Chapter 1 – Back to the Basics
1.2 Trichology – The Science of Hair
When you are colouring hair, why must you consider the hair itself?
The Hair Strand
Each hair strand is made up of 3 layers:
- Cuticle – the outer covering made up of overlapping layers of scales. How these scales sit directly affects it’s porosity, which determines how the hair will absorb moisture and chemicals.
- Cortex – the second layer, gives hair its strength and elasticity and also houses melanin, which is the basis of natural hair colour.
- Medulla – The inner core, or pith, of the hair strand gives hair its structure and is often missing from very fine hair.
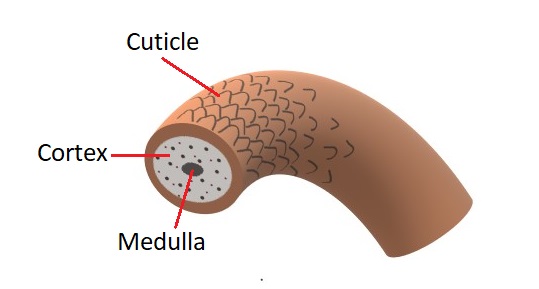
These various structural properties of the hair itself, as well as the hair’s natural melanin, will have a direct influence on the end result of a colouring service.
Melanin
Firstly, let’s revisit melanin. What is it, and why is it important?
There are two types of melanin that reside within the cortex of the hair strand:
- Eumelanin – black or brown pigment
- Pheomelanin – red or yellow pigment
Varying combination, concentration, and size of these two pigments produce every natural hair colour that exists. For example:
A heavy concentration of eumelanin, with a sprinkling of pheomelanin, results in dark brown or black hair:

A light concentration of eumelanin, with a sprinkling of pheomelanin, results in light brown or blonde hair.

A heavy concentration of pheomelanin, with a good amount eumelanin, results in a deep Auburn red shade of hair.
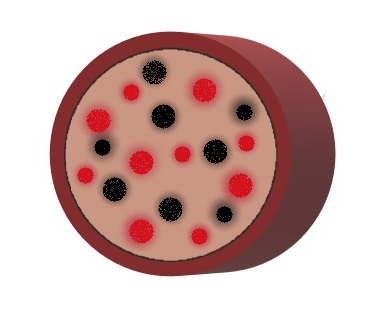
When hair is lifted with an oxidative colour or bleach, eumelanin is more easily obliterated than pheomelanin. This becomes more apparent when you look at the underlying pigments at each of the ten levels:

Notice how the underlying pigments range from dark red to palest yellow. This is because pheomelanin is tougher to remove, so when a client tells you that their hair “lifts warm,” you can assure them that that is the case for everyone!
When hair is coloured, the underlying pigment will affect the formula based on whether you want to neutralize or enhance these warm pigments. For example, does the client desire a cool chocolate brown hair colour or a more golden-brown hue? You will then use the colour wheel to create an appropriate formula.
When going darker with a low-level developer, the underlying pigment will not be exposed, but you still must consider the existing tone of the client’s hair when formulating for the desired result.
Hair Condition
When consulting with a client, you must also assess the condition of the hair. There are three main characteristics to look at: Porosity, elasticity, and texture. All three physical factors will influence which products to choose and how to process the colour.
Porosity
Porosity refers to the hair’s ability to absorb moisture or chemicals. Porosity is influenced by how the cuticle scales sit in relation to each other.
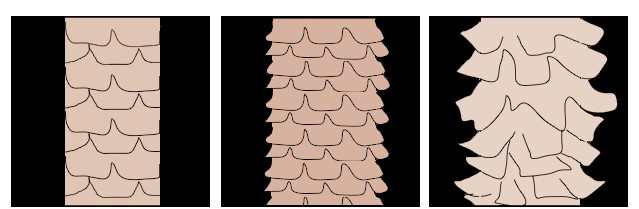 Resistant Porosity Average Porosity Extreme Porosity
Resistant Porosity Average Porosity Extreme Porosity
Elasticity
Elasticity is the hair’s ability to stretch and return to its original shape without snapping.
Texture
Texture refers to the diameter of the hair strand and is generally described as fine, medium, and coarse.
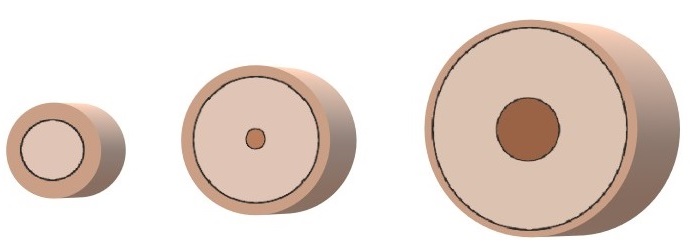
Fine Medium Coarse
With these basics fresh in your mind, let’s move on to how the various colouring products work, and how to decide which product is best for the client.
Media Attributions
- All images in this chapter are by A. Magtiza and are under a CC BY 4.0 Licence.
The outer layer of a hair strand made up of overlapping scales.
The second layer of a hair strand, which provides hair with its strength and elasticity.
The inner core of a hair strand, which gives hair its structure. Often missing from very fine hair.
Pigment that resides in the hair's cortex which gives hair its hue.
Any pigments that are exposed as hair is lightened through the 10 levels of lift.
The hair's ability to absorb moisture or chemicals.
The hair's ability to stretch and return to its original shape without snapping.
The diameter of the hair strand. Texture can be described as fine, medium, or coarse.
Hair that does not readily absorb moisture or chemical products. Cuticle scales are tightly packed and smooth.
Hair absorbs moisture and chemical products at a common rate. Cuticle scales are intact and slightly raised.
Hair readily absorbs moisture and chemical products. Cuticle scales are lifted and/or damaged.

