Water
67 Water Hardness and pH
Water is classified as either soft or hard:
- Soft water contains relatively few minerals and lathers easily.
- Hard water is rich in minerals such as calcium and magnesium, which is the cause of “scale” in kettles.
Water hardness is usually expressed as the number of parts per million (ppm) of calcium carbonate present in the water (see Table 19).
| Type of Water | Hardness |
|---|---|
| Soft water | 10–50 ppm |
| Slightly hard water | 50–100 ppm |
| Hard water | 100–200 ppm |
| Very hard water | Over 200 ppm |
Regions with soft water (1 ppm to 50 ppm) include the Pacific Northwest from Oregon up through British Columbia. The hard water regions (100+ ppm) include the Canadian Prairies, the U.S. Midwest, and the southwestern states of New Mexico and Arizona. In a sense, the hardness of water is the other side of the coin to alkalinity. In general terms, rainy climates such as the Pacific Northwest have acid water. Rain leaches out much of the mineral ions in the soil, replacing them with hydrogen ions. The result is that the water is rich in hydrogen and thus acidic (soft). The reverse is the case in the dry regions, where moisture evaporates, leaving the minerals intact. The result is water rich in minerals and thus alkaline (hard). Note that this explanation is a simplification as other factors such as the type of bedrock have an effect on water hardness as well.
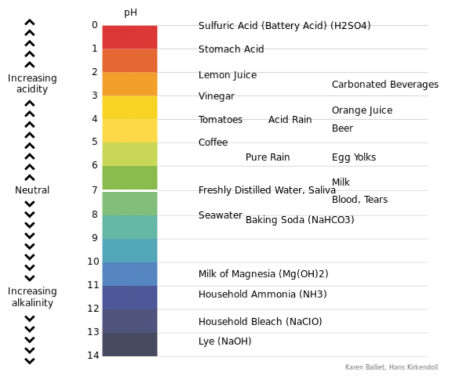
The acidity or alkalinity of all substances, water in this case, is measured in terms of an index number and expressed as pH = hydrogen ion concentration. The scale ranges between 0 and 14. For baking, the ideal is water with a pH of just below 7.
pH above 7 = alkaline
pH of 7 = neutral
Effects on Baking
Most municipal supplies of water contain chlorine, which is used to ensure the purity of the water. Some cities add fluoride to their water supply to stop tooth decay. Neither chlorine nor fluoride is present in large enough quantities to affect dough in any way. In addition, most municipal water is treated to reduce excessive acidity, since this could be corrosive for the water lines. It is therefore unlikely that bakers using municipal water need to be concerned about extremely acidic water.
Soft water is another matter, as it can lead to sticky dough. An addition of yeast food, or a reduction in dough water, will help. Alkaline water tends to tighten the dough and retard fermentation, since enzymes work best in slightly acidic dough.
If there is a possibility of water problems, a sample should be forwarded to a laboratory for a complete analysis.
Image Descriptions
Figure 23 long description: A visual representation of pH with values indicated for common substances. The acidic range is the following: pH 0 is sulfuric acid (battery acid); pH 1 is stomach acid; pH 2 is lemon juice; pH 2.5 is carbonated beverages; pH 3 is vinegar; pH 3.5 is orange juice; pH 4 is tomatoes and acid rain; pH 4.5 is beer; pH 5 is coffee; pH 5.5 is pure rain and egg yolks; and pH 6.5 is milk. Saliva and freshly distilled water are neutral at pH 7. The alkaline range is the following: pH 7.2=5 is blood and tears; pH 8 is seawater; pH 8.2 is baking soda; pH 10.5 is milk of magnesia; pH 11.5 is household ammonia; pH 12.5 is household bleach; pH 13.5 is lye. [Return to Figure 23]
Media Attributions
- Power of Hydrogen (pH) Chart © Hans Kirkendoll is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license

