Unit 5. Electronic communication
Topic B: Email
Click play on the following audio player to listen along as you read this section.
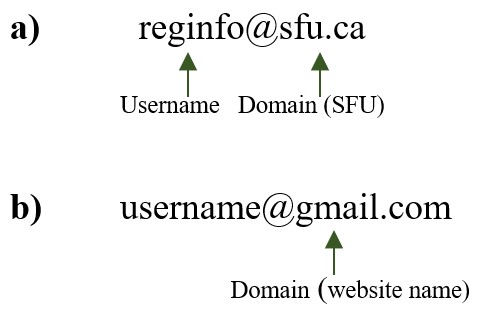
Email Address
An email address consists of three parts:
- Username of the recipient.
- @ sign (pronounced “at” sign) – every email address consists of an @ sign.
- Domain (the email service provider – an organization/company, or a website name).
Some popular free email service providers include
- Gmail (username@gmail.com)
- Outlook (username@outlook.com)
- Yahoo! Mail (username@yahoo.com)
- ProtonMail (username@protonmail.com)
- Zoho (username@zoho.com)
- AOL (username@aol.com)
Create an Email Account
This is how you can create a Gmail account.
- On your computer, open a browser window and go to Gmail.
![]()
- Click Create an account (top right of screen).

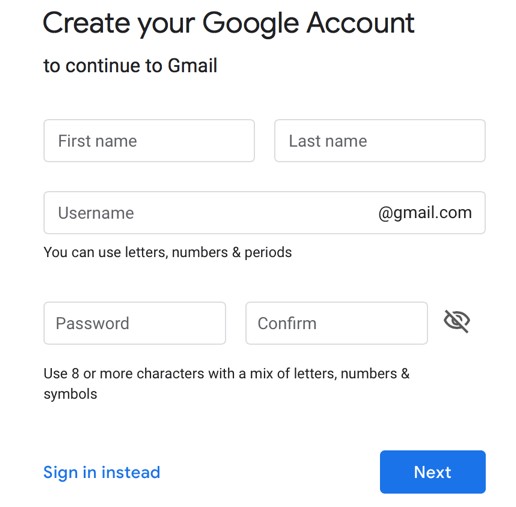
- Enter your first name, late name, username, and password (twice). Click Next.
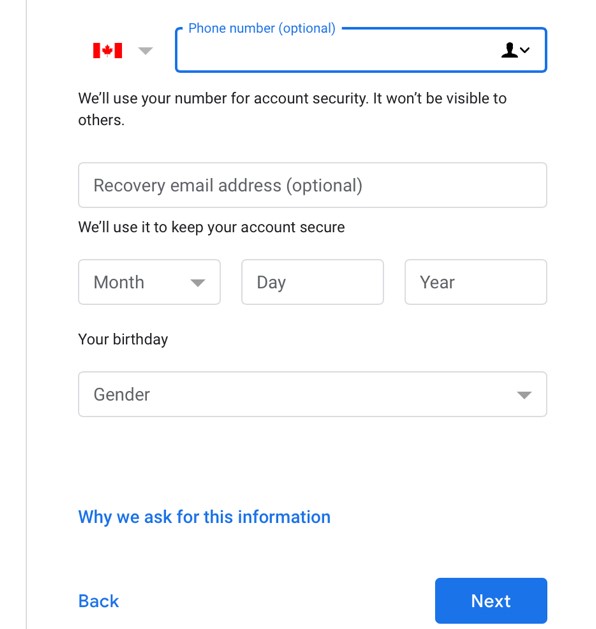
- Provide the additional information, including your birthday and gender. Click Next.
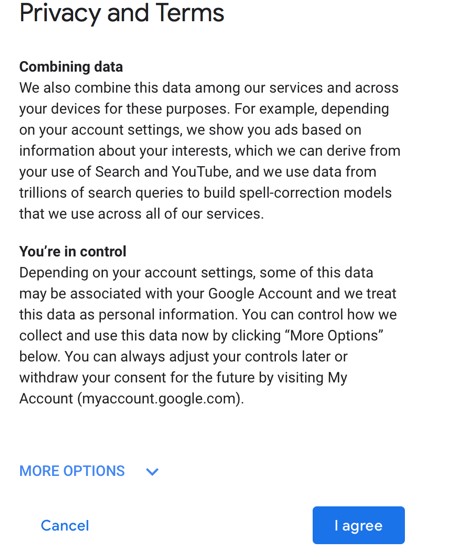
- Scroll down and click I agree.
Your account will be created and ready to send and receive emails.
Send and Receive Email
How to send an email
- Log into your personal email account (such as Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo! Mail, etc.) or log into your institutional email (many colleges and universities give students an email address).
- Click Compose (if using Gmail) or something similar. (For example, in Outlook, click New.)
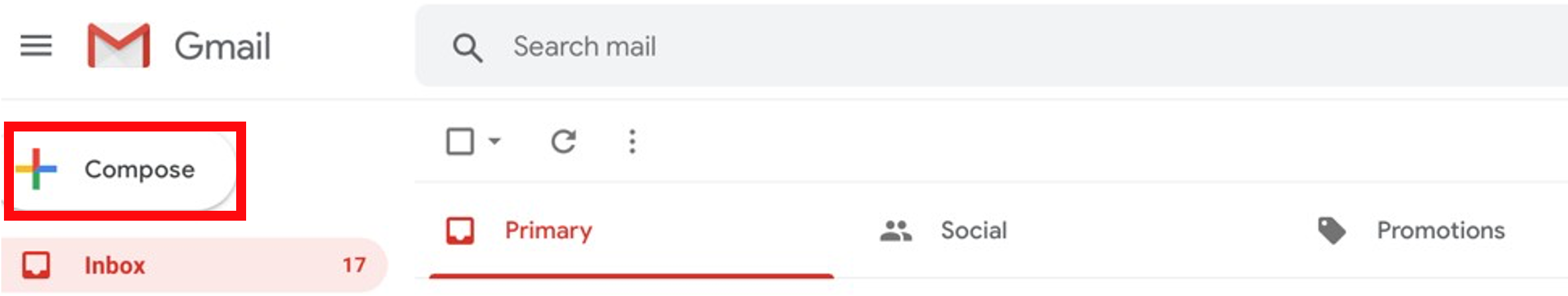
- Enter a recipient’s email address in the To field. You can also add recipients in the Cc and Bcc fields.
- Enter a subject (the topic or heading of your email).
- Type your message in the main body field.
- Click Send.
Cc and Bcc
- Cc (carbon or courtesy copy) – Entering a person’s email address in the “Cc” field means that person will receive a copy of the email (for their information).
- Bcc (blind carbon copy) – Bcc is similar to that of Cc except that the email address is invisible to the people in the “To” or “Cc” fields. Use Bcc if you don’t want the other people to see who else has received a copy of the email.
Send Emails with Attachments
You can attach different types of files to send through email, including PDFs, images, and more. This is how you attach a file to an email:
- Log in to your email account.
- Click Compose (Gmail) or something similar (e.g., New in Outlook).
- Enter a recipient’s email address in the To field.
- Enter a subject.
- Type your message in the main body field.
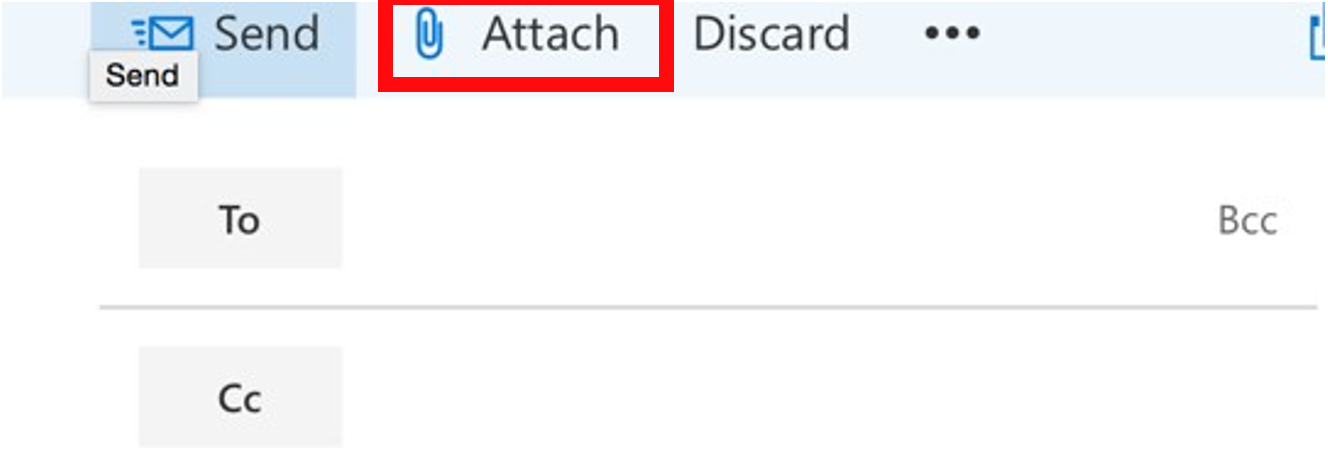
- Click Attach or something similar. (Note that the Attach option is often represented as a paperclip icon).

- Select the file you want to attach from your computer’s folder.
- Click the Choose or Select button (or another similar button) to attach the file to your email.
- Click Send.
Mail System Folders
- Inbox folder – the place where incoming emails are received and stored (incoming emails arrive in “Inbox” folder).
- Sent Items (or Sent) folder – the email you’ve sent will be saved in the “Sent Items” (or “Sent Mail”) folder.
- Drafts folder – an unfinished email will be automatically saved to your “Drafts” folder.
- Deleted Items folder: every email that you deleted will be moved to the “Deleted Items” folder.
- It’s a good idea to empty your “Deleted Items” folder from time to time in order to save space.
- To empty the Deleted Items folder: Right-click the Deleted Items folder and click Empty folder, then Ok.
entering a person's email address in the “Cc” field means that person will receive a copy of the email (for their information).
Bcc is similar to that of Cc except that the email address is invisible to the people in the “To” or “Cc” fields. Use Bcc if you don't want the other people to see who else has received a copy of the email.
an email folder where incoming emails are received and stored.
an email folder that saves copies of emails that you have sent.
an email folder that automatically saves unfinished emails.
an email folder that saves all emails that have been deleted.

