human life is worth living, or rather that it can be and ought to be made worth living
- The judgment that, in a given society, specific possibilities exist for the amelioration of human life and specific ways and means of realizing these possibilities
Critical sociology therefore rejects the notion of a value-free social science, but does not thereby become a moral exercise or an individual “subjective” value preference as a result. Being critical in the context of sociology is about using objective, empirical knowledge to assess the possibilities and barriers to improving or “ameliorating” human life.
Historical Materialism
The tradition of historical materialism that developed from Karl Marx’s work is one of the central frameworks of critical sociology. As we noted in the discussion of Marx above, historical materialism concentrates on the study of how our everyday lives are structured by the connection between relations of power and economic processes. The basis of this approach begins with the macro-level question of how specific relations of power and specific economic formations have developed historically. These form the context in which the institutions, practices, beliefs, and social rules (norms) of everyday life are situated. The elements that make up a culture—a society’s shared practices, values, beliefs, and artifacts—are structured by the society’s economic mode of production: the way human societies act upon their environment and its resources in order to use them to meet their needs. Hunter-gatherer, agrarian, feudal, and capitalist modes of production have been the economic basis for very different types of society throughout world history.

It is not as if this relationship is always clear to the people living in these different periods of history, however. Often the mechanisms and structures of social life are obscure. For example, it might not have been clear to the Scots who were expelled from their ancestral lands in Scotland during the Highland clearances of the 18th and 19th centuries and who emigrated to the Red River settlements in Rupert’s Land (now Manitoba) that they were living through the epochal transformation from feudalism to capitalism. This transition was nevertheless the context for the decisions individuals and families made to emigrate from Scotland and attempt to found the Red River Colony. It might also not have been clear to them that they were participating in the development of colonial power relationships between the indigenous people of North America and the Europeans that persist up until today. Through contact with the Scots and the French fur traders, the Cree and Anishinabe were gradually drawn out of their own indigenous modes of production and into the developing global capitalist economy as fur trappers and provisioners for the early European settlements. It was a process that eventually led to the loss of control over their lands, the destruction of their way of life, the devastating spread of European diseases, the imposition of the Indian Act, the establishment of the residential school system, institutional and everyday racism, and an enduring legacy of intractable social problems.
In a similar way, historical materialism analyzes the constraints that define the way individuals review their options and make their decisions in present-day society. From the types of career to pursue to the number of children to have, the decisions and practices of everyday life must be understood in terms of the 20th century shift to corporate ownership and the 21st century context of globalization in which corporate decisions about investments are made.
The historical materialist approach emphasizes three components (Naiman 2012). The first is that everything in society is related—it is not possible to study social processes in isolation. The second is that everything in society is dynamic (i.e., in a process of continuous social change). It is not possible to study social processes as if they existed outside of history. The third is that the tensions that form around relationships of power and inequality in society are the key drivers of social change. In the language of Marx, these tensions are based on “contradictions” built into the organization of the economic or material relationships that structure our livelihoods, our relationships to each other, our relationship to the environment, and our place within the global community. It is not possible to study social processes as if they were independent of the historical formations of power that both structure them and destabilize them.
Feminism
Another major school of critical sociology is feminism. From the early work of women sociologists like Harriet Martineau, feminist sociology has focused on the power relationships and inequalities between women and men. How can the conditions of inequality faced by women be addressed? As Harriet Martineau put it in Society in America (1837):
All women should inform themselves of the condition of their sex, and of their own position. It must necessarily follow that the noblest of them will, sooner or later, put forth a moral power which shall prostrate cant [hypocracy], and burst asunder the bonds (silken to some but cold iron to others) of feudal prejudice and usages. In the meantime is it to be understood that the principles of the Declaration of Independence bear no relation to half of the human race? If so, what is the ground of this limitation?
Feminist sociology focuses on analyzing the grounds of the limitations faced by women when they claim the right to equality with men.
Inequality between the genders is a phenomenon that goes back at least 4,000 years (Lerner 1986). Although the forms and ways in which it has been practised differ between cultures and change significantly through history, its persistence has led to the formulation of the concept of patriarchy. Patriarchy refers to a set of institutional structures (like property rights, access to positions of power, relationship to sources of income) that are based on the belief that men and women are dichotomous and unequal categories. Key to patriarchy is what might be called the dominant gender ideology toward sexual differences: the assumption that physiological sex differences between males and females are related to differences in their character, behaviour, and ability (i.e., their gender). These differences are used to justify a gendered division of social roles and inequality in access to rewards, positions of power, and privilege. The question that feminists ask therefore is: How does this distinction between male and female, and the attribution of different qualities to each, serve to organize our institutions (e.g., the family, law, the occupational structure, religious institutions, the division between public and private) and to perpetuate inequality between the sexes?
Feminism is a distinct type of critical sociology. There are considerable differences between types of feminism, however; for example, the differences often attributed to the first wave of feminism in the 19th and early 20th centuries, the second wave of feminism from the 1950s to the 1970s, and the third wave of feminism from the 1980s onward. Despite the variations between different types of feminist approach, there are four characteristics that are common to the feminist perspective:
- Gender is a central focus or subject matter of the perspective.
- Gender relations are viewed as a problem: the site of social inequities, strains, and contradictions.
- Gender relations are not immutable: they are sociological and historical in nature, subject to change and progress.
- Feminism is about an emancipatory commitment to change: the conditions of life that are oppressive for women need to be transformed.
One of the keen sociological insights that emerged with the feminist perspective in sociology is that “the personal is political.” Many of the most immediate and fundamental experiences of social life—from childbirth to who washes the dishes to the experience of sexual violence—had simply been invisible or regarded as unimportant politically or socially. Dorothy Smith’s development of standpoint theory was a key innovation in sociology that enabled these issues to be seen and addressed in a systematic way (Smith 1977). She recognized from the consciousness-raising exercises and encounter groups initiated by feminists in the 1960s and1970s that many of the immediate concerns expressed by women about their personal lives had a commonality of themes. These themes were nevertheless difficult to articulate in sociological terms let alone in the language of politics or law.
Part of the issue was sociology itself. Smith argued that instead of beginning sociological analysis from the abstract point of view of institutions or systems, women’s lives could be more effectively examined if one began from the “actualities” of their lived experience in the immediate local settings of “everyday/everynight” life. She asked, What are the common features of women’s everyday lives? From this standpoint, Smith observed that women’s position in modern society is acutely divided by the experience of dual consciousness. Every day women crossed a tangible dividing line when they went from the “particularizing work in relation to children, spouse, and household” to the institutional world of text-mediated, abstract concerns at work, or in their dealings with schools, medical systems, or government bureaucracies. In the abstract world of institutional life, the actualities of local consciousness and lived life are “obliterated” (Smith 1977). While the standpoint of women is grounded in bodily, localized, “here and now” relationships between people, due to their obligations in the domestic sphere, society is organized through “relations of ruling,” which translate the substance of actual lived experiences into abstract bureaucratic categories. Power and rule in society, especially the power and rule that constrain and coordinate the lives of women, operate through a problematic “move into transcendence” that provides accounts of social life as if it were possible to stand outside of it. Smith argued that the abstract concepts of sociology, at least in the way that it was taught at the time, only contributed to the problem.
Criticism
Whereas critical sociologists often criticize positivist and interpretive sociology for their conservative biases, the reverse is also true. In part the issue is about whether sociology can be “objective,” or value-neutral, or not. However, at a deeper level the criticism is often aimed at the radical nature of critical analyses. Marx’s critique of capitalism and the feminist critique of patriarchy for example led to very interesting insights into how structures of power and inequality work, but from a point of view that sees only the most revolutionary transformation of society as a solution.
Critical sociology is also criticized from the point of view of interpretive sociology for overstating the power of dominant groups to manipulate subordinate groups. For example, media representations of women are said to promote unobtainable standards of beauty or to reduce women to objects of male desire. This type of critique suggests that individuals are controlled by media images rather than recognizing their independent ability to reject media influences or to interpret media images for themselves. In a similar way, critical sociology is criticized for implying that people are purely the products of macro-level historical forces rather than individuals with a capacity for individual and collective agency. To be fair, Marx did argue that “Men make their own history;” it is just that they “do not make it just as they please; they do not make it under circumstances chosen by themselves, but under circumstances encountered, given, and transmitted from the past” (Marx 1851).
Making Connections: Sociology in the Real World
Farming and Locavores: How Sociological Perspectives Might View Food Consumption
The consumption of food is a commonplace, daily occurrence, yet it can also be associated with important moments in our lives. Eating can be an individual or a group action, and eating habits and customs are influenced by our cultures. In the context of society, our nation’s food system is at the core of numerous social movements, political issues, and economic debates. Any of these factors might become a topic of sociological study.
A structural-functional approach to the topic of food consumption might be interested in the role of the agriculture industry within the nation’s economy and how this has changed from the early days of manual-labour farming to modern mechanized production. Food production is a primary example of how human systems adapt to environmental systems. In many respects the concerns of environmentalists and others with respect to the destructive relationship between industrial agriculture and the ecosystem are the results of a dysfunctional system of adaptation. The concept of sustainable agriculture points to the changes needed to return the interface between humans and the natural environment to a state of dynamic equilibrium.
A sociologist viewing food consumption through a symbolic interactionist lens would be more interested in micro-level topics, such as the symbolic use of food in religious rituals, or the role it plays in the social interaction of a family dinner. This perspective might also study the interactions among group members who identify themselves based on their sharing a particular diet, such as vegetarians (people who don’t eat meat) or locavores (people who strive to eat locally produced food). The increasing concern that people have with their diets speaks to the way that the life of the biological body is as much a symbolic reality, interpreted within contemporary discourses on health risks and beauty, as it is a biological reality.
A critical sociologist might be interested in the power differentials present in the regulation of food, exploring where people’s right to information intersects with corporations’ drive for profit and how the government mediates those interests. Or a critical sociologist might be interested in the power and powerlessness experienced by local farmers versus large farming conglomerates. In the documentary Food Inc., the plight of farmers resulting from Monsanto’s patenting of seed technology is depicted as a product of the corporatization of the food industry. Another topic of study might be how nutrition varies between different social classes.
1.4. Why Study Sociology?

When Bernard Blishen picked up the phone one day in 1961, he was surprised to hear Chief Justice Emmett Hall on the other end of the line asking him to be the research director for the newly established Royal Commission on Health Services. Publically funded health care had been introduced for the first time in Canada that year by a socialist Co-operative Commonwealth Federation (CCF) government in Saskatchewan amid bitter controversy. Doctors in Saskatchewan went on strike and private health care insurers mounted an expensive anti-public health care campaign. Because it was a Conservative government commission, appointed by Prime Minister John Diefenbaker, Blishen’s colleagues advised him that it was going to be a whitewash document to defend the interests of private medical care. However, Blishen took on the project as a challenge, and when the commission’s report was published it advocated that the Saskatchewan plan be adopted nationally (Vaughan 2004).
Blishen went on to work in the field of medical sociology and also created a widely used index to measure socioeconomic status known as the Blishen scale. He received the Order of Canada in 2011 in recognition of his contributions to the creation of public health care in Canada.
Since it was first founded, many people interested in sociology have been driven by the scholarly desire to contribute knowledge to this field, while others have seen it as way not only to study society, but also to improve it. Besides the creation of public health care in Canada, sociology has played a crucial role in many important social reforms such as equal opportunity for women in the workplace, improved treatment for individuals with mental and learning disabilities, increased recognition and accommodation for people from different ethnic backgrounds, the creation of hate crime legislation, the right of aboriginal populations to preserve their land and culture, and prison system reforms.
The prominent sociologist Peter L. Berger (1929– ), in his 1963 book Invitation to Sociology: A Humanistic Perspective, describes a sociologist as “someone concerned with understanding society in a disciplined way.” He asserts that sociologists have a natural interest in the monumental moments of people’s lives, as well as a fascination with banal, everyday occurrences. Berger also describes the “aha” moment when a sociological theory becomes applicable and understood:
[T]here is a deceptive simplicity and obviousness about some sociological investigations. One reads them, nods at the familiar scene, remarks that one has heard all this before and don’t people have better things to do than to waste their time on truisms—until one is suddenly brought up against an insight that radically questions everything one had previously assumed about this familiar scene. This is the point at which one begins to sense the excitement of sociology (Berger 1963).
Sociology can be exciting because it teaches people ways to recognize how they fit into the world and how others perceive them. Looking at themselves and society from a sociological perspective helps people see where they connect to different groups based on the many different ways they classify themselves and how society classifies them in turn. It raises awareness of how those classifications—such as economic and status levels, education, ethnicity, or sexual orientation—affect perceptions.
Sociology teaches people not to accept easy explanations. It teaches them a way to organize their thinking so that they can ask better questions and formulate better answers. It makes people more aware that there are many different kinds of people in the world who do not necessarily think the way they do. It increases their willingness and ability to try to see the world from other people’s perspectives. This prepares them to live and work in an increasingly diverse and integrated world.
Sociology in the Workplace
Employers continue to seek people with what are called “transferable skills.” This means that they want to hire people whose knowledge and education can be applied in a variety of settings and whose skills will contribute to various tasks. Studying sociology can provide people with this wide knowledge and a skill set that can contribute to many workplaces, including:
- An understanding of social systems and large bureaucracies
- The ability to devise and carry out research projects to assess whether a program or policy is working
- The ability to collect, read, and analyze statistical information from polls or surveys
- The ability to recognize important differences in people’s social, cultural, and economic backgrounds
- Skills in preparing reports and communicating complex ideas
- The capacity for critical thinking about social issues and problems that confront modern society (Department of Sociology, University of Alabama)
Sociology prepares people for a wide variety of careers. Besides actually conducting social research or training others in the field, people who graduate from college with a degree in sociology are hired by government agencies, nongovernmental organizations, and corporations in fields such as social services, counselling (e.g., family planning, career, substance abuse), designing and evaluating social policies and programs, health services, polling and independent research, market research, and human resources management. Even a small amount of training in sociology can be an asset in careers like sales, public relations, journalism, teaching, law, and criminal justice.
Making Connections: Sociology in the Real World
Please “Friend” Me: Students and Social Networking
The phenomenon known as Facebook was designed specifically for students. Whereas earlier generations wrote notes in each other’s printed yearbooks at the end of the academic year, modern technology and the internet ushered in dynamic new ways for people to interact socially. Instead of having to meet up on campus, students can call, text, and Skype from their dorm rooms. Instead of a study group gathering weekly in the library, online forums and chat rooms help learners connect. The availability and immediacy of computer technology has forever changed the ways students engage with each other.
Now, after several social networks have vied for primacy, a few have established their place in the market and some have attracted niche audience. While Facebook launched the social networking trend geared toward teens and young adults, now people of all ages are actively “friending” each other. LinkedIn distinguished itself by focusing on professional connections, serving as a virtual world for workplace networking. Newer offshoots like Foursquare help people connect based on the real-world places they frequent, while Twitter has cornered the market on brevity.
These newer modes of social interaction have also spawned questionable consequences, such as cyberbullying and what some call FAD, or Facebook addiction disorder. In an international study of smartphone users aged 18 to 30, 60 percent say they are “compulsive” about checking their smartphones and 42 percent admit to feeling “anxious” when disconnected; 75 percent check their smartphones in bed; more than 33 percent check them in the bathroom and 46 percent email and check social media while eating (Cisco 2012). An International Data Corporation (IDC) study of 7,446 smartphone users aged 18 to 44 in the United States in 2012 found that:
- Half of the U.S. population have smartphones and of those 70 percent use Facebook. Using Facebook is the third most common smartphone activity, behind email (78 percent) and web browsing (73 percent).
- 61 percent of smartphone users check Facebook every day.
- 62 percent of smartphone users check their device first thing on waking up in the morning and 79 percent check within 15 minutes. Among 18-to-24-year-olds the figures are 74 percent and 89 percent, respectively.
- Smartphone users check Facebook approximately 14 times a day.
- 84 percent of the time using smartphones is spent on texting, emailing and using social media like Facebook, whereas only 16 percent of the time is spent on phone calls. People spend an average of 132 minutes a day on their smartphones including 33 minutes on Facebook.
- People use Facebook throughout the day, even in places where they are not supposed to: 46 percent use Facebook while doing errands and shopping; 47 percent when they are eating out; 48 percent while working out; 46 percent in meetings or class; and 50 percent while at the movies.
The study noted that the dominant feeling the survey group reported was “a sense of feeling connected” (IDC 2012). Yet, in the international study cited above, two-thirds of 18- to 30-year-old smartphone users said they spend more time with friends online than they do in person.
All of these social networks demonstrate emerging ways that people interact, whether positive or negative. Sociologists ask whether there might be long-term effects of replacing face-to-face interaction with social media. In an interview on the Conan O’Brian Show that ironically circulated widely through social media, the comedian Louis CK described the use of smartphones as “toxic.” They do not allow for children who use them to build skills of empathy because the children do not interact face to face, or see the effects their comments have on others. Moreover, he argues, they do not allow people to be alone with their feelings. “The thing is, you need to build an ability to just be yourself and not be doing something. That’s what the phones are taking away” (NewsComAu 2013). What do you think? How do social media like Facebook and communication technologies like smartphones change the way we communicate? How could this question be studied?
Key Terms
AGIL schema Talcott Parsons’ division of society into four functional requisites: Adaptation, Goal attainment, Integration, and Latent pattern maintenance
anomie a social condition or normlessness in which a lack of clear norms fails to give direction and purpose to individual actions
capitalism an economic system characterized by private or corporate ownership and production of goods and their sale in a competitive market
content the specific reasons or drives that motivate individuals to interact
critical sociology a theoretical perspective that focuses on inequality and power relations in society in order to achieve social justice and emancipation through their transformation
culture includes the group’s shared practices, values, beliefs, norms and artifacts
disenchantment of the world the replacement of magical thinking by technological rationality and calculation
dominant gender ideology the belief that physiological sex differences between males and females are related to differences in their character, behaviour, and ability
dramaturgical analysis a technique sociologists use in which they view society through the metaphor of theatrical performance
dual consciousness the experience of a fissure or dividing point in everyday life where one crosses a line between irreconcilable forms of consciousness or perspective
dynamic equilibrium a stable state in which all parts of a healthy society are working together properly
dysfunctions social patterns that have undesirable consequences for the operation of society
feminism the critical analysis of the way gender differences in society structure social inequality
figuration the process of simultaneously analyzing the behaviour of an individual and the society that shapes that behaviour
formal sociology a sociology that analytically separates the contents from the forms of social interaction to study the common forms that guide human behaviour
function the part a recurrent activity plays in the social life as a whole and the contribution it makes to structural continuity
functionalism (functionalist perspective) a theoretical approach that sees society as a structure with interrelated parts designed to meet the biological and social needs of individuals that make up that society
historical materialism an approach to understanding society that explains social change, human ideas, and social organization in terms of underlying changes in the economic (or material) structure of society
idealism an approach to understanding society that emphasizes that the nature of society and social change is determined by a society’s ideas, knowledge, and beliefs
idealist one who believes in idealism
interpretive sociology a perspective that explains human behaviour in terms of the meanings individuals attribute to it
labelling a social process in which an individual’s social identity is established through the imposition of a definition by authorities
latent functions the unrecognized or unintended consequences of a social process
law of three stages the three stages of evolution that societies develop through: theological, metaphysical, and positive
macro-sociology a wide-scale view of the role of social structures within a society
manifest functions sought consequences of a social process
mechanical solidarity social solidarity or cohesion through a shared collective consciousness with harsh punishment for deviation from the norms
metaphysical stage a stage of social evolution in which people explain events in terms of abstract or speculative ideas
micro-sociology the study of specific relationships between individuals or small groups
mode of production the way human societies act upon their environment and its resources in order to use them to meet their needs
multi-perspectival science a science that is divided into competing or diverse paradigms
organic solidarity social solidarity or cohesion through a complex division of labour and restitutive law
paradigms philosophical and theoretical frameworks used within a discipline to formulate theories, generalizations, and the experiments performed in support of them
patriarchy institutions of male power in society
positive stage a stage of social evolution in which people explain events in terms of scientific principles and laws
positivism (positivist perspective or positivist sociology) the scientific study of social patterns based on methodological principles of the natural sciences
Protestant ethic the duty to work hard in one’s calling
quantitative sociology statistical methods such as surveys with large numbers of participants
rationalization the general tendency of modern institutions and most areas of life to be transformed by the application of instrumental reason
reification referring to abstract concepts, complex processes or mutable social relationships as “things”
social action actions to which individuals attach subjective meanings
social facts the external laws, morals, values, religious beliefs, customs, fashions, rituals, and cultural rules that govern social life
social reform an approach to social change that advocates slow, incremental improvements in social institutions rather than rapid, revolutionary change of society as a whole
social solidarity the social ties that bind a group of people together such as kinship, shared location, and religion
society is a group of people whose members interact, reside in a definable area, and share a culture
sociological imagination the ability to understand how your own unique circumstances relate to that of other people, as well as to history in general and societal structures in particular
sociology the systematic study of society and social interaction
standpoint theory the examination of how society is organized and coordinated from the perspective of a particular social location or perspective in society
structural functionalism see functionalism
symbolic interactionism a theoretical perspective through which scholars examine the relationship of individuals within their society by studying their communication (language and symbols)
theological stage a stage of social evolution in which people explain events with respect to the will of God or gods
theory a proposed explanation about social interactions or society
tragedy of culture the tendency for the products of human cultural creation to accumulate and become increasingly complex, specialized, alienating, or oppressive
Verstehen German for “understanding”; in sociology it refers to the use of empathy, or putting oneself in another’s place, to understand the motives and logic of another’s action
Section Summary
1.1. What Is Sociology?
Sociology is the systematic study of society and social interaction. In order to carry out their studies, sociologists identify cultural patterns and social forces and determine how they affect individuals and groups. They also develop ways to apply their findings to the real world.
1.2. The History of Sociology
Sociology was developed as a way to study and try to understand the changes to society brought on by the Industrial Revolution in the 18th and 19th centuries. Some of the earliest sociologists thought that societies and individuals’ roles in society could be studied using the same scientific methodologies that were used in the natural sciences, while others believed that is was impossible to predict human behaviour scientifically, and still others debated the value of such predictions. Those perspectives continue to be represented within sociology today.
1.3. Theoretical Perspectives
Sociologists develop theories to explain social events, interactions, and patterns. A theory is a proposed explanation of those patterns. Theories have different scales. Macro-level theories, such as structural functionalism and conflict theory, attempt to explain how societies operate as a whole. Micro-level theories, such as symbolic interactionism, focus on interactions between individuals.
1.4. Why Study Sociology?
Studying sociology is beneficial both for the individual and for society. By studying sociology people learn how to think critically about social issues and problems that confront our society. The study of sociology enriches students’ lives and prepares them for careers in an increasingly diverse world. Society benefits because people with sociological training are better prepared to make informed decisions about social issues and take effective action to deal with them.
Section Quiz
1.1. What Is Sociology?
1. Which of the following best describes sociology as a subject?
- the study of individual behaviour
- the study of cultures
- the study of society and social interaction
- the study of economics
2. Wright Mills once said that sociologists need to develop a sociological __________ to study how society affects individuals.
- culture
- imagination
- method
- tool
3. A sociologist defines society as a group of people who reside in a defined area, share a culture, and who:
- interact
- work in the same industry
- speak different languages
- practise a recognized religion
4. Seeing patterns means that a sociologist needs to be able to:
- compare the behaviour of individuals from different societies
- compare one society to another
- identify similarities in how social groups respond to social pressure
- compare individuals to groups
1.2. The History of Sociology
5. Which of the following was a topic of study in early sociology?
- astrology
- economics
- physics
- history
6. Which founder of sociology believed societies changed due to class struggle?
- Émile Comte
- Karl Marx
- Plato
- Herbert Spencer
7. The difference between positivism and interpretive sociology relates to:
- whether individuals like or dislike their society
- whether research methods use statistical data or person-to-person research
- whether sociological studies can predict or improve society
- all of the above
8. Which would a quantitative sociologists use to gather data?
- a large survey
- a literature search
- an in-depth interview
- a review of television programs
9. Weber believed humans could not be studied purely objectively because they were influenced by:
- drugs
- their culture
- their genetic makeup
- the researcher
1.3. Theoretical Perspectives
10. Which of these theories is most likely to look at the social world on a micro-level?
- structural functionalism
- conflict theory
- positivism
- symbolic interactionism
11. Who believed that the history of society was one of class struggle?
- Émile Durkheim
- Karl Marx
- Erving Goffmann
- George Herbert Mead
12. Who coined the phrase symbolic interactionism?
- Herbert Blumer
- Max Weber
- Lester F. Ward
- W. I. Thomas
13. A symbolic interactionist may compare social interactions to:
- behaviours
- conflicts
- human organs
- theatrical roles
14. Which research technique would most likely be used by a symbolic interactionist?
- surveys
- participant observation
- quantitative data analysis
- none of the above
15. Which sociologist described sociology as the study of social forms?
- Martineau
- Simmel
- Weber
- Becker
1.4. Why Study Sociology?
16. Studying Sociology helps people analyze data because they learn:
- interview techniques
- to apply statistics
- to generate theories
- all of the above
17. Berger describes sociologists as concerned with:
- monumental moments in people’s lives
- common everyday life events
- both a and b
- none of the above
Short Answer
- What do you think C. Wright Mills meant when he said that to be a sociologist, one had to develop a sociological imagination?
- Describe a situation in which a choice you made was influenced by societal pressures.
- What do you make of Karl Marx’s contributions to sociology? What perceptions of Marx have you been exposed to in your society, and how do those perceptions influence your views?
- Do you tend to place more value on qualitative or quantitative research? Why? Does it matter what topic is being studied?
- Which theory do you think better explains how societies operate—structural functionalism or conflict theory? Why?
- Do you think the way people behave in social interactions is more due to the cause and effect of external social constraints or more like actors playing a role in a theatrical production? Why?
- How do you think taking a sociology course might affect your social interactions?
- What sort of career are you interested in? How could studying sociology help you in this career?
Further Research
1.1. What Is Sociology?
Sociology is a broad discipline. Different kinds of sociologists employ various methods for exploring the relationship between individuals and society. Check out more about sociology at http://openstaxcollege.org/l/what-is-sociology.
1.2. The History of Sociology
Many sociologists helped shape the discipline. To learn more about prominent sociologists and how they changed sociology check out http://openstaxcollege.org/l/ferdinand-toennies.
1.3. Theoretical Perspectives
People often think of all conflict as violent, but many conflicts can be resolved nonviolently. To learn more about nonviolent methods of conflict resolution check out the Albert Einstein Institution http://openstaxcollege.org/l/ae-institution
1.4. Why Study Sociology?
Social communication is rapidly evolving due to ever improving technologies. To learn more about how sociologists study the impact of these changes check out http://openstaxcollege.org/l/media
References
1.1. What Is Sociology?
CBC. 2010. “Part 3: Former Gang Members,” The Current, CBC Radio. September 14. Retrieved February 24, 2014, from http://www.cbc.ca/thecurrent/2010/09/september-14-2010.html
Durkheim, Émile. 1951 [1897]. Suicide: A Study in Sociology. New York: Free Press.
Elias, Norbert. 1978. What Is Sociology? New York: Columbia University Press.
Mills, C. Wright. 2000 [1959]. The Sociological Imagination. 40th ed. New York: Oxford University Press.
Office of the Correctional Investigator. 2013. “Backgrounder: Aboriginal Offenders—A Critical Situation.” Government of Canada. Retrieved February 24, 2014 from http://www.oci-bec.gc.ca/cnt/rpt/oth-aut/oth-aut20121022info-eng.aspx
Pollan, Michael. 2006. The Omnivore’s Dilemma: A Natural History of Four Meals. NY: Penguin Press.
Simmel, Georg. 1971 [1908]. “The problem of sociology.” Pp. 23–27 in Georg Simmel: On individuality and social forms, edited by D. Levine. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Smith, Dorothy. 1999. Writing the Social: Critique, Theory, and Investigations. Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
Statistics Canada. 2013. “Overweight and obese adults (self-reported), 2012.” Statistics Canada Health Fact Sheets. Catalogue 82-625-XWE. Retrieved February 24, 2014, from http://www.statcan.gc.ca/pub/82-625-x/2013001/article/11840-eng.htm
Becker, Howard and Harry Barnes. 1961. Social Thought from Lore to Science (Volume 1). New York: Dover Publications.
Collins, Randall and Michael Makowsky. 1989. The Discovery of Society. New York: Random House.
Comte, August. 1975 [1830]. “The Nature and Importance of the Positive Philosophy.” In Auguste Comte and positivism : the essential writings, edited by Gertrud Lenzer. NY: Harper and Row.
Durkheim, Émile. 1964 [1895]. The Rules of Sociological Method, 8th ed., edited by J. Mueller, E. George and E. Caitlin. Translated by S. Solovay. New York: Free Press.
Durkheim, Émile 1997 [1895]. “The Rules of Sociological Method.” Pp. 207–211 in Classical Sociological Theory: A Reader, edited by Ian McIntosh. New York: New York University Press.
Durkheim, Émile 1997 [1897]. “Suicide: A Study in Sociology.” Pp. 212–231 in Classical Sociological Theory: A Reader, edited by Ian McIntosh. New York: New York University Press.
Durkheim, Émile 1997 [1912]. “Religion and Society.” Pp. 232–247 in Classical Sociological Theory: A Reader, edited by Ian McIntosh. New York: New York University Press.
Fauré, Christine, Jacques Guilhaumou, Jacques Vallier, and Françoise Weil. 2007 [1999]. Des Manuscrits de Sieyès, 1773–1799, Volumes I and II. Paris: Champion.
Lengermann, Patricia and Jill Niebrugge. 2007. The Women Founders: Sociology and Social Theory, 1830–1930. Longrove, Ill: Waveland Press.
Li, Peter. 1996. The Making of Post-War Canada. Toronto: Oxford University Press.
Marx, Karl. 1867. Capital: A Critique of Political Economy. Hamburg: Otto Meissner Verlag.
Marx, Karl and Friedrich Engels. 1977 [1848]. The Communist Manifesto. Pp. 221–247 in Karl Marx: Selected Writings, edited by David McLellan. Toronto: Oxford University Press.
McDonald, Lynn. 1998. Women Theorists on Society and Politics. Waterloo: Wilfrid Laurier University Press.
Simmel, Georg. 1971 [1908]. “The problem of sociology.” Pp. 23–27 in Georg Simmel: On individuality and social forms, edited by D. Levine. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Simmel, Georg. 1971 [1910]. “Sociability.” Pp. 127–140 in Georg Simmel: On individuality and social forms, edited by D. Levine. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Simmel, Georg. (1971[1903]). “Metropolis and Mental Life.” Pp. 324–339 in Georg Simmel: On individuality and social forms, edited by D. Levine. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Statistics Canada. 2011 Women in Canada: A Gender Based Statistical Report. (Catalogue no. 89-503-X). Retrieved January 31, 2014 from http://www.statcan.gc.ca/pub/89-503-x/89-503-x2010001-eng.pdf
Weber, Max. 1958 [1904]. The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism. New York: Charles Scribner’s Sons.
Weber, Max. 1969 [1919]. “Science as a Vocation.” Pp. 129-158 in From Max Weber: Essays in Sociology, edited by H.H. Gerth and C.W. Mills. NY: Oxford University Press.
Weber, Max. 1997 [1922]. “Definitions of Sociology and Social Action.” Pp 157–164 Classical Sociological Theory: A Reader, edited by Ian McIntosh. NY: New York University Press.
Wollstonecraft, Mary. 1792. A Vindication of the Rights of Women with Strictures on Moral and Political Subjects. London: Joseph Johnson.
Zeitlin, Irving. 1997. Ideology and the Development of Sociological Theory. Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Allan, Kenneth. 2006. Contemporary Social and Sociological Theory: Visualizing Social Worlds. Thousand Oaks, CA: Pine Forge Press.
Becker, Howard. 1963. Outsiders : Studies in the Sociology of Deviance. New York: Macmillan.
Bibby, Reginald. 2012. A New Day: The Resilience & Restructuring of Religion in Canada. Lethbridge: Project Canada Books
Blumer, H. 1969. Symbolic Interactionism: Perspective and Method. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Bryant, Christopher. 1985. Positivism in Social Theory and Research. New York: St. Martin’s Press.
Davis, Kingsley and Wilbert Moore. 1944. “Some Principles of Stratification.” Americam Sociological Review. 10(2):242–249.
Drengson, Alan. 1983. Shifting Paradigms: From Technocrat to Planetary Person. Victoria, BC: Light Star Press.
Durkheim, Émile. 1984 [1893]. The Division of Labor in Society. New York: Free Press.
Durkheim, Émile. 1964 [1895]. The Rules of Sociological Method, edited by J. Mueller, E. George and E. Caitlin. 8th ed. Translated by S. Solovay. New York: Free Press.
Goffman, Erving. 1958. The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life. Edinburgh: University of Edinburgh, Social Sciences Research Centre.
Habermas, 1972. Knowledge and Human Interests. Boston: Beacon Press.
Herman, Nancy J. and Larry T. Reynolds. 1994. Symbolic Interaction: An Introduction to Social Psychology. Lanham, MD: Altamira Press.
LaRossa, R. and D.C. Reitzes. 1993. “Symbolic Interactionism and Family Studies.” Pp. 135–163 in Sourcebook of Family Theories and Methods: A Contextual Approach, edited by P. G. Boss, W. J. Doherty, R. LaRossa, W. R. Schumm, and S. K. Steinmetz. New York: Springer.
Lerner, Gerda. 1986. The Creation of Patriarchy. NY: Oxford University Press.
Marcuse, Herbert. 1964. One Dimensional Man: Studies in the Ideology of Advanced Industrial Society. Boston: Beacon Press.
Martineau, Harriet. 1837. Society in America. New York: Saunders and Otley. Retrieved February 24, 2014 from https://archive.org/details/societyinamerica02martiala
Maryanski, Alexandra and Jonathan Turner. 1992. The Social Cage: Human Nature and the Evolution of Society. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Marx, Karl. 1977 [1845]. “Theses on Feuerbach.” Pp. 156–158 in Karl Marx: Selected Writings, edited by David McLellan. Toronto: Oxford University Press.
Marx, Karl. 1977 [1851]. The Eighteenth Brumaire of Louis Bonaparte. Pp. 300–325 in Karl Marx: Selected Writings, edited by David McLellan. Toronto: Oxford University Press.
Marx, Karl. 1978 [1843]. “For a Ruthless Criticism of Everything Existing.” Pp. 12–15 in The Marx-Engels Reader, edited by R. C. Tucker. New York: W. W. Norton.
Mead, G.H. 1934. Mind, Self and Society. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Naiman, Joanne. 2012. How Societies Work, (5th ed.). Black Point, NS: Fernwood Publishing.
Parsons, T. 1961. Theories of Society: Foundations of Modern Sociological Theory. New York: Free Press.
Smith, Dorothy. 1977. Feminism and Marxism: A Place to Begin, a Way to Go. Vancouver: New Star Books.
Spencer, Herbert. 1898. The Principles of Biology. New York: D. Appleton and Company.
Weber, Max. 1997 [1922]. “Definitions of Sociology and Social Action.” Pp 157–164 in Classical Sociological Theory: A Reader, edited by Ian McIntosh. NY: New York University Press.
Berger, Peter L. 1963. Invitation to Sociology: A Humanistic Perspective. New York: Anchor Books.
Cisco. 2102. Gen Y: New Dawn for Work, Play, Identity Cisco Connected World Technology Report. Retrieved February 4, 2012 from http://www.cisco.com/en/US/solutions/ns341/ns525/ns537/ns705/ns1120/2012-CCWTR-Chapter1-Global-Results.pdf
Department of Sociology, University of Alabama. N.d. Is Sociology Right for You?. Huntsville: University of Alabama. Retrieved January 19, 2012 from http://www.uah.edu/la/departments/sociology/about-sociology/why-sociology
IDC. 2012. Always Connected: How Smartphones and Social Media Keep Us Connected IDC Research Report. Retrieved February 4, 2014 from https://fb-public.app.box.com/s/3iq5x6uwnqtq7ki4q8wk
NewsComAu. 2013. “Comedian Louis CK’s compelling philosophy: ‘Smartphones are toxic’.” NewsComAu September 21. Retrieved February 4, 2014 from http://www.news.com.au/technology/gadgets/comedian-louis-ck8217s-compelling-philosophy-8216smartphones-are-toxic8217/story-fn6vihic-1226724328876
Vaughan, Frederick. 2004. Aggressive in Pursuit: The Life of Justice Emmett Hall. Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
Solutions to Section Quiz
1. C | 2. B | 3. A | 4. C | 5. B | 6. B | 7. C | 8. A | 9. B | 10. D | 11. B | 12. A | 13. D | 14. B | 15. B | 16. D | 17. C
Image Attributions
Figure 1.1 Canada Day National Capital by Derek Hatfield (http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Canada_Day_National_Capital.jpg) used under CC BY 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/deed.en)
Figure 1.2. Il (secondo?) bacio più famoso della storia: Vancouver Riot Kiss by Pasquale Borriello (https://www.flickr.com/photos/pazca/5844049845/in/photostream/) used under CC BY 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0/)
Figure 1.4 c Ibn Khaldun by Waqas Ahmed (http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Ibn_Khaldun.jpg) used under CC BY-SA 3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/deed.en);
Figure 1.5. Newton-WilliamBlake by William Blake (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Newton_(Blake)#mediaviewer/File:Newton-WilliamBlake.jpg) is in the public domain (http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Public_domain#Material_in_the_public_domain)
Figure 1.6 Hon. T.C. Douglas by Lieut. G. Barry Gilroy (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Tommycropped.jpg) is in public domain
Figure 1.8. Harriet Martineau portrait (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Harriet_martineau_portrait.jpg) is in the public domain (http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Public_domain#Material_in_the_public_domain).
Figure 1.9. Emile Durkheim (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Emile_Durkheim.jpg) is in the public domain (http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Public_domain#Material_in_the_public_domain).
Figure 1.10. Max Weber (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Max_Weber_1917.jpg) is in the public domain (http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Public_domain#Material_in_the_public_domain).
Figure 1.11. Georg Simmel by Julius Cornelius Schaarwächter (http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Georg_Simmel.jpg) is in the public domain (http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Public_domain#Material_in_the_public_domain).
Figure 1.14. Hon. T.C. Douglas, Premier of Saskatchewan by Lieut. G. Barry Gilroy (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Tommycropped.jpg) is in public domain.
Figure 1.15. The Last of the Clan by Thomas Faed (http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Thomas_Faed_-_The_Last_of_the_Clan.JPG) is in the public domain (http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Public_domain#Material_in_the_public_domain).

