Grammar
73 Sentence Basics
In this chapter, please refer to the following grammar key:
- Subjects are underlined.
- Verbs are in bold.
- LV means linking verb
- HV means helping verb
- V means action verb
- N means noun
- Adj mean adjective
- Adv means adverb
- DO means direct object
- IO means indirect object
Components of a Sentence
Clearly written, complete sentences require key information: a subject, a verb and a complete idea. A sentence needs to make sense on its own. Sometimes, complete sentences are also called independent clauses. A clause is a group of words that may make up a sentence. An independent clause is a group of words that may stand alone as a complete, grammatically correct thought. The following sentences show independent clauses in curly brackets:
All complete sentences have at least one independent clause. You can identify an independent clause by reading it on its own and looking for the subject and the verb.
Subjects
When you read a sentence, you may first look for the subject, or what the sentence is about. The subject usually appears at the beginning of a sentence as a noun or a pronoun. A noun is a word that identifies a person, place, thing, or idea. A pronoun is a word that replaces a noun. Common pronouns are I, he, she, it, you, they, and we.
In these sentences, the subject is a person: Malik. The pronoun He replaces and refers back to Malik.
In the first sentence, the subject is a place: computer lab. In the second sentence, the pronoun It substitutes for computer lab as the subject.
In the first sentence, the subject is a thing: project. In the second sentence, the pronoun It stands in for the project.
Compound Subjects
A sentence may have more than one person, place, or thing as the subject. These subjects are called compound subjects. Compound subjects are useful when you want to discuss several subjects at once.
Prepositional Phrases
You will often read a sentence that has more than one noun or pronoun in it. You may encounter a group of words that includes a preposition with a noun or a pronoun. Prepositions connect a noun, pronoun, or verb to another word that describes or modifies that noun, pronoun, or verb. Common prepositions include in, on, under, near, by, with, and about. A group of words that begin with a preposition is called a prepositional phrase. A prepositional phrase begins with a preposition and modifies or describes a word. It cannot act as the subject of a sentence. The following phrases inside curly brackets are examples of prepositional phrases.
Exercise
Read the following sentences. Underline the subjects, and circle the prepositional phrases.
- The gym is open until nine o’clock tonight.
- We went to the store to get some ice.
- The student with the most extra credit will win a homework pass.
- Maya and Tia found an abandoned cat by the side of the road.
- The driver of that pickup truck skidded on the ice.
- Anita won the race with time to spare.
- The people who work for that company were surprised about the merger.
- Working in haste means that you are more likely to make mistakes.
- The soundtrack has over sixty songs in languages from around the world.
- His latest invention does not work, but it has inspired the rest of us.
Verbs
Once you locate the subject of a sentence, you can move on to the next part of a complete sentence: the verb. A verb is often an action word that shows what the subject is doing. A verb can also link the subject to a describing word. There are three types of verbs that you can use in a sentence: action verbs, linking verbs, or helping verbs.
Action Verbs
A verb that connects the subject to an action is called an action verb. An action verb answers the question what is the subject doing? In the following sentences, the action verbs are in bold.
The dog barked at the jogger.
He gave a short speech before we ate.
Barked and gave are action verbs.
Linking Verbs
A verb can often connect the subject of the sentence to a describing word. This type of verb is called a linking verb because it links the subject to a describing word. In the following sentences, the linking verbs are in bold.
The coat was old and dirty.
The clock seemed broken.
Was and seemed are linking verbs.
If you have trouble telling the difference between action verbs and linking verbs, remember that an action verb shows that the subject is doing something, whereas a linking verb simply connects the subject to another word that describes or modifies the subject. A few verbs can be used as either action verbs or linking verbs.
Action verb: The boy looked for his glove.
Linking verb: The boy looked tired.
Although both sentences use the same verb looked, the two sentences have completely different meanings. In the first sentence, the verb describes the boy’s action. In the second sentence, the verb describes the boy’s appearance.
Helping Verbs
A third type of verb you may use as you write is a helping verb. Helping verbs are verbs that are used with the main verb to describe a mood or tense. Helping verbs are usually a form of be, do, or have. The word can is also used as a helping verb.
Is is the helping verb. Known is the main verb.
Does is the helping verb. Speak up is the main verb.
Have is the helping verb. Seen is the main verb.
Can is the helping verb. Tell is the main verb.
Whenever you write or edit sentences, keep the subject and verb in mind. As you write, ask yourself these questions to keep yourself on track:
- Subject: Who or what is the sentence about?
- Verb: Which word shows an action or links the subject to a description?
Exercise
Copy each sentence onto your own sheet of paper and circle the verb(s). Name the type of verb(s) used in the sentence in the space provided (LV, HV, or V).
- The cat sounds ready to come back inside. ________
- We have not eaten dinner yet. ________
- It took four people to move the broken-down car. ________
- The book was filled with notes from class. ________
- We walked from room to room, inspecting for damages. ________
- Harold was expecting a package in the mail. ________
- The clothes still felt damp even though they had been through the dryer twice. ________
- The teacher who runs the studio is often praised for his restoration work on old masterpieces. ________
Sentence Structure, Including Fragments and Run-ons
Now that you know what makes a complete sentence—a subject and a verb—you can use other parts of speech to build on this basic structure. Good writers use a variety of sentence structures to make their work more interesting. This section covers different sentence structures that you can use to make longer, more complex sentences.
Sentence Patterns
Six basic subject-verb patterns can enhance your writing. A sample sentence is provided for each pattern. As you read each sentence, take note of where each part of the sentence falls. Notice that some sentence patterns use action verbs and others use linking verbs.
Subject – Verb
Subject – Linking Verb – Noun
Subject – Linking Verb – Adjective
Subject – Verb – Adverb
Subject – Verb – Direct Object
When you write a sentence with a direct object (DO), make sure that the DO receives the action of the verb.
Subject – Verb – Indirect Object – Direct Object
In this sentence structure, an indirect object explains to whom or to what the action is being done. The indirect object is a noun or pronoun, and it comes before the direct object in a sentence.
My coworker is the subject. Gave is the verb. Me is the indirect object. Reports is the direct object.
Exercise
- Use what you have learned so far to bring variety in your writing. Write six sentences that practice each basic sentence pattern. When you have finished, label each part of the sentence (S, V, LV, N, Adj, Adv, DO, IO).
- Find an article in a newspaper, a magazine, or online that interests you. Bring it to class or post it online. Then, looking at a classmate’s article, identify one example of each part of a sentence (S, V, LV, N, Adj, Adv, DO, IO). Please share or post your results.
Fragments
The sentences you have encountered so far have been independent clauses. As you look more closely at your past writing assignments, you may notice that some of your sentences are not complete. A sentence that is missing a subject or a verb is called a fragment. A fragment may include a description or may express part of an idea, but it does not express a complete thought.
Fragment: Children helping in the kitchen.
Complete sentence: Children helping in the kitchen often make a mess.
You can easily fix a fragment by adding the missing subject or verb. In the example, the sentence was missing a verb. Adding often make a mess creates an subject-verb-noun sentence structure.
See whether you can identify what is missing in the following fragments.
Fragment: Told her about the broken vase.
Complete sentence: I told her about the broken vase.
Fragment: The store down on Main Street.
Complete sentence: The store down on Main Street sells music.
Common Sentence Errors
Fragments often occur because of some common error, such as starting a sentence with a preposition, a dependent word, an infinitive or a gerund. If you use the six basic sentence patterns when you write, you should be able to avoid these errors and thus avoid writing fragments.
When you see a preposition, check to see that it is part of a sentence containing a subject and a verb. If it is not connected to a complete sentence, it is a fragment, and you will need to fix this type of fragment by combining it with another sentence. You can add the prepositional phrase to the end of the sentence. If you add it to the beginning of the other sentence, insert a comma after the prepositional phrase.
Example A:
Incorrect: After walking over two miles. John remembered his wallet.
Correct: After walking over two miles, John remembered his wallet.
Correct: John remembered his wallet after walking over two miles.
Example B
Incorrect: The dog growled at the vacuum cleaner. When it was switched on.
Correct: When the vacuum cleaner was switched on, the dog growled.
Correct: The dog growled at the vacuum cleaner when it was switched on.
Clauses that start with a dependent word—such as since, because, without, or unless—are similar to prepositional phrases. Like prepositional phrases, these clauses can be fragments if they are not connected to an independent clause containing a subject and a verb. To fix the problem, you can add such a fragment to the beginning or end of a sentence. If the fragment is added at the beginning of a sentence, add a comma.
Incorrect: Because we lost power. The entire family overslept.
Correct: Because we lost power, the entire family overslept.
Correct: The entire family overslept because we lost power.
Incorrect: He has been seeing a physical therapist. Since his accident.
Correct: Since his accident, he has been seeing a physical therapist.
Correct: He has been seeing a physical therapist since his accident.
When you encounter a word ending in -ing in a sentence, identify whether or not this word is used as a verb in the sentence. You may also look for a helping verb. If the word is not used as a verb or if no helping verb is used with the -ing verb form, the verb is being used as a noun. An -ing verb form used as a noun is called a gerund.
Verb: I was working on homework until midnight.
Noun: Working until midnight makes me tired the next morning.
Once you know whether the -ing word is acting as a noun or a verb, look at the rest of the sentence. Does the entire sentence make sense on its own? If not, what you are looking at is a fragment. You will need to either add the parts of speech that are missing or combine the fragment with a nearby sentence.
Incorrect: Taking deep breaths. Saul prepared for his presentation.
Correct: Taking deep breaths, Saul prepared for his presentation.
Correct: Saul prepared for his presentation. He was taking deep breaths.
Incorrect: Congratulating the entire team. Sarah raised her glass to toast their success.
Correct: She was congratulating the entire team. Sarah raised her glass to toast their success.
Correct: Congratulating the entire team, Sarah raised her glass to toast their success.
Another error in sentence construction is a fragment that begins with an infinitive. An infinitive is a verb paired with the word to; for example, to run, to write, or to reach. Although infinitives are verbs, they can be used as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs. You can correct a fragment that begins with an infinitive by either combining it with another sentence or adding the parts of speech that are missing.
Incorrect: We needed to make three hundred more paper cranes. To reach the one thousand mark.
Correct: We needed to make three hundred more paper cranes to reach the one thousand mark.
Correct: We needed to make three hundred more paper cranes. We wanted to reach the one thousand mark.
Exercise
Copy the following sentences and identify the fragments. Then combine the fragment with the independent clause to create a complete sentence.
- Working without taking a break. We try to get as much work done as we can in an hour.
- I needed to bring work home. In order to meet the deadline.
- Unless the ground thaws before spring break. We won’t be planting any tulips this year.
- Turning the lights off after they were done in the kitchen. Kris tries to conserve energy whenever possible.
- You’ll find what you need if you look. On the shelf next to the potted plant.
- To find the perfect apartment. Deidre scoured the classifieds each day.
Run-on Sentences
Just as short, incomplete sentences can be problematic, lengthy sentences can be problematic too. Sentences with two or more independent clauses that have been incorrectly combined are known as run-on sentences. A run-on sentence may be either a fused sentence or a comma splice.
Fused sentence: A family of foxes lived under our shed young foxes played all over the yard.
Comma splice: We looked outside, the kids were hopping on the trampoline.
When two complete sentences are combined into one without any punctuation, the result is a fused sentence. When two complete sentences are joined by a comma, the result is a comma splice. Both errors can easily be fixed.
Punctuation
One way to correct run-on sentences is to correct the punctuation. For example, adding a period will correct the run-on by creating two separate sentences.
Run-on: There were no seats left, we had to stand in the back.
Correct: There were no seats left. We had to stand in the back.
Using a semicolon between the two complete sentences will also correct the error. A semicolon allows you to keep the two closely related ideas together in one sentence. When you punctuate with a semicolon, make sure that both parts of the sentence are independent clauses.
Run-on: The accident closed both lanes of traffic we waited an hour for the wreckage to be cleared.
Complete sentence: The accident closed both lanes of traffic; we waited an hour for the wreckage to be cleared.
When you use a semicolon to separate two independent clauses, you may wish to add a transition word to show the connection between the two thoughts. After the semicolon, add the transition word and follow it with a comma.
Run-on: The project was put on hold we didn’t have time to slow down, so we kept working.
Complete sentence: The project was put on hold; however, we didn’t have time to slow down, so we kept working.
Coordinating Conjunctions
You can also fix run-on sentences by adding a comma and a coordinating conjunction. A coordinating conjunction acts as a link between two independent clauses. Common coordinating conjunctions are for, and, nor, but, or, yet, and so.
These are the seven coordinating conjunctions that you can use: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, and so. Use these words appropriately when you want to link the two independent clauses. The acronym FANBOYS will help you remember this group of coordinating conjunctions.
Run-on: The new printer was installed, no one knew how to use it.
Complete sentence: The new printer was installed, but no one knew how to use it.
Dependent Words
Adding dependent words is another way to link independent clauses. Like the coordinating conjunctions, dependent words show a relationship between two independent clauses.
Run-on: We took the elevator, the others still got there before us.
Complete sentence: Although we took the elevator, the others got there before us.
Run-on: Cobwebs covered the furniture, the room hadn’t been used in years.
Complete sentence: Cobwebs covered the furniture because the room hadn’t been used in years.
Image Descriptions
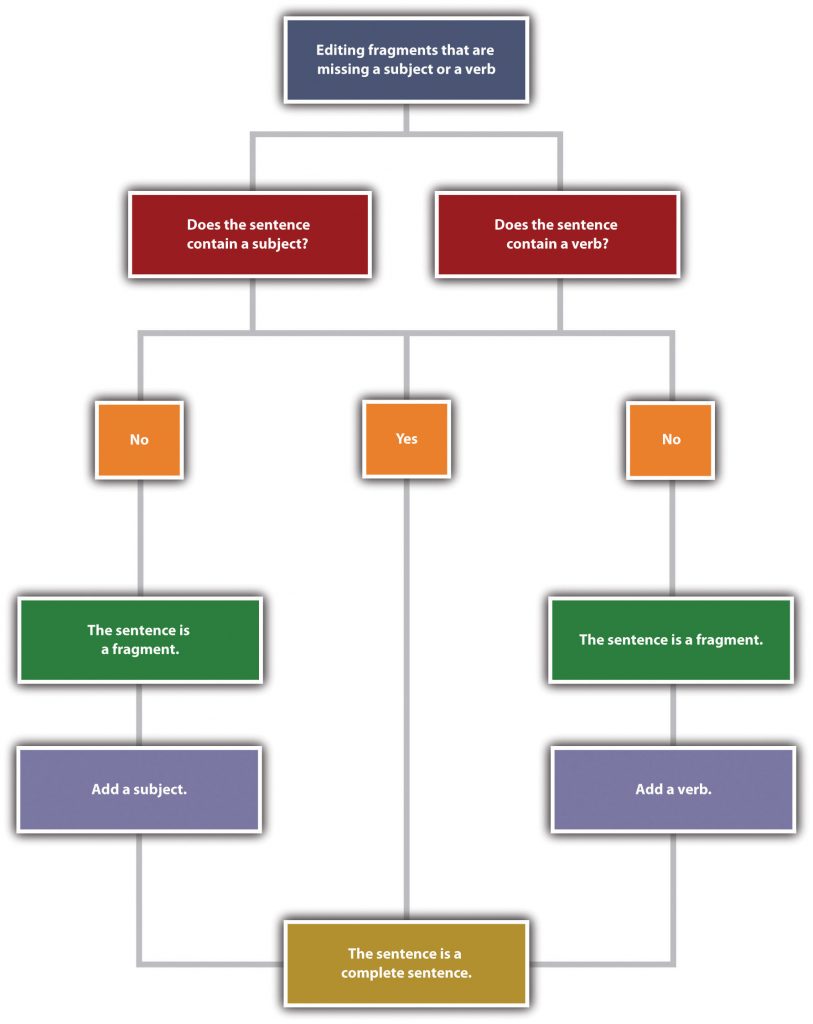
A decision tree for editing sentence fragments that are missing a subject or a verb:
- Does the sentence contain a subject?
- If yes, go to #2.
- If no, the sentence is a fragment. Add a subject to make it a complete sentence. Then go to #2.
- Does the sentence contain a verb?
- If yes, the sentence is a complete sentence.
- If no, the sentence is a fragment. Add a verb to make it a complete sentence.
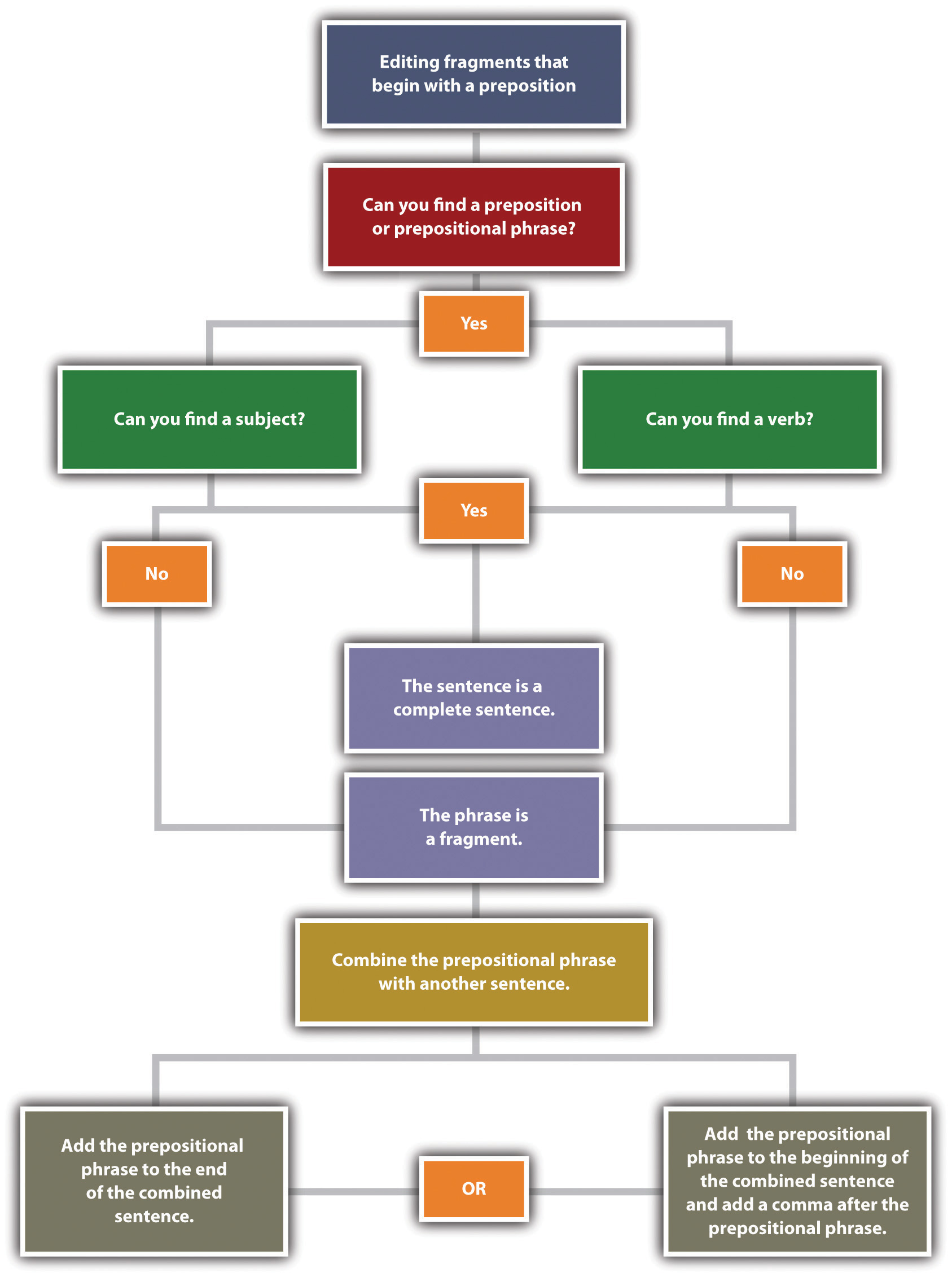
A decision tree for editing fragments that begin with a preposition:
- Can you find a preposition or prepositional phrase?
- Can you find a subject?
- If yes, go to #3.
- If no, go to #4.
- Can you find a verb?
- If yes, the sentence is a complete sentence.
- If no, go to #4.
- The phrase is a fragment. Combine the prepositional phrase with another sentence. Add the prepositional phrase to the end of the combined sentence or add the prepositional phrase to the beginning of the combined sentence and add a comma after the prepositional phrase.
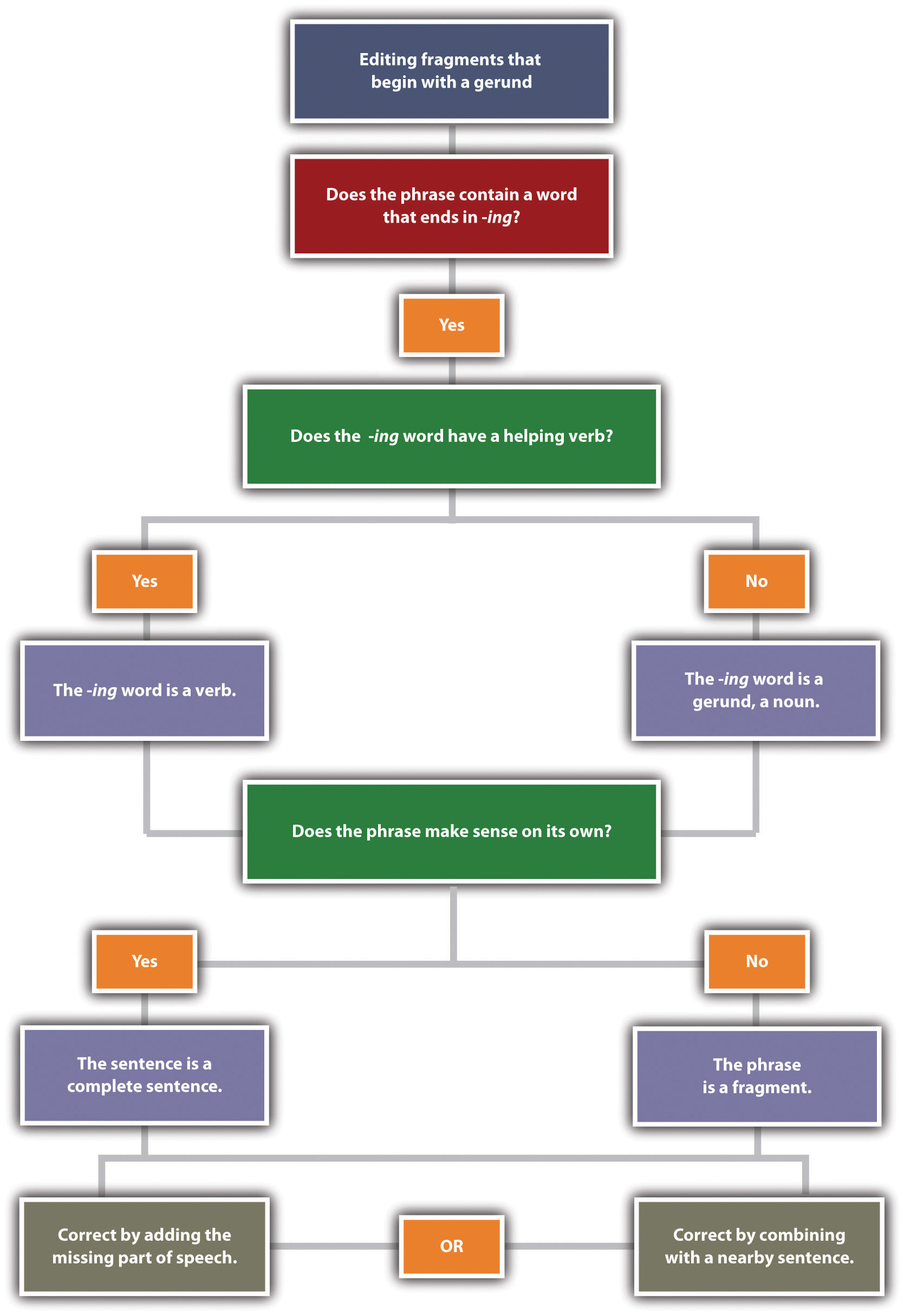
A decision tree for editing fragments that begin with a gerund:
- Does the phrase contain a word that ends in -ing?
- Does the -ing word have a helping verb?
- If yes, the -ing word is a verb. Go to
- If no, the -ing word is a gerund, a noun.
- Does the phrase make sense on its own?
- If yes, the sentence is a complete sentence.
- If no, go to #4.
- The phrase is a fragment. Correct by adding the missing part of speech or correct by combining with a nearby sentence.
Text Attributions
- This chapter was adapted from “Sentence Writing” in Writing for Success by a publisher who has requested that they and the original author not receive attribution (and republished by University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing), which is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 Licence. Adapted by Allison Kilgannon.
Media Attributions
- Editing Fragments by The Saylor Foundation is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 Licence.
- Editing Fragments that Begin with a Preposition by The Saylor Foundation is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 Licence.
- Editing Fragments That Begin with Gerunds by The Saylor Foundation is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 Licence.

