Chapter 14. The Animal Body: Basic Form and Function
14.1 Animal Form and Function
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the various types of body plans that occur in animals
Animals vary in form and function. From a sponge to a worm to a goat, an organism has a distinct body plan that limits its size and shape. Animals’ bodies are also designed to interact with their environments, whether in the deep sea, a rainforest canopy, or the desert. Therefore, a large amount of information about the structure of an organism’s body (anatomy) and the function of its cells, tissues and organs (physiology) can be learned by studying that organism’s environment.
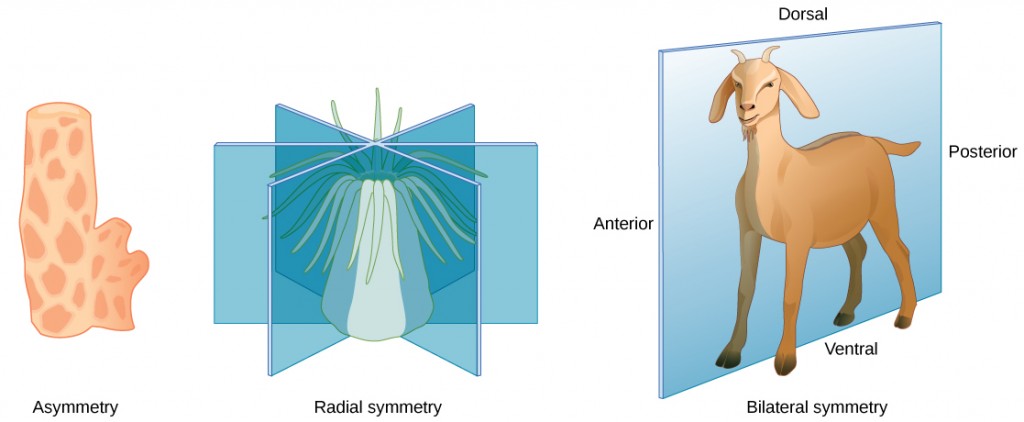
Animal body plans follow set patterns related to symmetry. They are asymmetrical, radial, or bilateral in form as illustrated in Figure 14.2. Asymmetrical animals are animals with no pattern or symmetry; an example of an asymmetrical animal is a sponge. Radial symmetry, as illustrated in Figure 14.2, describes when an animal has an up-and-down orientation: any plane cut along its longitudinal axis through the organism produces equal halves, but not a definite right or left side. This plan is found mostly in aquatic animals, especially organisms that attach themselves to a base, like a rock or a boat, and extract their food from the surrounding water as it flows around the organism. Bilateral symmetry is illustrated in the same figure by a goat. The goat also has an upper and lower component to it, but a plane cut from front to back separates the animal into definite right and left sides. Additional terms used when describing positions in the body are anterior (front), posterior (rear), dorsal (toward the back), and ventral (toward the stomach). Bilateral symmetry is found in both land-based and aquatic animals; it enables a high level of mobility.
Limiting Effects of Diffusion on Size and Development
The exchange of nutrients and wastes between a cell and its watery environment occurs through the process of diffusion. All living cells are bathed in liquid, whether they are in a single-celled organism or a multicellular one. Diffusion is effective over a specific distance and limits the size that an individual cell can attain. If a cell is a single-celled microorganism, such as an amoeba, it can satisfy all of its nutrient and waste needs through diffusion. If the cell is too large, then diffusion is ineffective and the center of the cell does not receive adequate nutrients nor is it able to effectively dispel its waste.
An important concept in understanding how efficient diffusion is as a means of transport is the surface to volume ratio. Recall that any three-dimensional object has a surface area and volume; the ratio of these two quantities is the surface-to-volume ratio. Consider a cell shaped like a perfect sphere: it has a surface area of 4πr2, and a volume of (4/3)πr3. The surface-to-volume ratio of a sphere is 3/r; as the cell gets bigger, its surface to volume ratio decreases, making diffusion less efficient. The larger the size of the sphere, or animal, the less surface area for diffusion it possesses.
The solution to producing larger organisms is for them to become multicellular. Specialization occurs in complex organisms, allowing cells to become more efficient at doing fewer tasks. For example, circulatory systems bring nutrients and remove waste, while respiratory systems provide oxygen for the cells and remove carbon dioxide from them. Other organ systems have developed further specialization of cells and tissues and efficiently control body functions. Moreover, surface-to-volume ratio applies to other areas of animal development, such as the relationship between muscle mass and cross-sectional surface area in supporting skeletons, and in the relationship between muscle mass and the generation of dissipation of heat.
Concept in Action

Visit this interactive site to see an entire animal (a zebrafish embryo) at the cellular and sub-cellular level. Use the zoom and navigation functions for a virtual nanoscopy exploration.
Animal Bioenergetics
All animals must obtain their energy from food they ingest or absorb. These nutrients are converted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP) for short-term storage and use by all cells. Some animals store energy for slightly longer times as glycogen, and others store energy for much longer times in the form of triglycerides housed in specialized adipose tissues. No energy system is one hundred percent efficient, and an animal’s metabolism produces waste energy in the form of heat. If an animal can conserve that heat and maintain a relatively constant body temperature, it is classified as a warm-blooded animal and called an endotherm. The insulation used to conserve the body heat comes in the forms of fur, fat, or feathers. The absence of insulation in ectothermic animals increases their dependence on the environment for body heat.
The amount of energy expended by an animal over a specific time is called its metabolic rate. The rate is measured variously in joules, calories, or kilocalories (1000 calories). Carbohydrates and proteins contain about 4.5 to 5 kcal/g, and fat contains about 9 kcal/g. Metabolic rate is estimated as the basal metabolic rate (BMR) in endothermic animals at rest and as the standard metabolic rate (SMR) in ectotherms. Human males have a BMR of 1600 to 1800 kcal/day, and human females have a BMR of 1300 to 1500 kcal/day. Even with insulation, endothermal animals require extensive amounts of energy to maintain a constant body temperature. An ectotherm such as an alligator has an SMR of 60 kcal/day.
Energy Requirements Related to Body Size
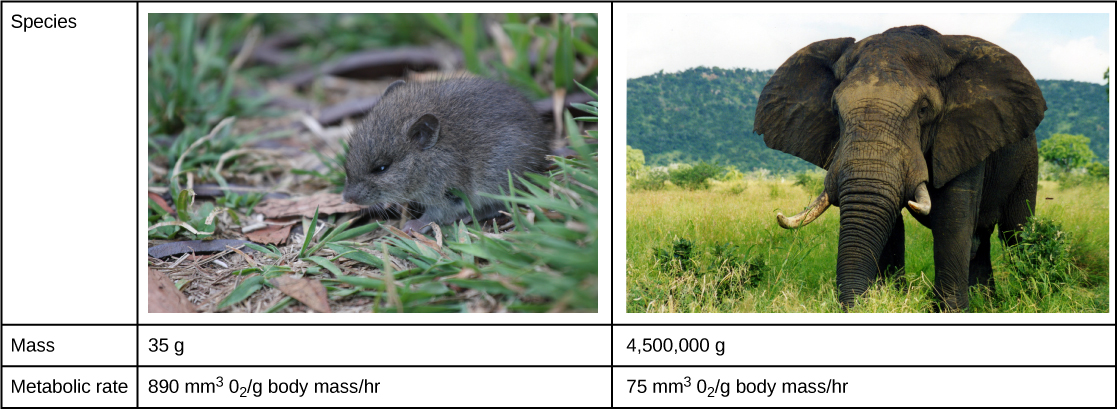
Smaller endothermic animals have a greater surface area for their mass than larger ones (Figure 14.4). Therefore, smaller animals lose heat at a faster rate than larger animals and require more energy to maintain a constant internal temperature. This results in a smaller endothermic animal having a higher BMR, per body weight, than a larger endothermic animal.

Energy Requirements Related to Levels of Activity
The more active an animal is, the more energy is needed to maintain that activity, and the higher its BMR or SMR. The average daily rate of energy consumption is about two to four times an animal’s BMR or SMR. Humans are more sedentary than most animals and have an average daily rate of only 1.5 times the BMR. The diet of an endothermic animal is determined by its BMR. For example: the type of grasses, leaves, or shrubs that an herbivore eats affects the number of calories that it takes in. The relative caloric content of herbivore foods, in descending order, is tall grasses > legumes > short grasses > forbs (any broad-leaved plant, not a grass) > subshrubs > annuals/biennials.
Energy Requirements Related to Environment
Animals adapt to extremes of temperature or food availability through torpor. Torpor is a process that leads to a decrease in activity and metabolism and allows animals to survive adverse conditions. Torpor can be used by animals for long periods, such as entering a state of hibernation during the winter months, in which case it enables them to maintain a reduced body temperature. During hibernation, ground squirrels can achieve an abdominal temperature of 0° C (32° F), while a bear’s internal temperature is maintained higher at about 37° C (99° F).
If torpor occurs during the summer months with high temperatures and little water, it is called estivation. Some desert animals use this to survive the harshest months of the year. Torpor can occur on a daily basis; this is seen in bats and hummingbirds. While endothermy is limited in smaller animals by surface to volume ratio, some organisms can be smaller and still be endotherms because they employ daily torpor during the part of the day that is coldest. This allows them to conserve energy during the colder parts of the day, when they consume more energy to maintain their body temperature.
Animal Body Planes and Cavities
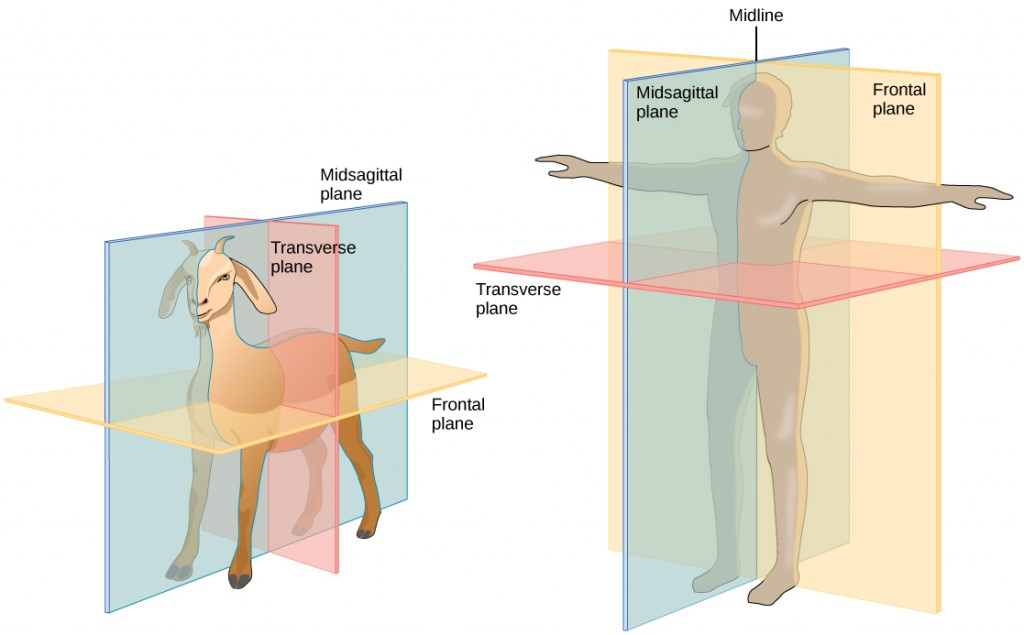
A standing vertebrate animal can be divided by several planes. A sagittal plane divides the body into right and left portions. A midsagittal plane divides the body exactly in the middle, making two equal right and left halves. A frontal plane (also called a coronal plane) separates the front from the back. A transverse plane (or, horizontal plane) divides the animal into upper and lower portions. This is sometimes called a cross section, and, if the transverse cut is at an angle, it is called an oblique plane. Figure 14.5 illustrates these planes on a goat (a four-legged animal) and a human being.
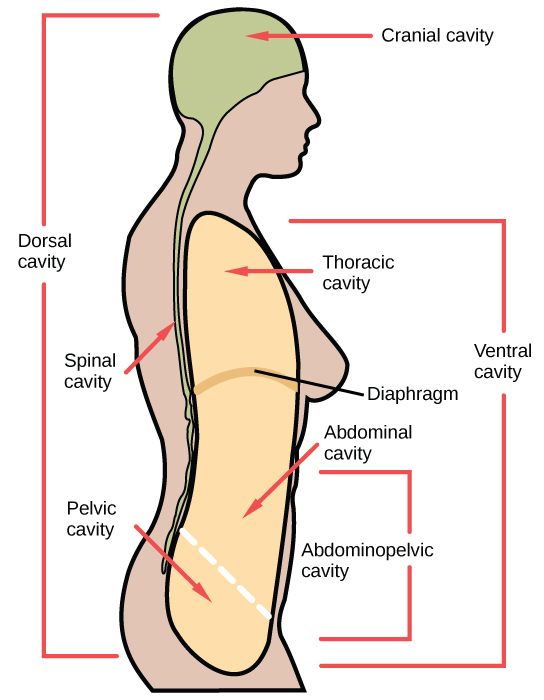
Vertebrate animals have a number of defined body cavities, as illustrated in Figure 14.6. Two of these are major cavities that contain smaller cavities within them. The dorsal cavity contains the cranial and the vertebral (or spinal) cavities. The ventral cavity contains the thoracic cavity, which in turn contains the pleural cavity around the lungs and the pericardial cavity, which surrounds the heart. The ventral cavity also contains the abdominopelvic cavity, which can be separated into the abdominal and the pelvic cavities.
Physical Anthropologist
Physical anthropologists study the adaption, variability, and evolution of human beings, plus their living and fossil relatives. They can work in a variety of settings, although most will have an academic appointment at a university, usually in an anthropology department or a biology, genetics, or zoology department.
Non-academic positions are available in the automotive and aerospace industries where the focus is on human size, shape, and anatomy. Research by these professionals might range from studies of how the human body reacts to car crashes to exploring how to make seats more comfortable. Other non-academic positions can be obtained in museums of natural history, anthropology, archaeology, or science and technology. These positions involve educating students from grade school through graduate school. Physical anthropologists serve as education coordinators, collection managers, writers for museum publications, and as administrators. Zoos employ these professionals, especially if they have an expertise in primate biology; they work in collection management and captive breeding programs for endangered species. Forensic science utilizes physical anthropology expertise in identifying human and animal remains, assisting in determining the cause of death, and for expert testimony in trials.
Glossary
asymmetrical: describes animals with no axis of symmetry in their body pattern
basal metabolic rate (BMR): metabolic rate at rest in endothermic animals
cartilage: type of connective tissue with a large amount of ground substance matrix, cells called chondrocytes, and some amount of fibers
chondrocyte: cell found in cartilage
columnar epithelia: epithelia made of cells taller than they are wide, specialized in absorption
connective tissue: type of tissue made of cells, ground substance matrix, and fibers
cuboidal epithelia: epithelia made of cube-shaped cells, specialized in glandular functions
dorsal cavity: body cavity on the posterior or back portion of an animal; includes the cranial and vertebral cavities
ectotherm: animal incapable of maintaining a relatively constant internal body temperatureendotherm: animal capable of maintaining a relatively constant internal body temperature
estivation: torpor in response to extremely high temperatures and low water availability
fibrous connective tissue: type of connective tissue with a high concentration of fibers
fusiform: animal body shape that is tubular and tapered at both ends
hibernation: torpor over a long period of time, such as a winter
homeostasis: dynamic equilibrium maintaining appropriate body functions
lacuna: space in cartilage and bone that contains living cells
matrix: component of connective tissue made of both living and non-living (ground substances) cells
midsagittal plane: plane cutting through an animal separating the individual into even right and left sides
negative feedback loop: feedback to a control mechanism that increases or decreases a stimulus instead of maintaining it
osteon: subunit of compact bone
positive feedback loop:feedback to a control mechanism that continues the direction of a stimulus
sagittal plane: plane cutting through an animal separating the individual into right and left sides
set point: midpoint or target point in homeostasis
squamous epithelia: type of epithelia made of flat cells, specialized in aiding diffusion or preventing abrasion
standard metabolic rate (SMR): metabolic rate at rest in ectothermic animals
stratified epithelia: multiple layers of epithelial cells
torpor: decrease in activity and metabolism that allows an animal to survive adverse conditions
ventral cavity: body cavity on the anterior or front portion of an animal that includes the thoracic cavities and the abdominopelvic cavities