2.5 Routine Practices and Personal Protective Equipment
Routine Practices
Routine practices are the infection prevention and control (IPC) practices to use in the routine care of all clients at all times in all health care settings and are determined by the circumstances of the client, the environment, and the care activity to be performed. This is often referred to medical asepsis or clean technique, used to describe measures for reducing and preventing the spread of organisms (Perry, Potter & Ostendorf, 2014).
Routine practices include:
- Point-of-care-risk assessment
- Hand hygiene program (including point-of-care ABHR)
- Source control (triage, early diagnosis and treatment, respiratory hygiene, spatial separation)
- Client placement, accommodation, and flow
- Aseptic technique
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Sharps safety and prevention of bloodborne pathogen transmission
- Management of the client care environment:
- Cleaning of the client care environment
- Cleaning and disinfection of non-critical client care equipment
- Handling of waste and linen
The routine precautions taken to prevent transmission of infectious microorganisms are used in the care of all persons.
Routine practices apply to all clients. They prevent the spread of infection from:
- Blood
- All body fluids, secretions and excretions (except sweat)
- Non-intact skin (skin with open breaks)
- Mucous membranes
Routine Practices Overview
Wash hands
- Before handling client
- After contact with blood and/or bodily fluids or any contaminated items
- After gloves are removed
Wear gloves
- When your hands are likely to come in contact with blood and/or bodily fluids and contaminate items
- For contact with mucous membranes and non-intake skin
- Remove gloves between clients
Client care equipment
- Handle client care equipment with care to prevent contaminating the environment (there maybe unknown sources of blood or bodily fluids)
Linen
- Place used and contaminated linen directly into the linen hamper
- Do not put used linen on the floor (spreads germs beyond the client’s environment)
- Keep dirty linen away from your body
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)

Following routine practices and additional precautions involves the use of PPE personal protective equipment and requires health care providers to wear gloves, gowns, and eye protection. Each agency/facility will have a policy and procedures for when and what types of PPE the health care staff should use. Donning (putting on) and doffing (taking off) requires the provider to follow the proper order of putting on and taking of the PPE to ensure infection control. Figures 2.5.2 and 2.5.3 offer you the correct procedures for donning and doffing PPE.
While it is important to use personal protective equipment when it is appropriate, it is equally important to know how to remove your PPE!
If you walk around the facility wearing any PPE (like gloves), you will spread germs.

The following videos presented by the Provincial Infection Control Network of British Columbia (PICNET) demonstrate the techniques for Donning and Doffing PPE.
PPE Donning for Medical Mask by LearningHub (2022) on YouTube
PPE Doffing for Medical Mask by LearningHub (2022) on YouTube
Image descriptions
Figure 2.5.2 Putting on (Donning) Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
An infographic by Alberta Health Services describing 5 steps of putting on or donning personal protective equipment:
- Hand Hygiene
- Using an alcohol-based hand rub is the preferred way to clean your hands.
- If your hands look or feel dirty, soap and water must be used to wash your hands.
- Gown
- Make sure the gown covers from neck to knees to wrist.
- Tie at the back of neck and waist.
- Procedure/Surgical mask and N95 respirator
- Procedure/Surgical mask
- Secure the ties or elastic around your head so the mask stays in place.
- Fit the moldable band to the nose bridge. Fit snugly to your face and below chin.
- N95 respirator. There are different styles of N95 respirators. They include: molded cup, flat-fold, and v-fold.
- Hold the N95 respirator in your hand.
- Position the N95 respirator under your chin with the nose piece up. Secure both of the elastic bands around your head so the N95 respirator stays in place.
- Use both hands to mold the metal band of the N95 respirator around the bridge of your nose.
- Seal check: Place both hands completely over the respirator, being careful not to disturb the position, and exhale sharply.
- Procedure/Surgical mask
- Eye protection or face shields
- Place over the eyes (or face).
- Adjust to fit.
- Gloves
- Pull the cuffs of the gloves over the cuffs of the gown.
[Back to Figure 2.5.2]
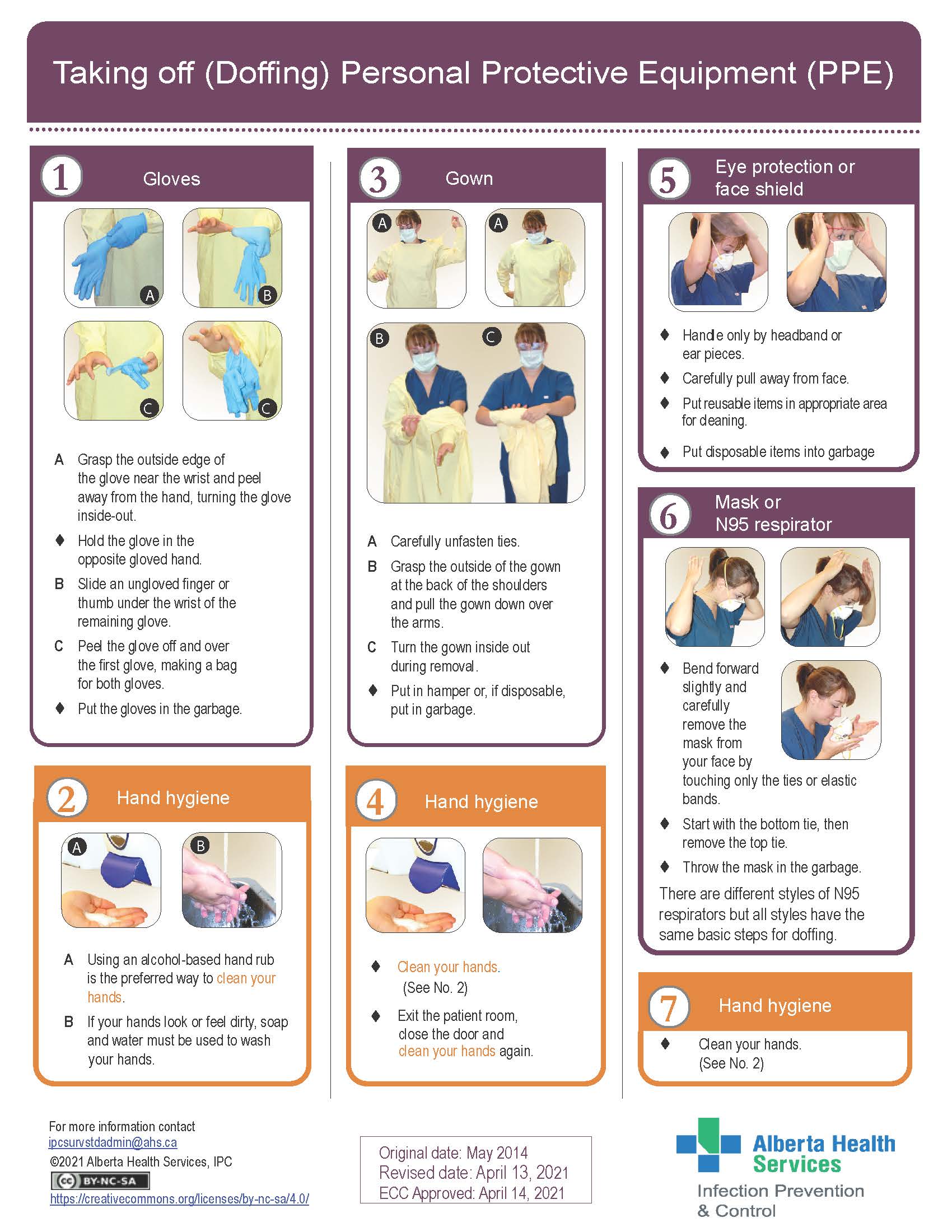
Figure 2.5.3 Taking off (Doffing) Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
An infographic by Alberta Health Services describing 7 steps of taking off or doffing personal protective equipment:
- Remove Gloves
- Grasp the outside edge of the glove near the wrist and peel away from the hand, turning the glove inside-out.
- Hold the glove in the opposite gloved hand.
- Slide an ungloved finger or thumb under the wrist of the remaining glove.
- Peel the glove off and over the first glove, making a bag for both gloves.
- Put the gloves in the garbage.
- Grasp the outside edge of the glove near the wrist and peel away from the hand, turning the glove inside-out.
- Hand hygiene
- Using an alcohol-based hand rub is the preferred way to clean your hands.
- If your hands look or feel dirty, soap and water must be used to wash your hands.
- Gown
- Carefully unfasten ties.
- Grasp the outside of the gown at the back of the shoulders and pull the gown down over the arms.
- Turn the gown inside out during removal.
- Put in hamper or, if disposable, put in garbage.
- Hand hygiene
- Clean your hands. (See No. 2)
- Exit the patient room, close the door and clean your hands again.
- Eye protection or face shield
- Handle only by headband or ear pieces.
- Carefully pull away from face.
- Put reusable items in appropriate area
for cleaning. - Put disposable items into garbage
- Mask or N95 Respirator. There are different styles of N95 respirators but all styles have the same basic steps for doffing.
- Bend forward slightly and carefully remove the mask from your face by touching only the ties or elastic bands.
- Start with the bottom tie, then remove the top tie.
- Throw the mask in the garbage
- Hand hygiene.
- Clean your hands. (See No. 2)
[Back to Figure 2.5.3]
A system of prevention and control practices recommended by the Public Agency of Canada to be used for all patients/residents/clients during all care to prevent and control all transmission of microorganisms in all health care settings.
Part of routine practice should be conducted by a health care provider before every client interaction to assess the likelihood of exposing themselves and others to infectious agents. This assessment informs the selection of appropriate actions and additional personal protective equipment to minimize the risk of exposure to infection.
Clothing or equipment worn to protect against hazards.

