Unit 6. Basic computer terminologies
Topic B: Types of computers
Click play on the following audio player to listen along as you read this section.
Classification of Computers by Size
- Supercomputers
- Mainframe computers
- Minicomputers
- Personal computers (PCs) or microcomputers
Supercomputers

Supercomputer – a powerful computer that can process large amounts of data and do a great amount of computation very quickly.
Supercomputers are used for areas related to:
- Science
- Engineering
- Education
- Defence
- Aerospace
Supercomputers are useful for applications involving very large databases or that require a great amount of computation.
Supercomputers are used for complex tasks, such as:
- Weather forecasting
- Climate research
- Scientific simulation
- Oil and gas exploration
- Quantum mechanics
- Cryptanalysis
Mainframe computers
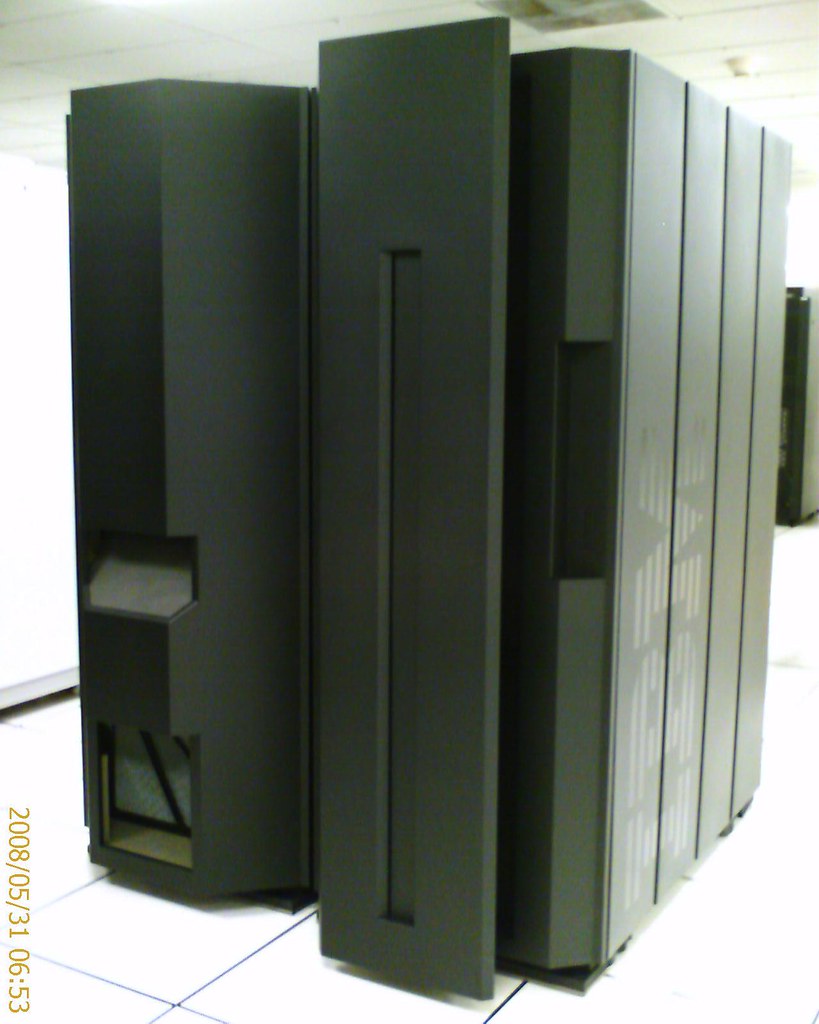

Mainframe computer – a high-performance computer used for large information processing jobs.
Mainframe computers are primarily used in :
- Institutions
- Research
- Academics
- Health care
- Libraries
- Large businesses
- Financial institutions
- Stock brokerage firms
- Insurance agencies
Mainframe computers are useful for tasks related to:
- Census taking
- Industry and consumer statistics
- Enterprise resource planning
- Transaction processing
- e-business and e-commerce
Minicomputers
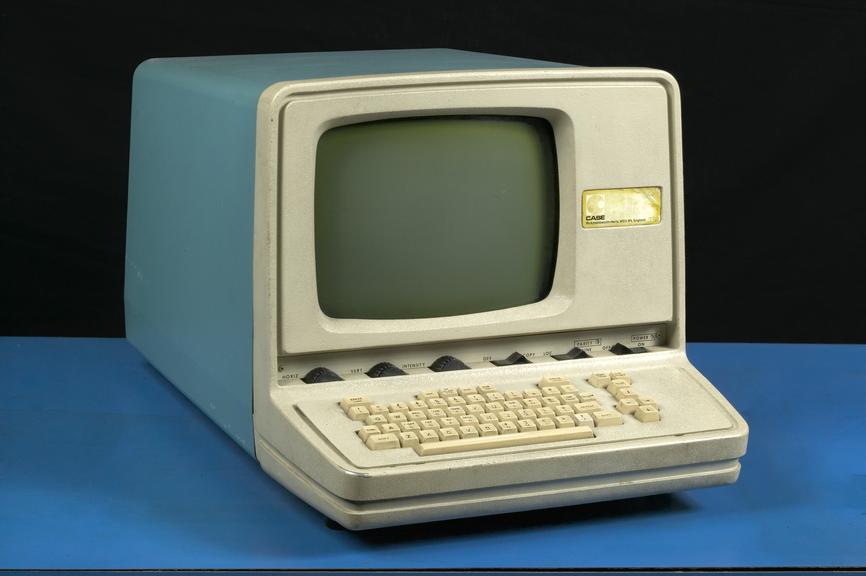

Minicomputer – a mid-range computer that is intermediate in size, power, speed, storage capacity, etc., between a mainframe and a microcomputer.
Minicomputers are used by small organizations.
“Minicomputer” is a term that is no longer used much. In recent years, minicomputers are often referred to as small or midsize servers (a server is a central computer that provides information to other computers).
Personal computers

Personal computer (PC) – a small computer designed for use by a single user at a time.
A PC or microcomputer uses a single chip (microprocessor) for its central processing unit (CPU).
“Microcomputer” is now primarily used to mean a PC, but it can refer to any kind of small computer, such as a desktop computer, laptop computer, tablet, smartphone, or wearable.
Types of personal computers
Desktop computer – a personal computer that is designed to stay at one location and fits on or under a desk. It typically has a monitor, keyboard, mouse, and a tower (system unit).

Laptop computer (or notebook) – A portable personal computer that is small enough to rest on the user’s lap and can be powered by a battery. It includes a flip down screen and a keyboard with a touchpad.

Tablet – A wireless touchscreen PC that is slightly smaller and weighs less than the average laptop.
Smartphone – A mobile phone that performs many of the functions of a personal computer.

a powerful computer that can process large amounts of data and do a great amount of computation very quickly.
a high-performance computer used for large information processing jobs.
a mid-range computer that is intermediate in size, power, speed, storage capacity, etc., between a mainframe and a microcomputer.
a central computer that provides information to other computers.
a small computer designed for use by a single user at a time. Also known as a PC or a microcomputer.
a personal computer that is designed to stay at one location and fits on or under a desk. It typically has a monitor, keyboard, mouse, and a tower (system unit).
a portable personal computer that is small enough to rest on the user's lap and can be powered by a battery. It includes a flip down screen and a keyboard with a touchpad. Also known as a notebook.
a wireless touchscreen PC that is slightly smaller and weighs less than the average laptop.
a mobile phone that performs many of the functions of a personal computer.

