Unit 6. Basic computer terminologies
Topic C: Basic computer terminologies and acronyms
Click play on the following audio player to listen along as you read this section.
Basic Internet Terms and Acronyms
Internet – A globally connected massive computer network system.
World Wide Web (WWW or the web) – A system of Internet servers that is made from millions of interlinked websites and web pages.
Firewall – A network security device designed to prevent unauthorized access to or from a network.
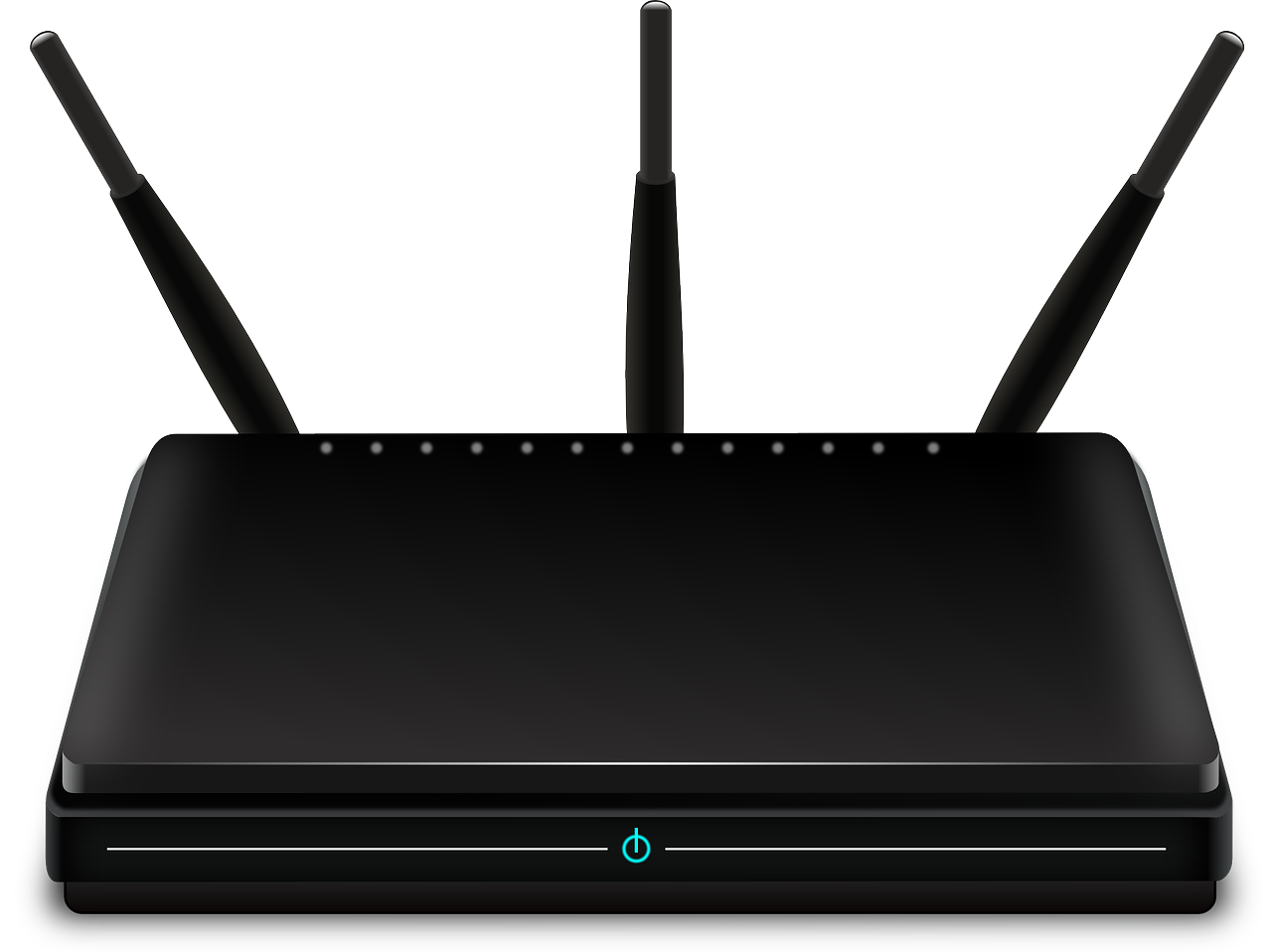
Router – A device that transfers data between computer networks to provide access to the Internet.
ISP (Internet Service Provider) – A company that provides Internet service to customers.
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) – A set of rules (a protocol) for transferring and accessing data using the web.
URL (Uniform Resource Locator) – A web address of a specific web page or file on the Internet. An example is https://www.princegeorgecitizen.com.
IP (Internet Protocol) – A set of rules (a protocol) for sending data from one computer to another on the Internet. Each computer has a unique IP address that distinguishes it from all other computers on the Internet.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) – A set of rules (a protocol) for transferring files between computers over the Internet.
Cookie – A small text file stored in a user’s computer by a website that the user has visited so that it can remember something about the user at a later time. For example, cookies are used for online shopping. Without cookies, login information would have to be entered before every product was added to the shopping cart.
Link (hyperlink) – A word, phrase, image, etc., within a file or web page that a user can click on to jump to another document, section of the same document, or web page.
Basic Computer Terms and Acronyms
PC (Personal Computer) – a small computer designed for use by a single user at a time.
Mac (Macintosh) – a type of personal computer made by Apple Inc. It runs a version of the macOS (Apple’s operating system, pronounced “mack-oh-ess”).

OS (Operating System) – a powerful program that controls and coordinates a computer’s hardware devices and runs software and applications. Examples includes Windows, Android, OS X, and Linux.
Reboot – to shut down and restart a computer, allowing its operating system and programs to be reloaded.
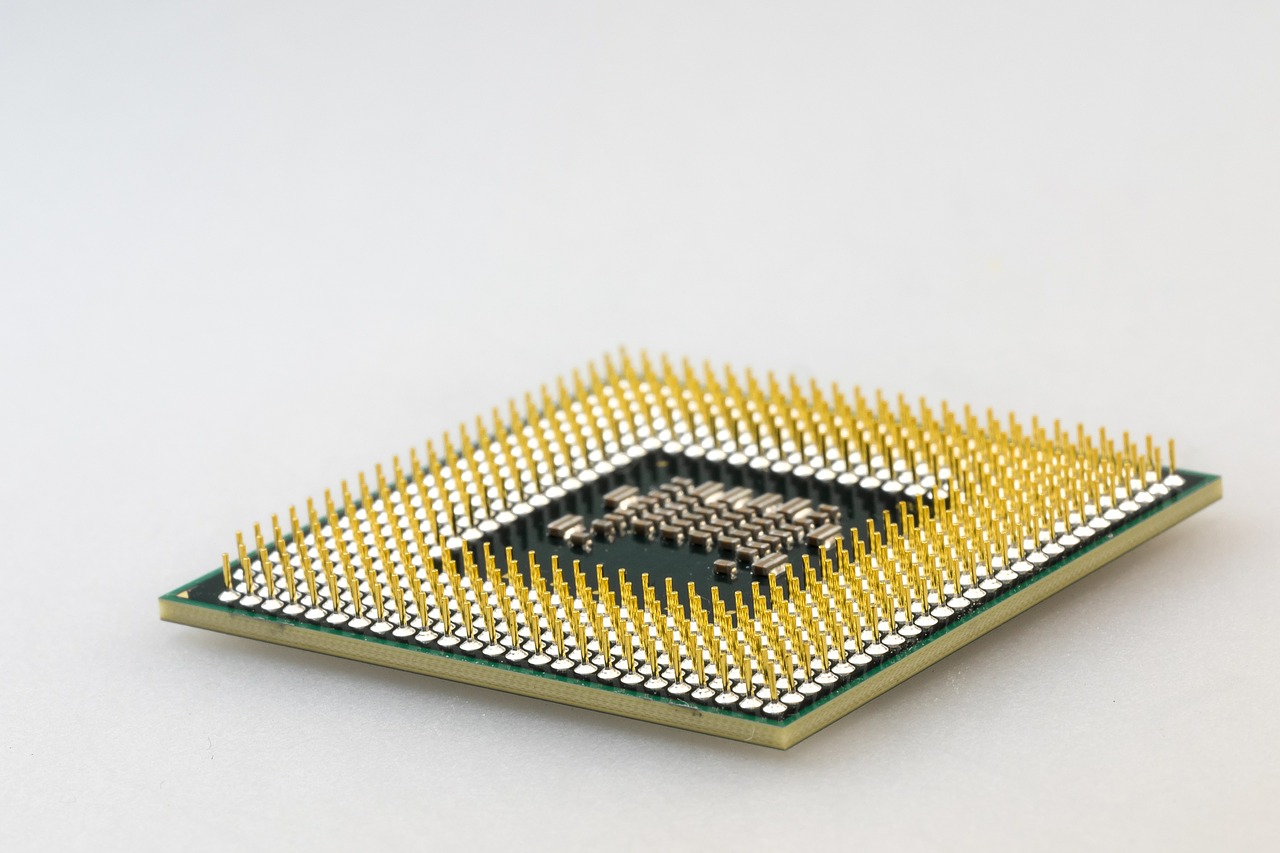
CPU (Central Processing Unit) – the brain or engine of a computer, where most of the processing and operations take place.
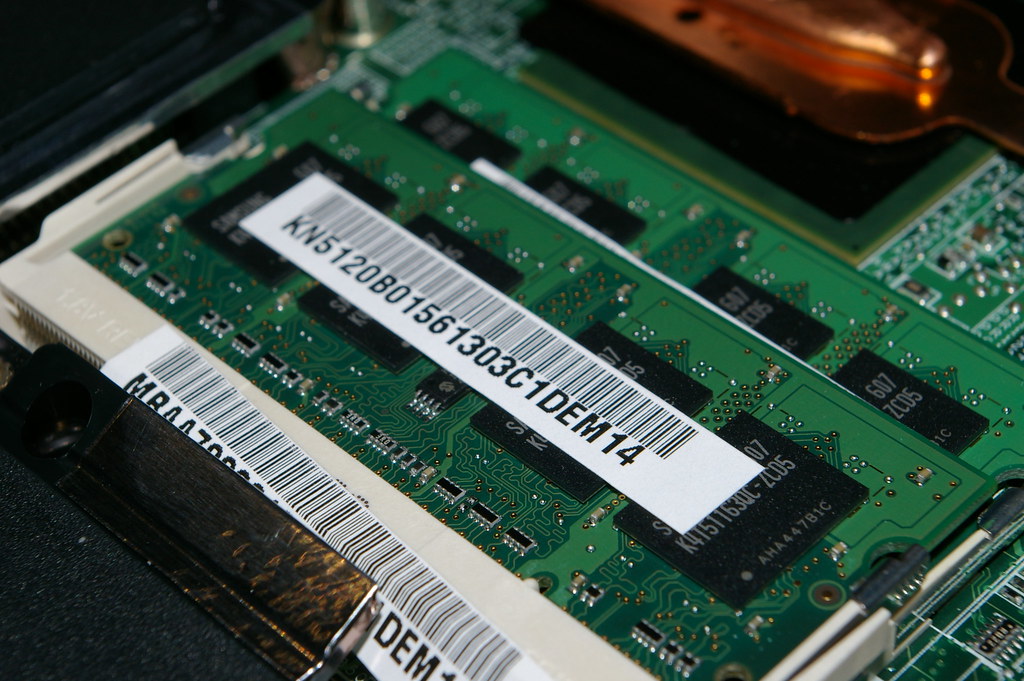
RAM (Random-Access Memory) – a type of data storage (memory element) used in computers that temporarily stores programs and data. RAM is a kind of volatile memory, meaning its contents are lost when the computer is turned off.
ROM (read-only memory) – A type of data storage used in computers that permanently stores data and programs. ROM is a kind of non-volatile memory, meaning its contents are retained even when the computer is turned off.

Bits and Bytes

Bit (Binary Digit) – the smallest, most basic unit of measurement for computer data storage, represented as either a 0 or a 1. One byte is equal to 8 bits.
Byte (Binary Term) – a unit of measurement for data storage. One byte is equal to 8 bits.
| Data Storage Unit | Symbol | Power of 10 | One Unit Equals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Byte | B | 101 | 8 bits |
| Kilobyte | kB | 103 | 1024 B |
| Megabyte | MB | 106 | 1024 kB |
| Gigabyte | GB | 109 | 1024 MB |
| Terabyte | TB | 1012 | 1024 GB |
| Petabyte | PB | 1015 | 1024 TB |
a globally connected massive computer network system.
a system of Internet servers that is made from millions of interlinked websites and web pages. Abbreviated as WWW or the web.
a network security device designed to prevent unauthorized access to or from a network.
a device that transfers data between computer networks to provide access to the Internet.
a company that provides Internet service to customers.
short for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. A set of rules (a protocol) for transferring and accessing data using the web.
Short for Uniform Resource Locator. A web address of a specific web page or file on the Internet.
a set of rules (a protocol) for sending data from one computer to another on the Internet.
a set of rules (a protocol) for transferring files between computers over the Internet.
A small text file stored in a user's computer by a website that the user has visited so that it can remember something about the user at a later time.
a word, phrase, image, etc., within a file or web page that a user can click on to jump to another document, section of the same document, or web page. Also known as a hyperlink.
a small computer designed for use by a single user at a time. Also known as a PC or a microcomputer.
a type of personal computer made by Apple Inc. Short for Macintosh.
a software that controls and coordinates the computer hardware devices and runs other software and applications on a computer. It is the main part of system software and a computer will not function without it.
to shut down and restart a computer, allowing its operating system and programs to be reloaded.
The brain or engine of a computer, where most of the processing and operations take place.
a type of data storage (memory element) used in computers that temporarily stores programs and data. RAM is a kind of volatile memory, meaning its contents are lost when the computer is turned off.
a type of data storage used in computers that permanently stores data and programs. ROM is a kind of non-volatile memory, meaning its contents are retained even when the computer is turned off.
the smallest, most basic unit of measurement for computer data storage, represented as either a 0 or a 1. One byte is equal to 8 bits.
a unit of measurement for data storage. One byte is equal to 8 bits.

